Fig. 12.
Download original image
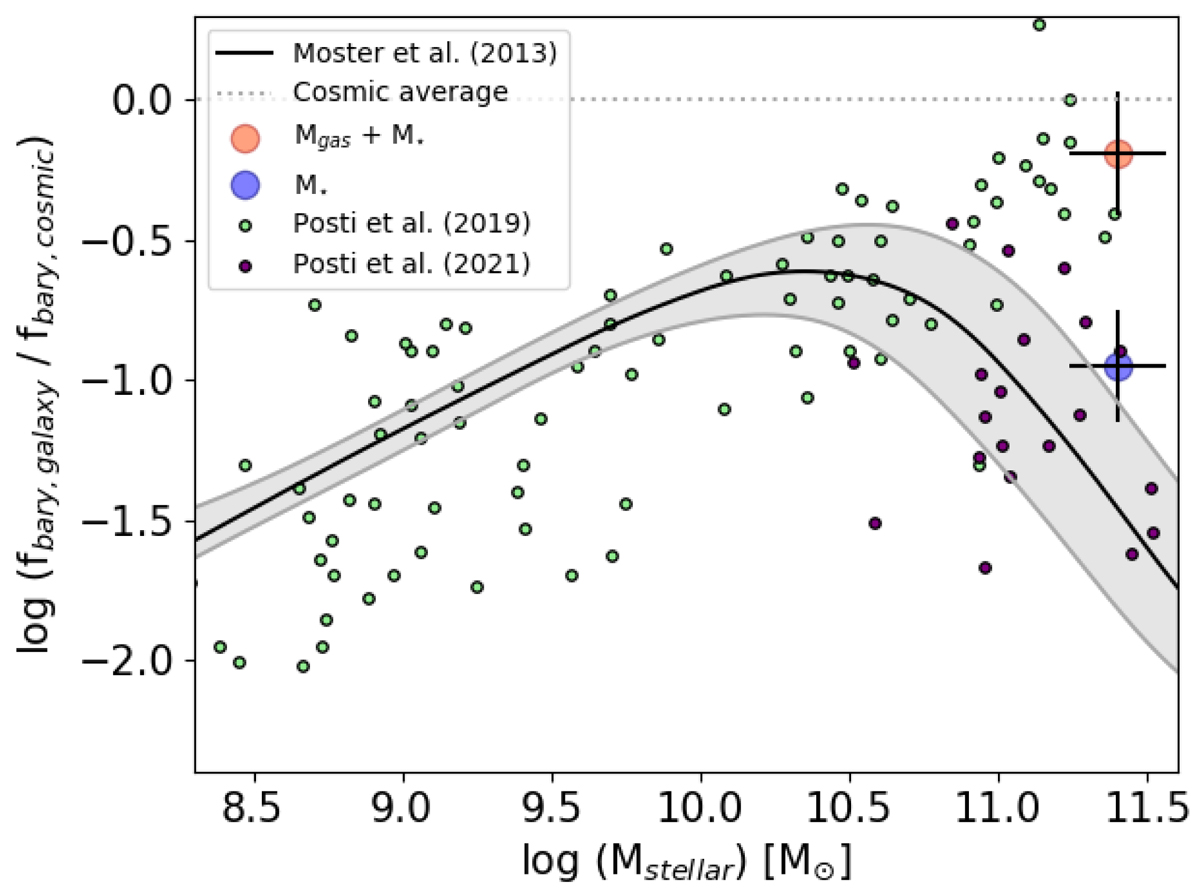
Comparison of the observed baryon fraction in galaxies, scaled by the cosmic baryon fraction. For J2345−0449 we show the ratio of stellar mass to dark-matter halo mass as blue dot. The red dot shows the ratio of baryonic mass (the sum of stellar mass, and mass of hot halo and molecular gas) to dark-matter halo mass. Values for other galaxies show the spiral galaxies of Posti et al. (2019, small green dots) and the early-type galaxies of Posti & Fall (2021, small violet dots), and include only stellar mass, fbary, galaxy = Mstellar/MDM. Even without including halo gas, their most massive spirals fall very near the cosmological limit of fbary, cosmic = Ωbaryon/ΩDM = 0.188, indicating that they have already transformed most of their infalling gas into stars. This is not the case for J2345−0449, which has about 2/3 of its baryons in the hot halo. It falls near the massive spiral galaxies when considering the full baryon content, and near the elliptical galaxies of Posti & Fall (2021) and the value expected from cosmic abundance matching (black line and gray error bars, Moster et al. 2013), when only considering the stellar mass.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


