Fig. 17.
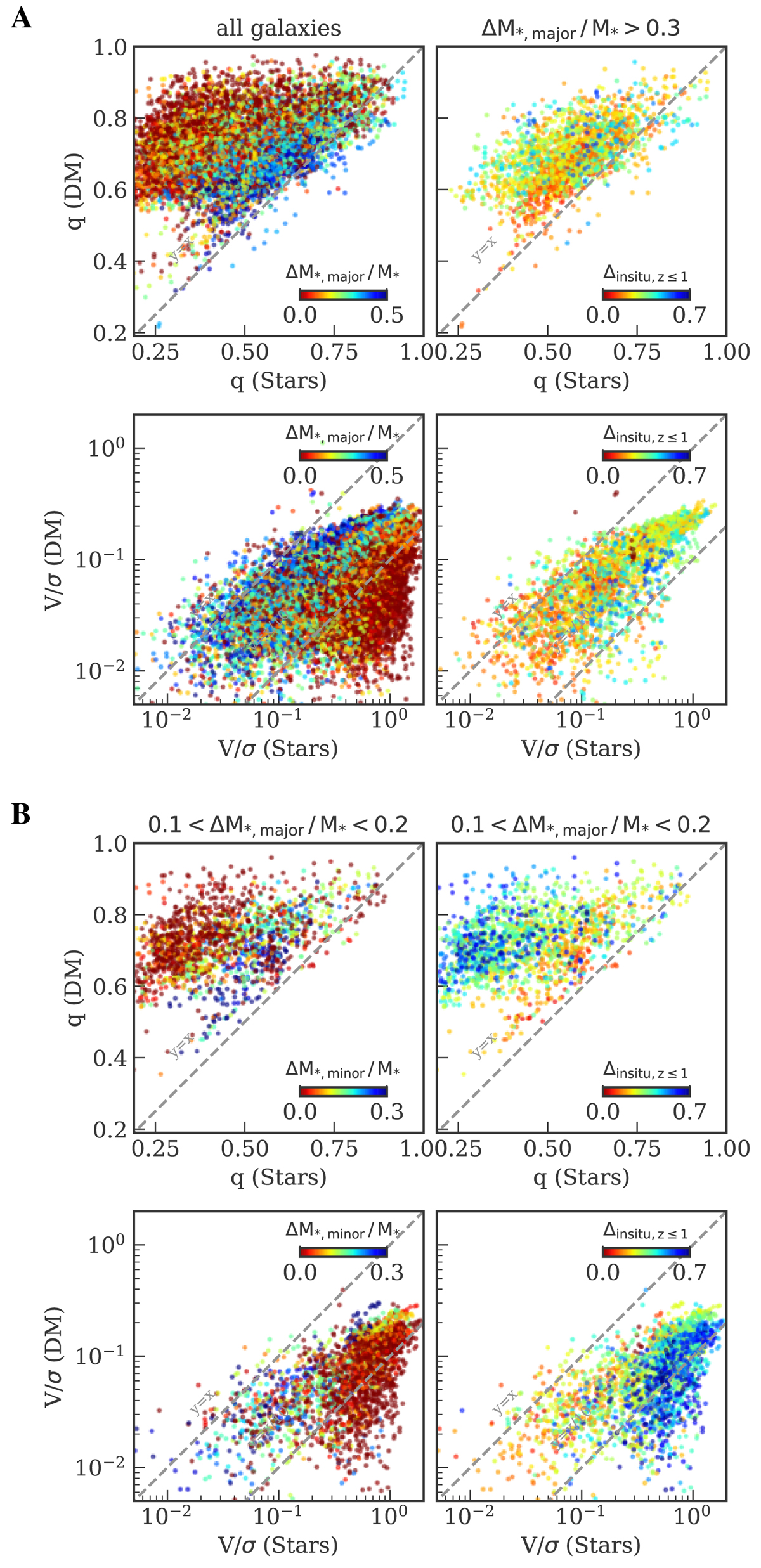
Coupling between stellar and dark matter components from major and minor mergers. A: major mergers. The left panels show all the TNG ETGs, color coded by their fraction of stellar mass accreted by major mergers. On the right we consider only galaxies with at least 30% of their stellar mass accreted from major mergers and color code them according to the fraction of recently produced in-situ stars Δinsitu, z ≤ 1. Major mergers cause the coupling between stellar and dark matter components, especially in galaxies that have not recently accreted cold gas. B: minor mergers. Here we consider galaxies with stellar mass fraction accreted from major mergers in the narrow range 0.1 < ΔM*, major/M* < 0.2. In the left panels, galaxies are color coded by the fraction of stellar mass accreted from minor mergers ΔM*, minor/M* and on the right by the fraction of recently produced in-situ stars Δinsitu, z ≤ 1. Dry minor mergers also help to set up the similarity between stellar and dark matter halo structure.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


