Fig. 6.
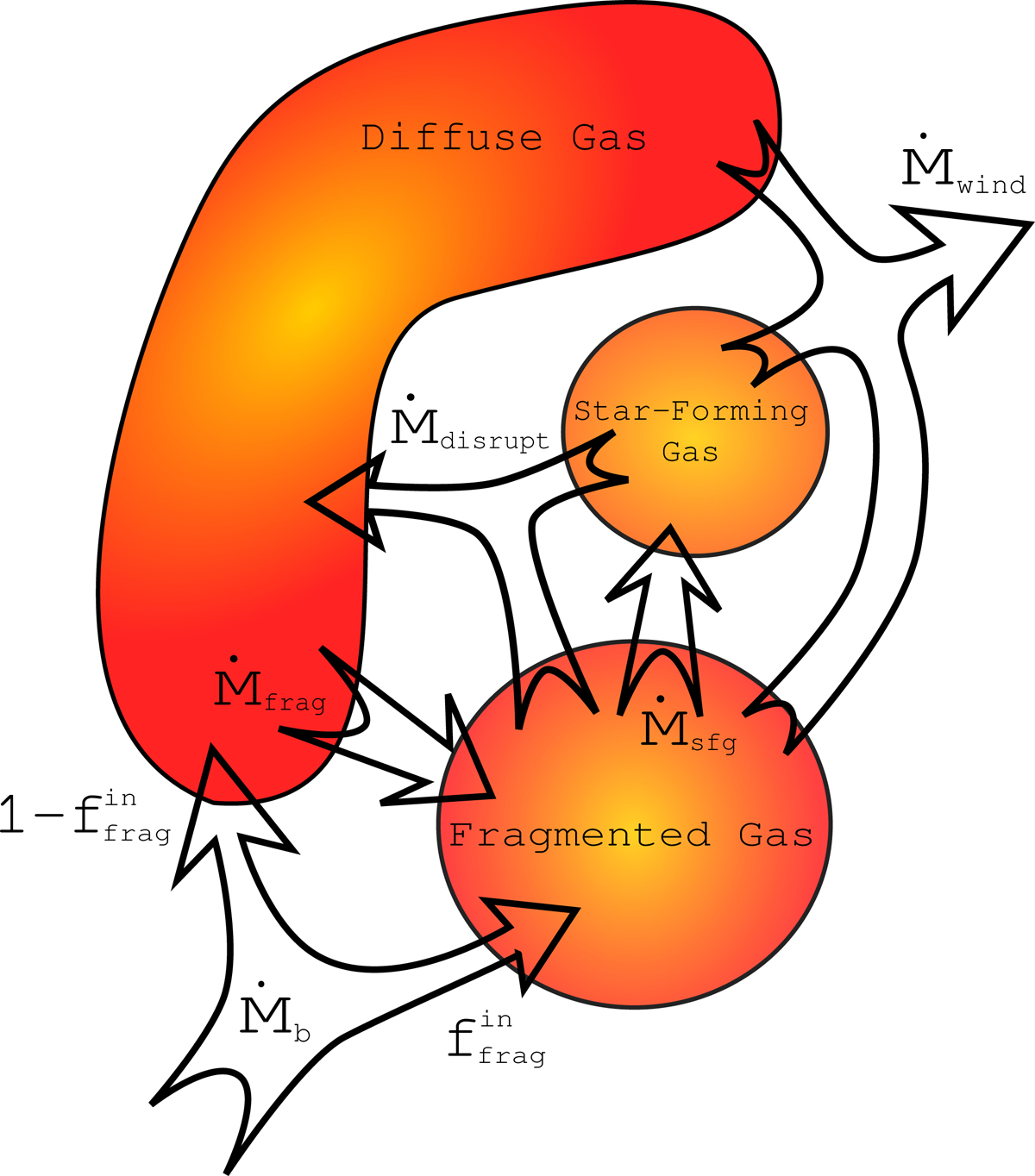
Diagram illustrating the flow of mass between the three gas reservoirs considered in our multiphase G.A.S. model. The star-forming reservoir contains the mass that is immediately available for star formation. It is fed by a turbulent cascade and gas fragmentation at a mass flow rate, Ṁsfg (Eq. (18)). The gas reservoir fragments at a rate, Ṁfrag (Eq. (14)). The diffuse gas reservoir is fed through the rates of two mechanisms: (1) gas accretion rate ![]() (Eq. (1)); and (2) the rate at which the fragmented and star-forming gas is disrupted via the energy injected by SNe and AGN, Ṁdisrupt (Eqs. (27) and (28)). Each of these three gas reservoirs contributes to the outflow rate, Ṁwind (Eqs. (24) and (26)).
(Eq. (1)); and (2) the rate at which the fragmented and star-forming gas is disrupted via the energy injected by SNe and AGN, Ṁdisrupt (Eqs. (27) and (28)). Each of these three gas reservoirs contributes to the outflow rate, Ṁwind (Eqs. (24) and (26)).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


