Fig. 10.
Download original image
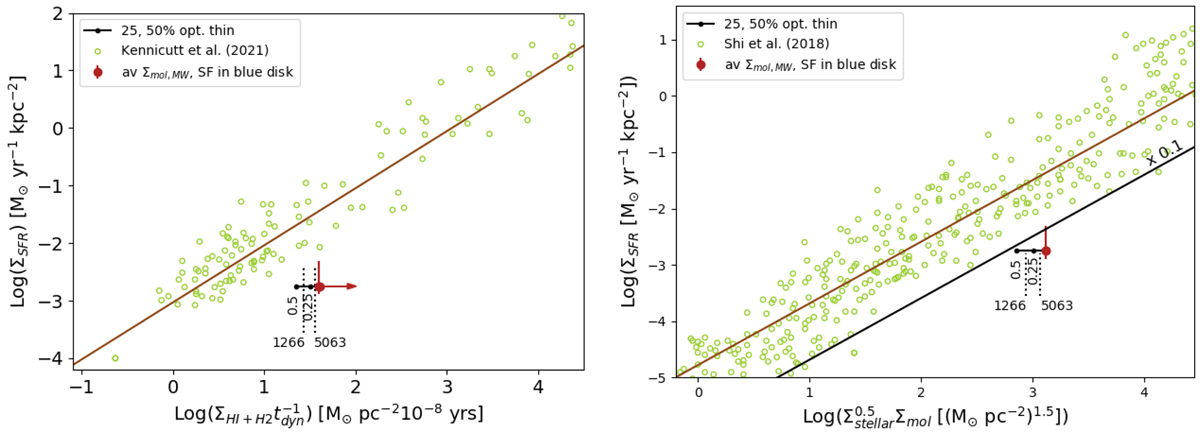
Alternative star-formation laws. Left: Silk–Elmegreen law, relating star-formation rate surface density with the gas-mass surface density divided by dynamical (rotational) time. The comparison sample is taken from Kennicutt & De Los Reyes (2021). The gas-mass surface density in J2345−0449 is a lower limit, because we have no HI measurement. Right: extended Schmidt-law, which takes into account stellar in addition to gas-mass surface density. The comparison sample is taken from Shi et al. (2018). Solid and dashed lines indicate the relationship by Shi et al. (2018) and 1σ scatter. As in Fig. 9, we show where J2345−0449 falls relative to normal star-forming galaxies, using the average star-formation rate and molecular gas-mass surface density. We also show where J2345−0449 would fall if 25 or 50 of the CO(1−0) line flux originated from optically thin gas. We also show the location of J2345−0449 if the fraction of optically thin gas was the same as previously observed in NGC 1266 and IC 5063. The error bar in both panels takes into account systematic uncertainties, and includes the SFR = 2.95 M⊙ yr−1 of total star-formation rate obtained by Dabhade et al. (2020) from WISE, the highest value currently given in the literature.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


