Fig. 1.
Download original image
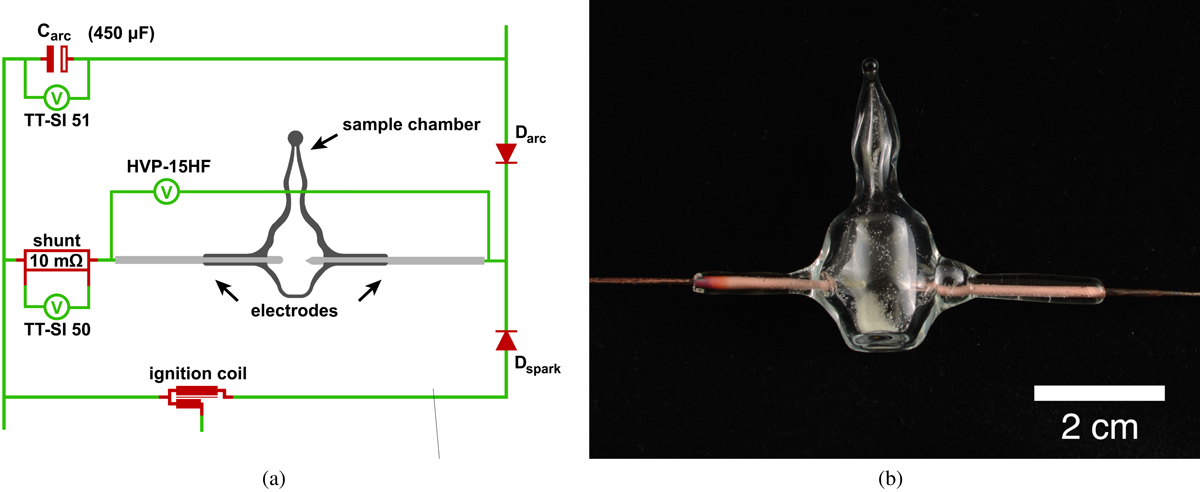
Experimental set-up. (a) Schematic illustration of the most relevant parts of the arc generation circuit connected to the sample chamber. A DC–DC converter charged three parallel capacitors (![]() ). The ignition coil was protected from the charging voltage of Carc by the diode Dspark. After Carc had reached the target voltage, the ignition coil generated a high-voltage peak up to 8 kV and produced an ionized channel between the electrodes (ignition spark). Diode Dspark became conductive, while Carc was protected by Darc from the high-voltage peak. After the electrical breakdown, the voltage decreased instantaneously. When the voltage had dropped below the charging voltage of Carc, the energy stored in Carc was released into the existing ionized channel, causing a high-energy arc discharge. (b) Sample chamber made of quartz glass. Two tungsten electrodes were embedded into the glass on opposite sides. The sample chamber was loaded with 30 mg of Mg2SiO4 particles.
). The ignition coil was protected from the charging voltage of Carc by the diode Dspark. After Carc had reached the target voltage, the ignition coil generated a high-voltage peak up to 8 kV and produced an ionized channel between the electrodes (ignition spark). Diode Dspark became conductive, while Carc was protected by Darc from the high-voltage peak. After the electrical breakdown, the voltage decreased instantaneously. When the voltage had dropped below the charging voltage of Carc, the energy stored in Carc was released into the existing ionized channel, causing a high-energy arc discharge. (b) Sample chamber made of quartz glass. Two tungsten electrodes were embedded into the glass on opposite sides. The sample chamber was loaded with 30 mg of Mg2SiO4 particles.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


