Fig. 4.
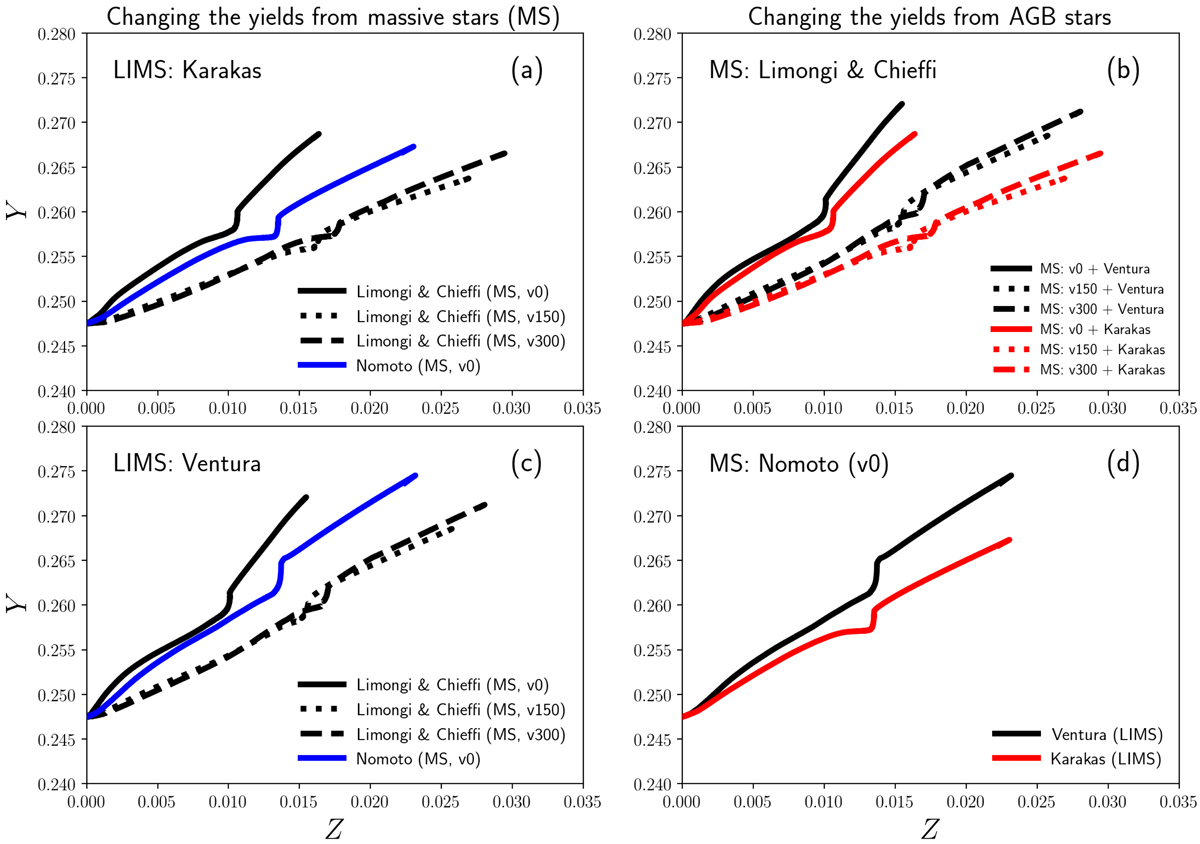
Effect of different nucleosynthesis yields for massive stars (panels a and c) and AGB stars (panels b and d) on the predicted Y vs. Z relation from a one-zone galaxy chemical evolution model with star formation efficiency SFE = 2 Gyr−1, infall timescale τ = 4 Gyr, and no galactic winds. For massive stars we explore the stellar yields of Nomoto et al. (2013), which are adopted in our cosmological simulations, and the stellar yields of Limongi & Chieffi (2018) for different stellar rotational velocities (v0, v150 and v300 represent rotational velocity v = 0, 150, and 300 km s−1, respectively). For AGB stars, we explore the stellar yields of Karakas (2010), adopted in our cosmological simulations, and those of Ventura et al. (2013); see also e.g. Vincenzo et al. (2016).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


