Fig. 1.
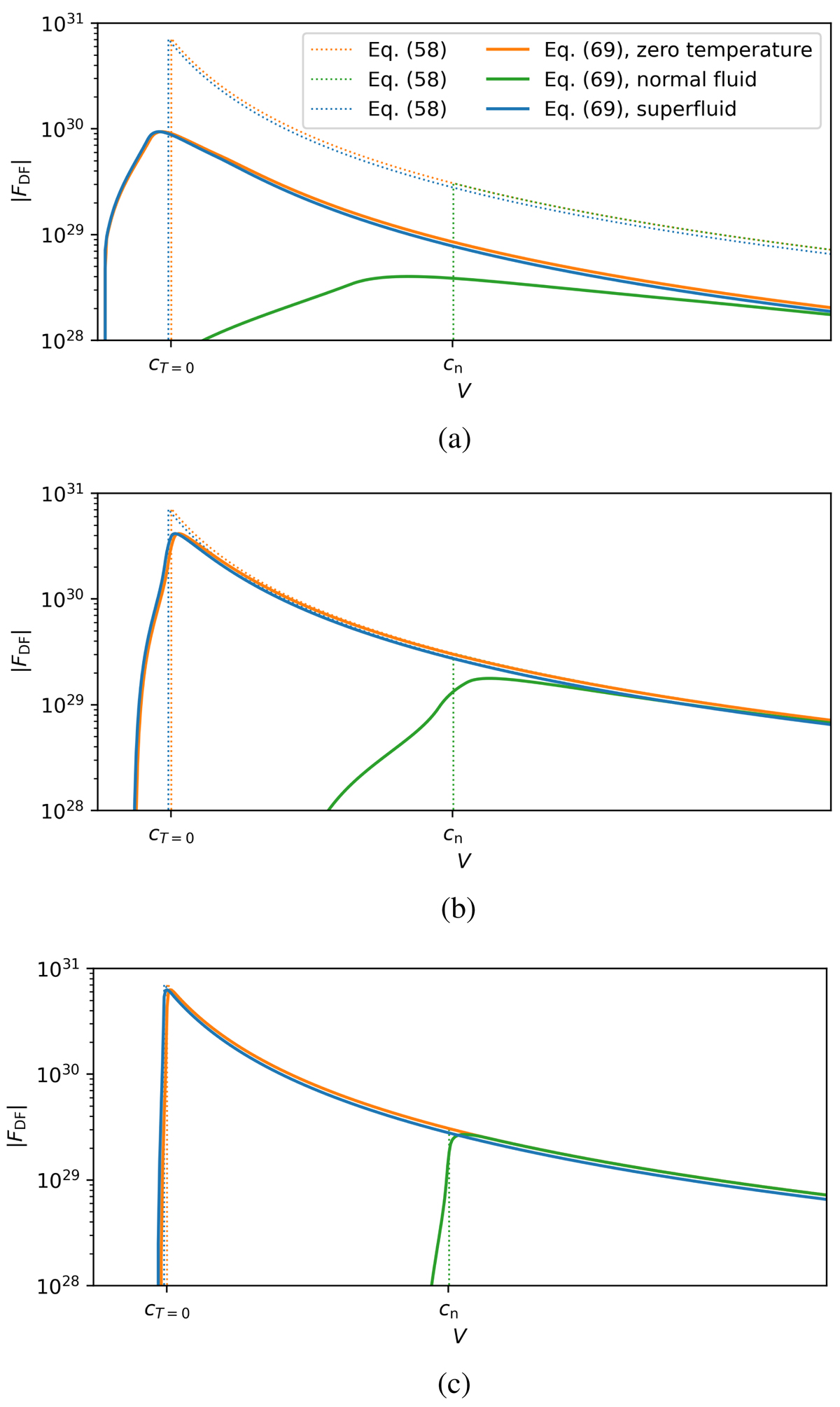
Dynamical friction from linear perturbation theory using the finite-time approach (solid lines) and the steady-state approach (dotted lines) as a function of V. As time passes, the finite-time result, Eq. (69), approaches the steady-state result, Eq. (58). In the zero-temperature limit, we have T = 0, while in the normal fluid case we have ρs = 0. (a) t = 0.1Rmax/V. (b) t = Rmax/V. (c) t = 10Rmax/V.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


