Fig. 2
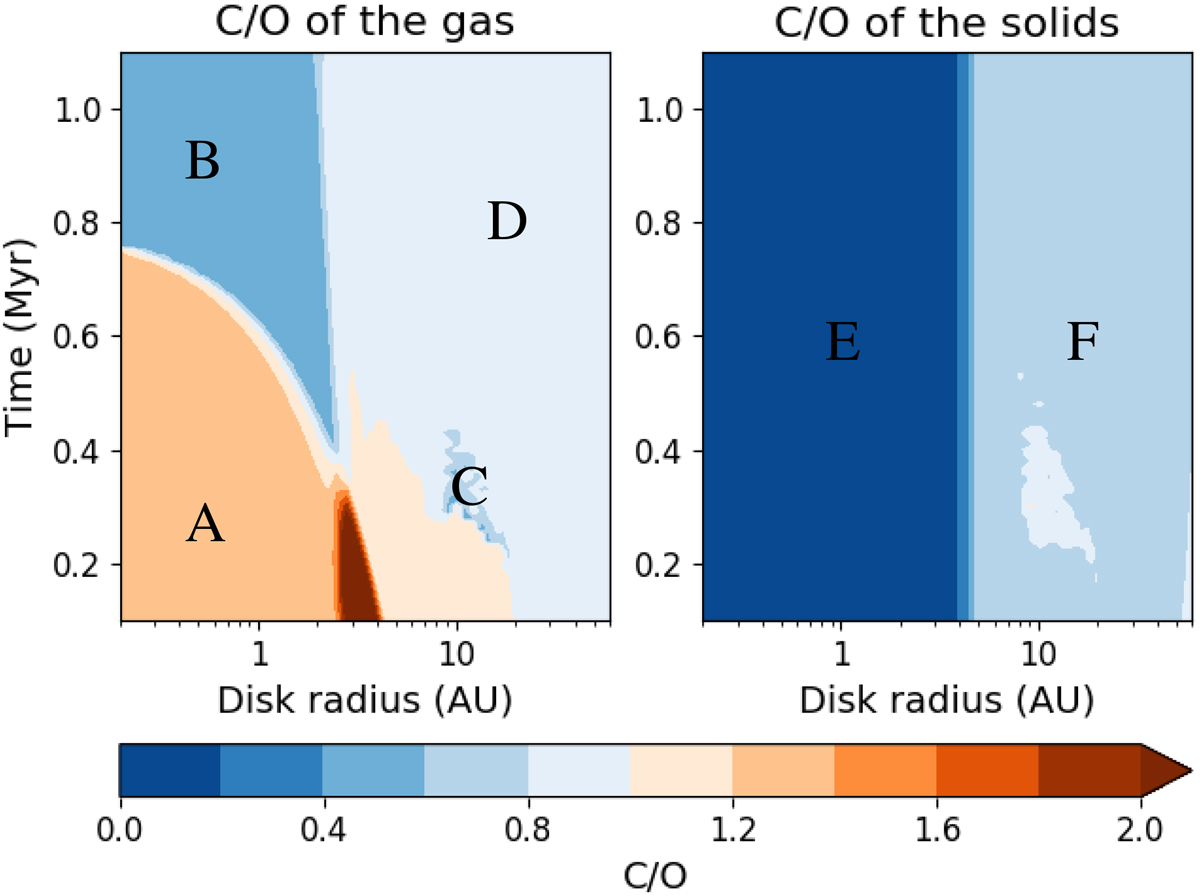
Evolution and radial distribution of the midplane C/O in the gas and solids in one of the disk models used for this work. Specifically, we show the chemistry of the disk in the reset scenario of refractory erosion, which governs the high C/O early on in the disk’s life (A). We similarly note the region of the disk with high and low water vapour abundances (B and D, respectively), the carbon-poor region due to refractory erosion (E), and a region where gaseous CO is converted to frozen CO2 (C). The more carbon-rich region (F) exists at larger radii than the carbon erosion front. Orange denotes carbon-rich regions (C/O > 1) while blue denotes carbon-poor regions (C/O < 1). The nominalvolatile C/O = 0.4 and the refractory C/O = 2.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


