Fig. 1
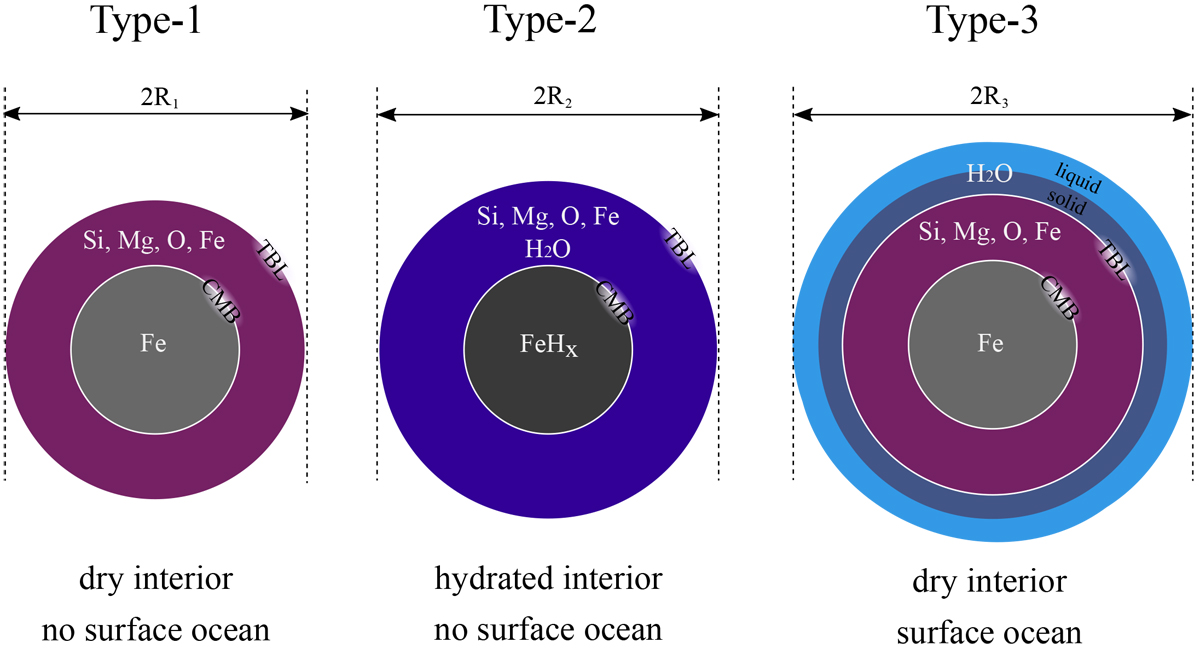
Schematic overview of the different planet types modelled in this study. All objects consist of a pure iron or iron hydride coreand a dry or hydrated Mg-silicate mantle. We have estimated the effect of hydration by comparing the dry planets (Type-1) with their hydrated counterparts (Type-2) at fixed composition and boundary conditions. We have then extracted the water content in the Type-2 planets and moved it into an isolated surface layer (Type-3) to assess the effect of ocean separation on the total radius at fixed composition and boundary conditions. The oceans of the Type-3 planets can consist of an upper liquid part and a lower solid part if the pressure at the bottom of the oceans is high enough to allow for the formation of high pressure ices.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


