Fig. 9
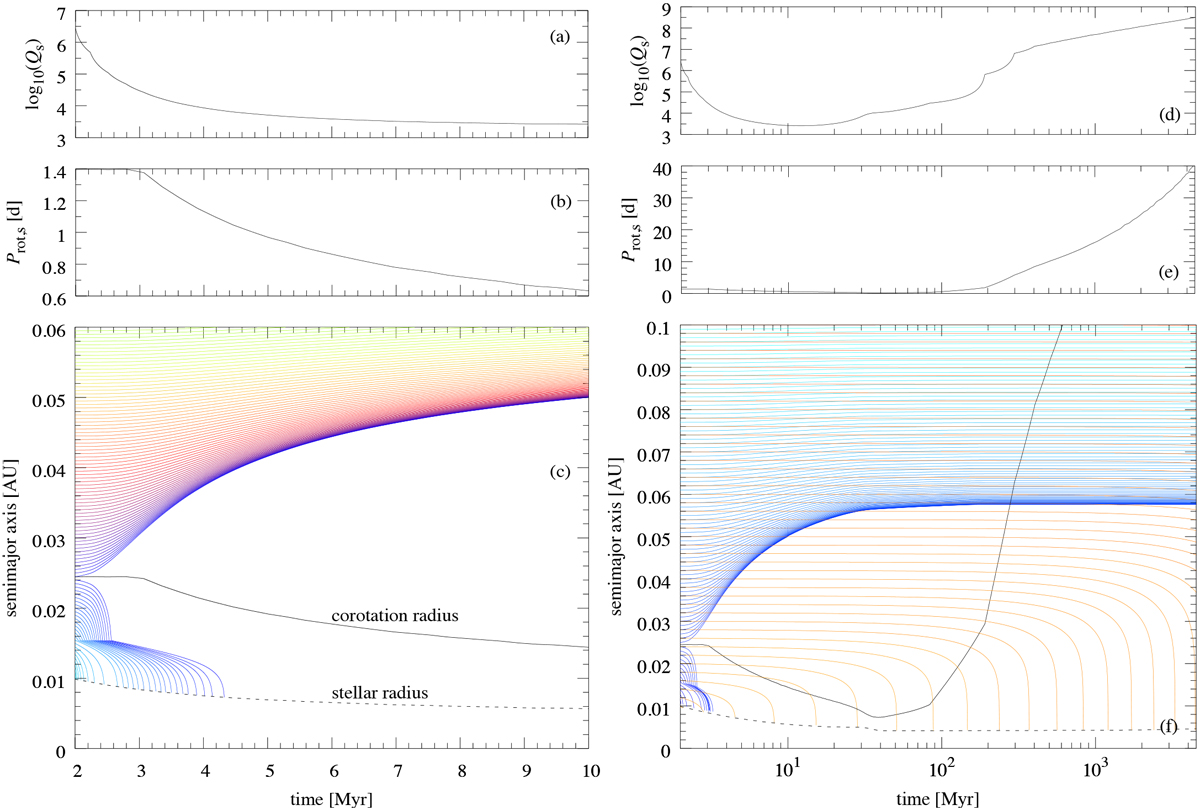
Evolution of the spin and orbital properties of a Sun-like star (initial rotation period 1.4 d, metallicity Z = 0.0134) as per Amard et al. (2016) and Bolmont & Mathis (2016) and orbital evolution of a hot-Jupiter population. (a) Frequency-averaged tidal dissipation factor. (b) Rotation period of the star during the first 10 Myr of stellar evolution. (c) Tidally driven orbital evolution of a single planet on a grid of 100 equally spaced initial orbits. Orbital decay is calculated via Eq. (7) (assuming e = 0) according to the dynamical tide model with stellar evolution as per a and b. (d) Stellar dissipation factor. (e) Stellar rotation period over the first 1 Gyr of stellar evolution. (f) Comparison of the planetary orbital evolution in the dynamical tide model (blue lines) and in the equilibrium tide model (orange lines, Q⋆ = 105).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


