Fig. 3
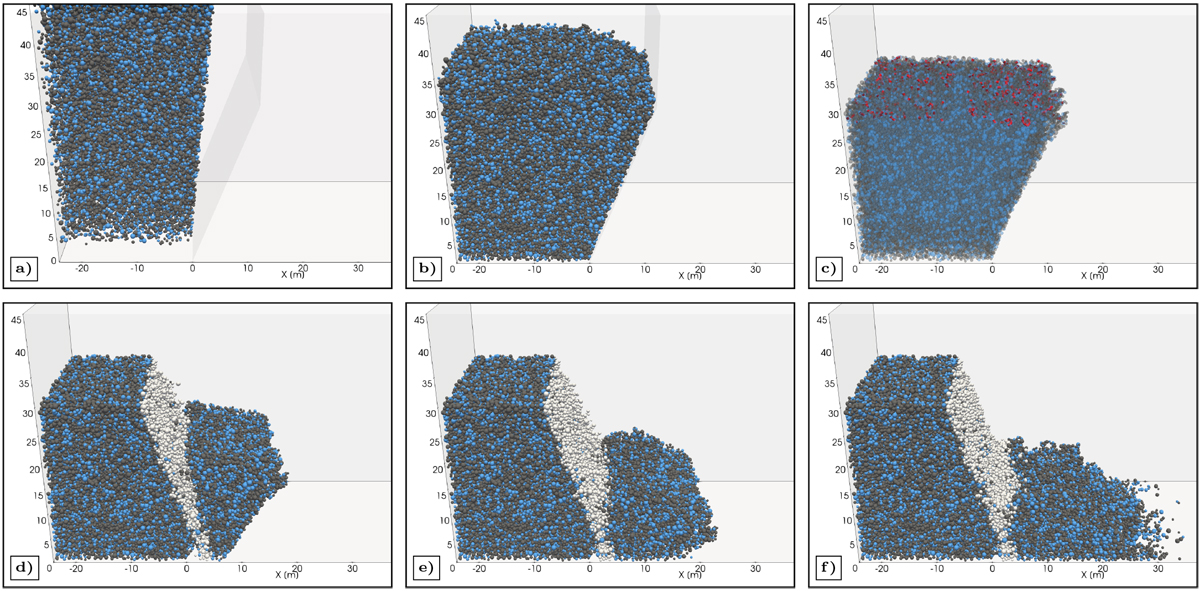
Construction and simulated collapse of a 30-m-high cliff made up of a 2:1 dust–ice mixture (65 000 computational parcels) with a sintered top layer of 3 m thickness. Top row: construction of the cliff. (a) Loose filling of a region confined by walls with noncontacting randomly sized and positioned dust (gray spheres) and ice (blue spheres) particles. (b) Compactionof the cliff to the bulk mass density and porosity of comet 67P. (c) Removal of particles beyond the given cliff height, formation of sinter bonds (thick red bars) between ice particles in the top layer of the cliff, and removal of the wall supporting the overhang. Bottom row: (d–f) Several stages after triggering the collapse. Representation as in Fig. 2. Particles in white are from the initial crack region.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


