Fig. 18.
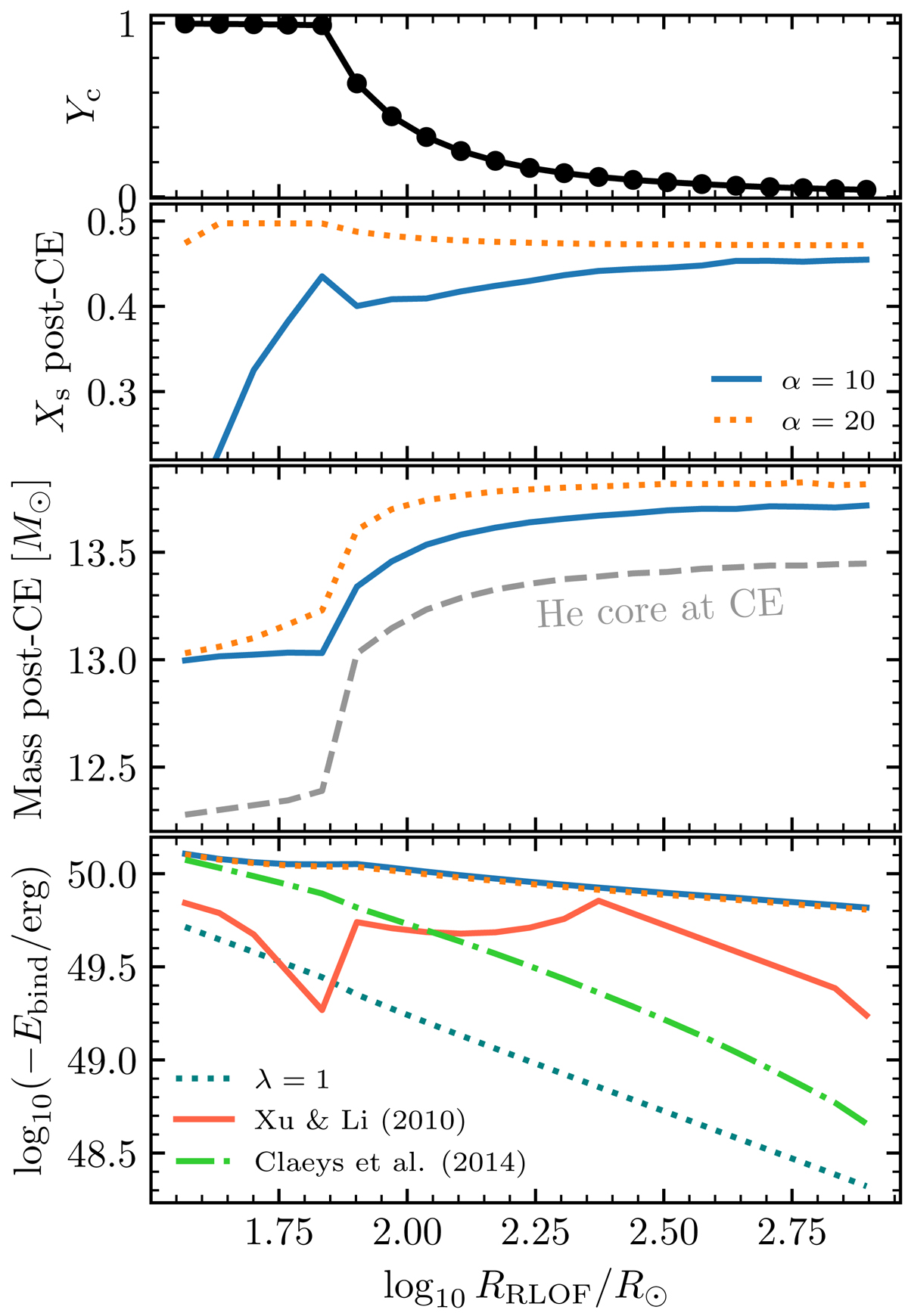
Properties after CE evolution for the case of donor stars with a radiative envelope, with artificially high values of αCE = 10, 20 in order to allow for a successful CE ejection. Simulations correspond to binary systems composed of a star with a ZAMS mass of 30 M⊙ and a BH companion of 3 M⊙, with periods ranging from 101 days to 103 days. Results are shown as a function of the radius of the star when it fills its Roche lobe. Top panel: central helium mass fraction Yc at the onset of CE, showing RLOF before and after the end of the HG as a large drop in Yc. Second panel: surface hydrogen mass fraction after envelope ejection. Third panel: stellar mass after envelope ejection, also showing the mass of the helium core defined as the innermost mass coordinate with Y > 0.01. Bottom panel: binding energy of the ejected envelope, as well as the binding energy that would be predicted by the Claeys et al. (2014) and Xu & Li (2010) fits, and the one corresponding to λ = 1.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


