Fig. 1.
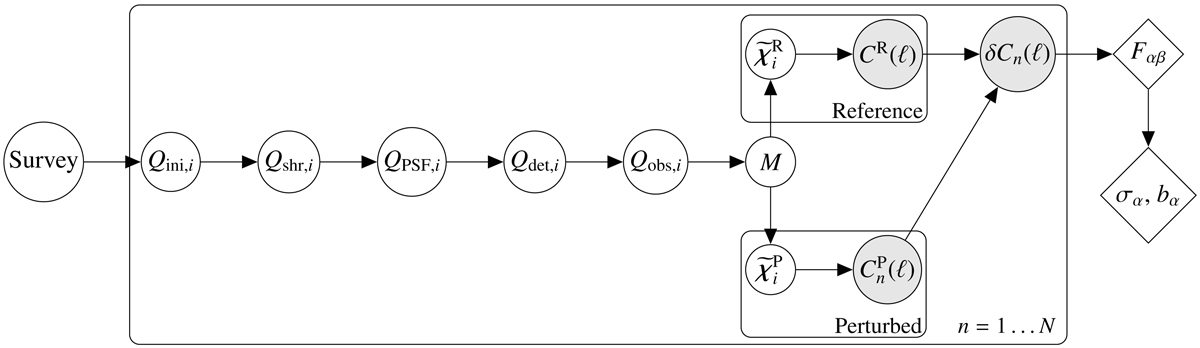
Overall structure of the concept as described in the main text. The quadrupole moments Q are initiated with intrinsic moments and then modified by incorporating the shear, PSF, and detector effects. Survey characteristics such as dither pattern, slew pattern, and observation time are entered in the initial catalogue. A measurement process M subsequently converts the observed moments to polarisations. The estimation of the galaxy polarisation is then made (as described in Eqs. (10) and (11)). This is done per object. Next a power spectrum for the reference and perturbed scenarios is computed. For the perturbed line the PSF and detector moments are drawn from distributions that represent the measurement uncertainty as described in the text. This process is repeated for 150 random realisations for the set of galaxies that are in the input catalogue. Finally the residual power spectrum is computed per realisation, and the statistics of each of the realisations is passed onto the Fisher matrix, from which uncertainties and biases of dark energy parameters are calculated. White circles indicate moment space, where modifications are performed on an object-by-object basis. Grey circles indicate ensemble average in the harmonic space. Diamonds show cosmological parameter space.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


