Fig. 1.
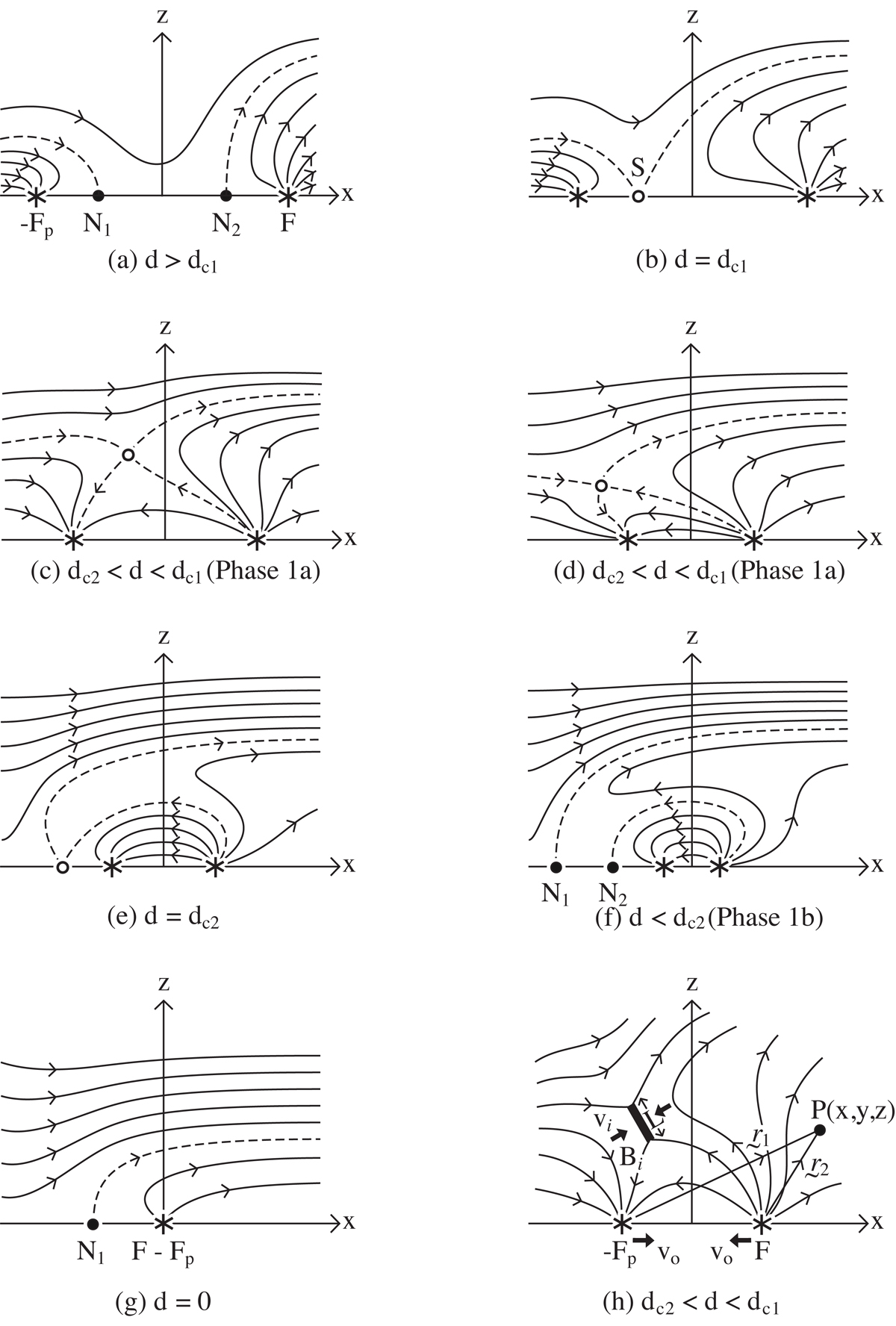
Overall behaviour of the magnetic field during the approach of two oppositely directed photospheric polarities (stars) of flux, −Fp and F, (where |Fp|< |F|) are separated by a distance, 2d, and situated in an overlying uniform horizontal magnetic field (B0). The magnetic field is axisymmetric, shown here in a vertical (y = 0) plane. Dashed curves show separatrix magnetic field lines and solid curves indicate other magnetic field lines. The separator is marked by an unfilled dot, and null points with solid dots. The field is shown for (a) d > dc1, when the two sources are far apart, (b) d = dc1, when the nulls coalesce at the photosphere (z = 0) and a separator first appears, (c) dc2 < d < dc1 (phase 1a), when the separator arches above the surface, (d) dc2 < d < dc1 (phase 1a), when the separator has moved to the left of the flux source −Fp, (e) d = dc2, when the separator falls back down to the photosphere and becomes a second-order null, (f) 0 < d < dc2 (phase 1b), when the null has bifurcated into two null points moving away from each other, and (g) d = 0, when the two sources have coalesced, leaving behind the remaining magnetic fragment of flux (F − Fp). Panel h: notation used to describe the reconnection process at a current sheet of length L.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


