Fig. 3
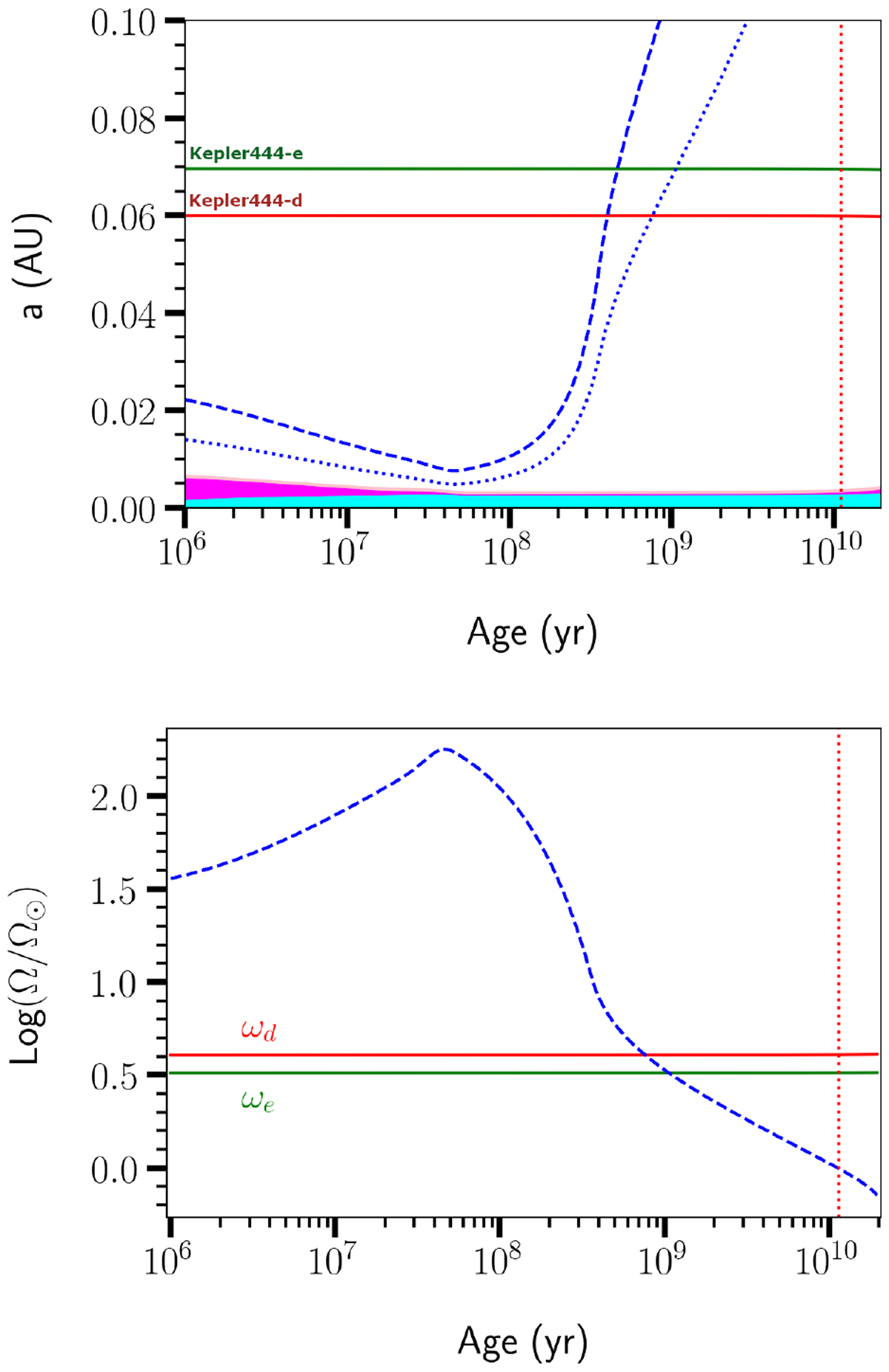
Top panel: orbital evolution of Kepler-444-d and e (solid red and green line, respectively), starting with the current value of the orbital distance (![]() ,
,
![]() ), at a fixed mass (Md = 0.1016 M⊕,
Me = 0.0921 M⊕) and host star initial angular rotation Ωin = 18 × Ω⊙. The vertical red-dotted line corresponds to the age of the system (age = 11 Gyr). The blue-dashed lines indicate the evolution of the corotation radii, the blue-dotted ones indicate the evolution of the minimum initial orbital distances below which dynamical tides are no longer active. The magenta area represents the extension of the stellar convective envelope, while the cyan area represents the stellar radiative core. Bottom panel: orbital angular velocity of the planets and the double of the host star angular velocity (blue-dashed line) as a function of time. Dynamical tides are active as long as the orbital frequency of the planets is lower than double the host star surface angular rotation.
), at a fixed mass (Md = 0.1016 M⊕,
Me = 0.0921 M⊕) and host star initial angular rotation Ωin = 18 × Ω⊙. The vertical red-dotted line corresponds to the age of the system (age = 11 Gyr). The blue-dashed lines indicate the evolution of the corotation radii, the blue-dotted ones indicate the evolution of the minimum initial orbital distances below which dynamical tides are no longer active. The magenta area represents the extension of the stellar convective envelope, while the cyan area represents the stellar radiative core. Bottom panel: orbital angular velocity of the planets and the double of the host star angular velocity (blue-dashed line) as a function of time. Dynamical tides are active as long as the orbital frequency of the planets is lower than double the host star surface angular rotation.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


