Fig. 6
Download original image
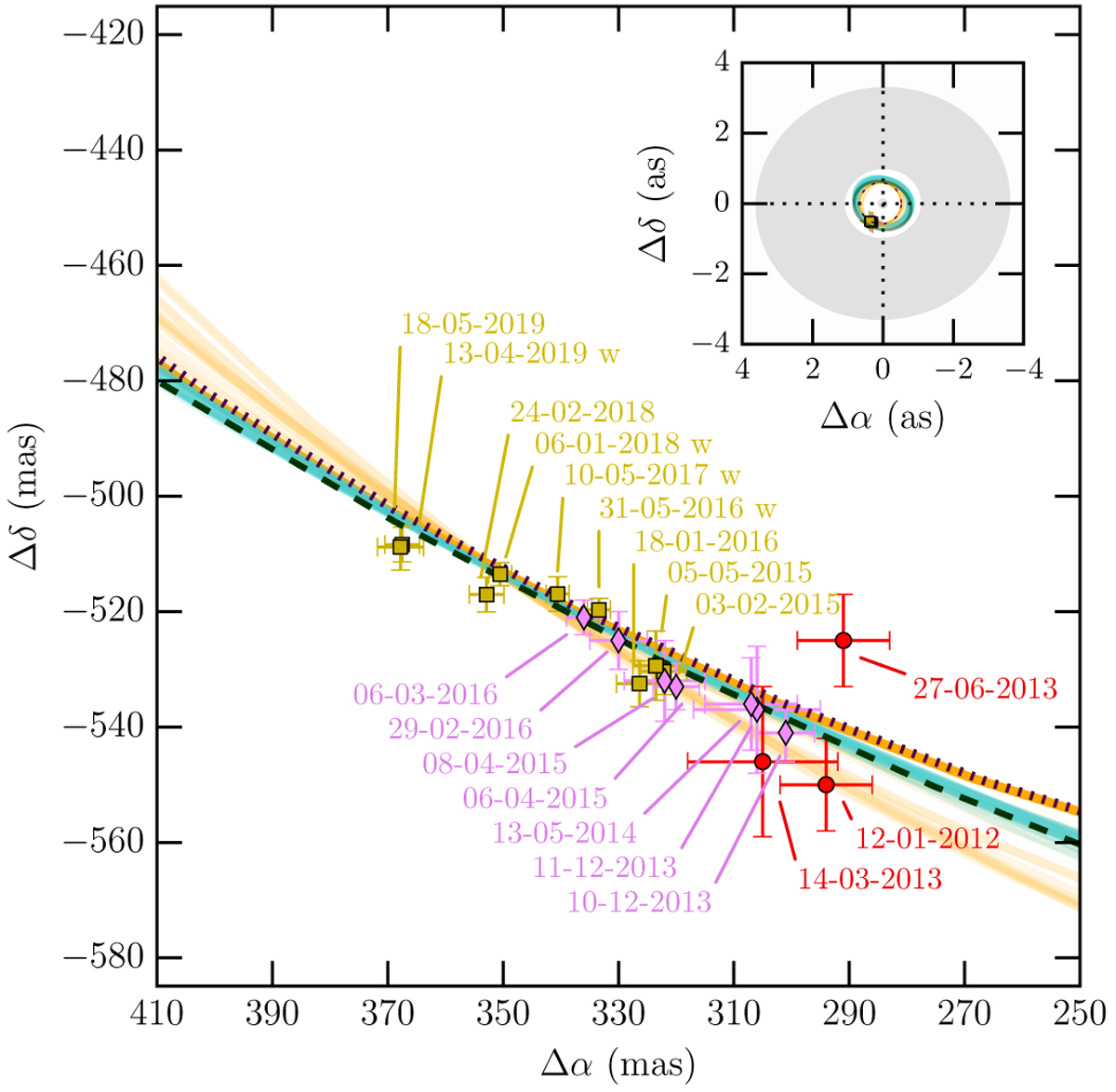
Astrometric positions of the planet HD 95086 b between 2012 and 2020 with three different instruments: SPHERE (yellow squares), GPI (pink diamonds), and NaCo (red circles) with 1σ error bars. The astrometric positions from SPHERE were computed with the SpeCal-TLOCI pipeline. The letter “w” in the legend indicates the observations imaged with satellite spots that enable finding the exact position of the star during the whole sequence and later recenter the frames if necessary. The green and orange solid lines correspond to a sample of the orbital solutions found by the MCMC orbital fit and the K-Stacker tools, respectively. The black dashed and dotted lines respectively represent the MCMC and K-Stacker orbits for which the corresponding orbital parameters are given in Table 4. For the MCMC tool, the orbit corresponds to the MAP (see text), whereas for K-Stacker it is the orbit closest to the mean of the orbital solutions. Both of these orbits are by construction true orbital solutions. Notes: The Feb2015 point from SPHERE is hidden by the two 2015 points from GPI; the two 2019 points are very close to each other. The insert (in the top right corner) shows the location of the planet relative to the cold outer belt and warm inner belt from Su et al. (2017).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


