Fig. 3
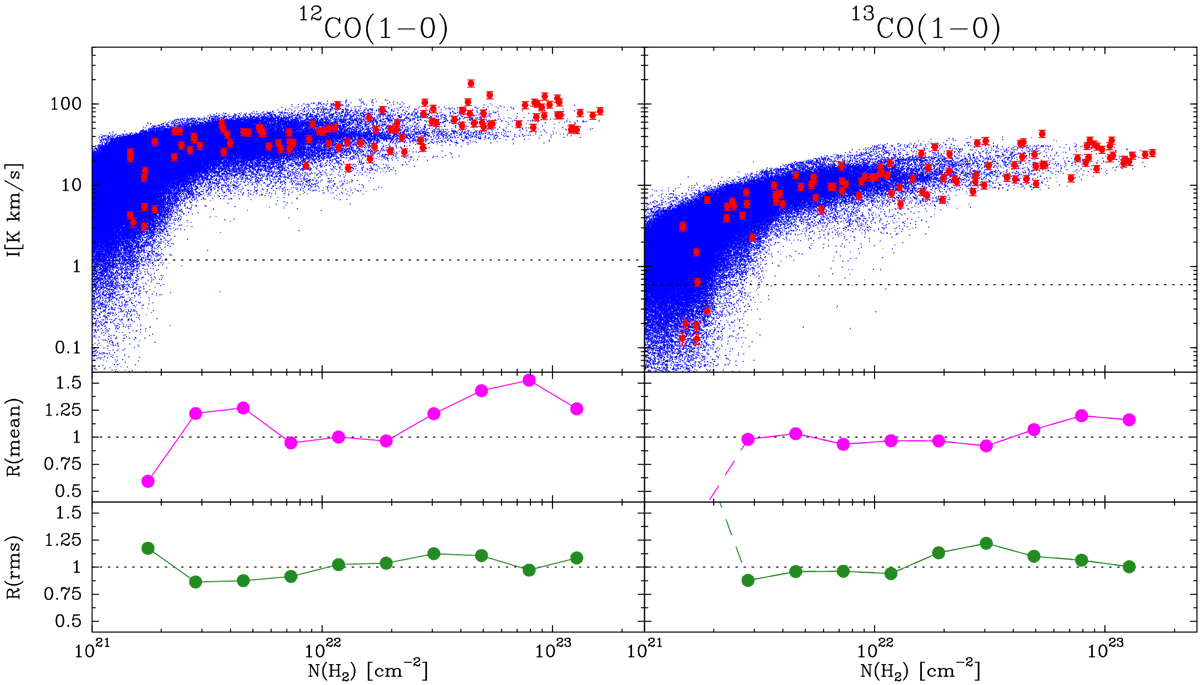
Comparison between sampling observations and COMPLETE full maps for 12CO(1–0) and 13CO(1–0). Top panels: scatter plots of the integrated intensity as a function of N(H2). The blue dots represent the results from the COMPLETE maps presented by Ridge et al. (2006) and each of them contains more than 2 × 105 spectra. The red symbols represent the 100 measurements obtained using stratified random sampling. The dotted lines mark the 3σ detection level of the COMPLETE maps. Middle panels: ratio between the mean intensity derived using the sampling data and the COMPLETE maps for each of the ten N(H2) bins in which the cloud was divided. For 13CO(1–0), the measurement in lowest N(H2) bin is not reliable since the sampling data show that the intensity often lies below the COMPLETE detection limit. Bottom panels: ratiobetween the rms derived using the sampling data and the COMPLETE maps. As with the mean values, the 13CO(1–0) measurement for the lowest N(H2) bin lies below the detection limit, so the rms estimate is not reliable. We note how both the mean and rms ratios for the two CO isotopologs lie in the vicinity of 1, indicating that the sampling method allows estimating the main emission parameters with an accuracy of about 50–20% depending on the parameter.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


