Fig. 12.
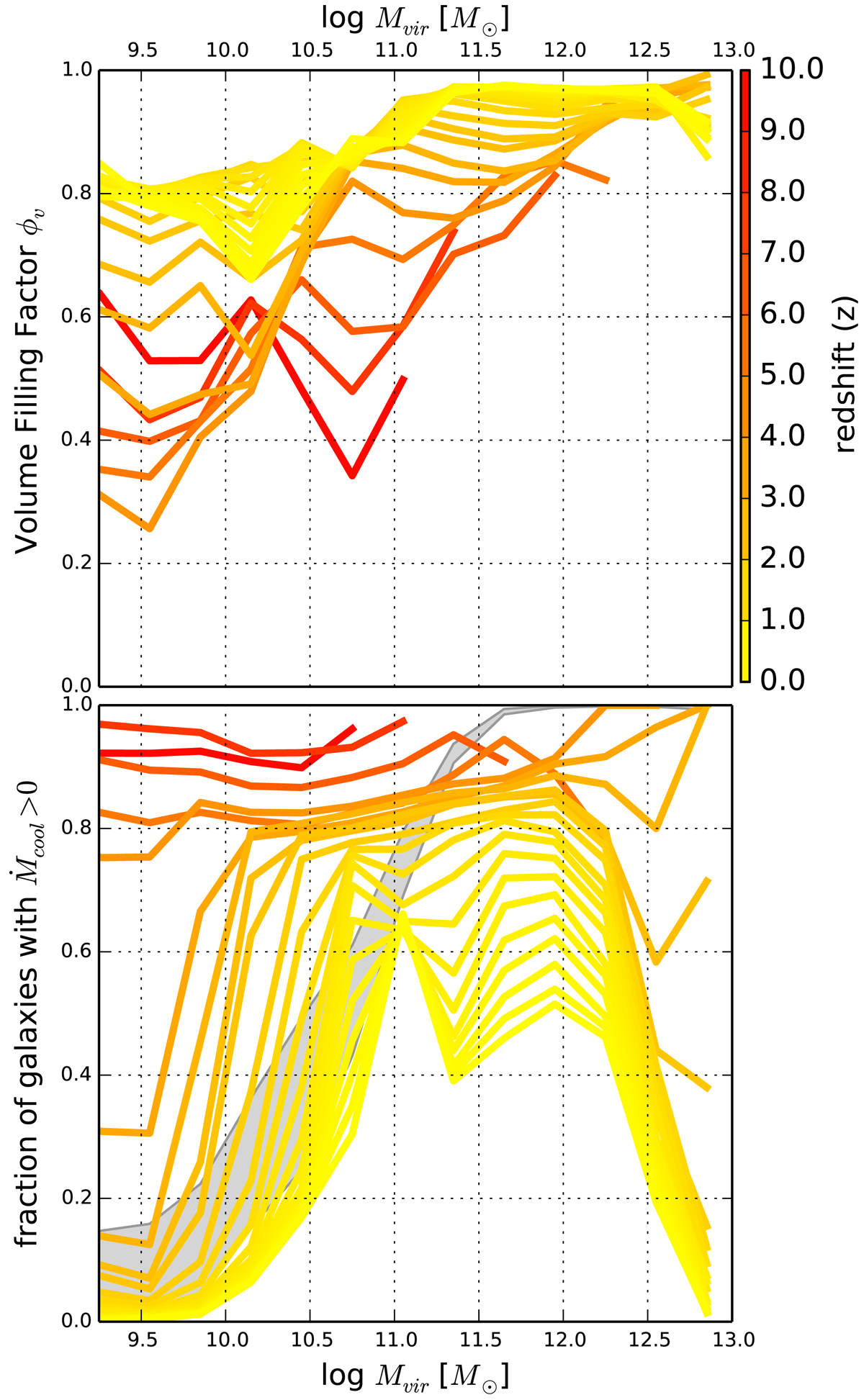
Upper panel: mean value of the volume filling factor, ϕ, of gas that is thermally unstable (Eq. (36)). The case ϕv = 1 implies that all the region within r = rcool is thermally unstable in our model. Lower panel: fraction of galaxies that are accreting radiatively cooling halo gas as a function of halo virial mass, Mvir. Different colours indicate this fraction as a function of redshift. The value of the redshift for each line is indicated in the colour bar on the right side of the upper panel. The grey area spans the range of the mean fraction of galaxies that are accreting hot gas for each halo mass summed over redshifts 0.1–10 (Eq. (2)). For example, for a halo mass of 1010.5 M⊙, the fraction of galaxies that have hot gas in the halo which is radiatively cooling can range between 30% and ∼55% depending on redshift.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


