Fig. 1
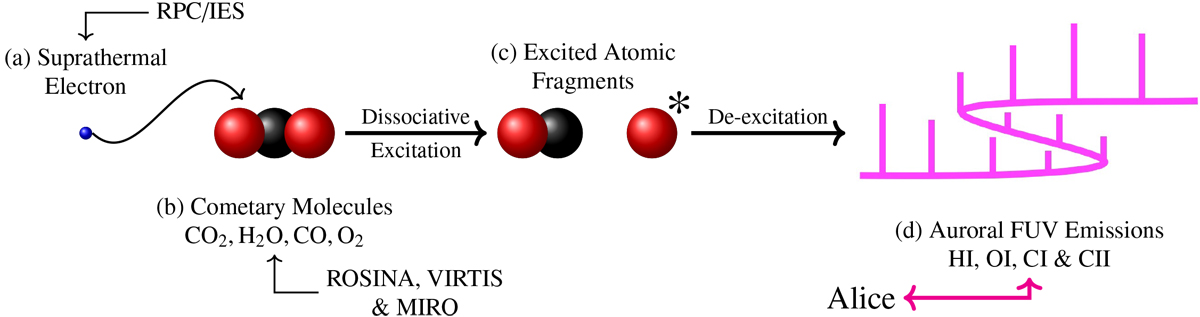
Schematic of the multi-instrument analysis used in this study to model FUV emissions driven by electron impact on cometary neutrals. From left to right: (a) suprathermal electrons present within the coma were measured using Ion and Electron Sensor of the Rosetta Plasma Consortium (RPC/IES) (see Sect. 2.4.2). (b) Neutral gas molecules in the coma. There were four major neutral species seen at 67P: CO2, H2 O, CO, and O2 (see Sect. 2.3). (c) A collision between a suprathermal electron and a cometary molecule causes the molecule to dissociate. A neutral fragment and an excited atom are produced. (d) The excited atom de-excites, releasing a photon in the FUV. These photons were observed with the Alice FUV imaging spectrograph (see Sect. 2.2).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


