Fig. 3
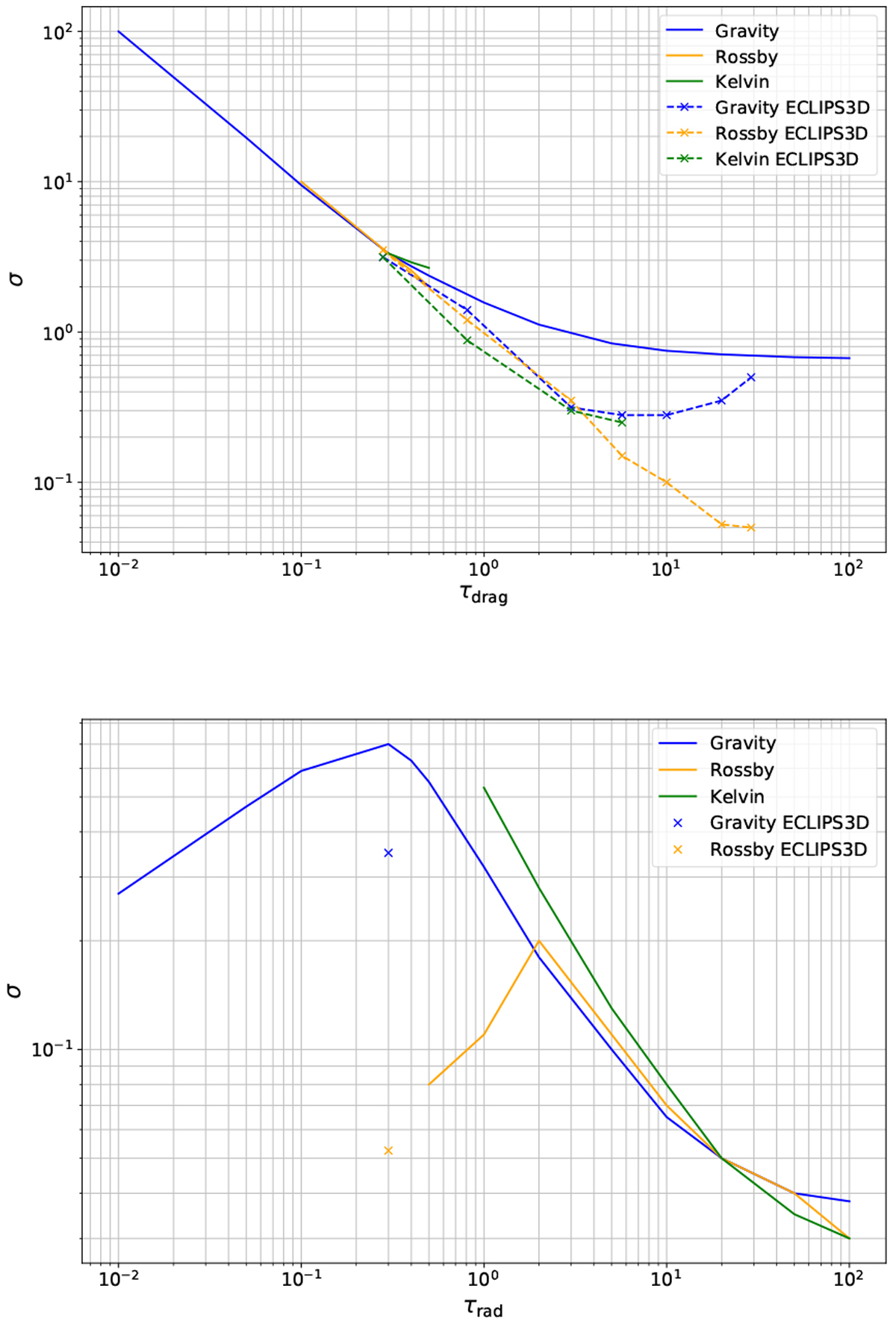
Typical decay rate σ for gravity and Rossby and Kelvin waves as a function of (top) τdrag for τrad= 0.3 and (bottom) τrad for τdrag = 20. The lines are values obtained using Eqs. (40), (50) while crosses are results from seven ECLIPS3D calculations.As τrad is not constant with depth in the ECLIPS3D results, we have chosen to use an arbitrary value of τrad = 0.3 for comparison. However, when τdrag increasesthe location where the wave exhibits its maximum perturbation, it moves to higher pressures which should correspond to an increase in the equivalent τrad. For the Rossby waves, the low τdrag limit has not been studied numerically as it is irrelevant for superrotation. Kelvin waves of comparable height with Rossby and gravity waves are only clearly identified in four ECLIPS3D calculations.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


