Fig. 9
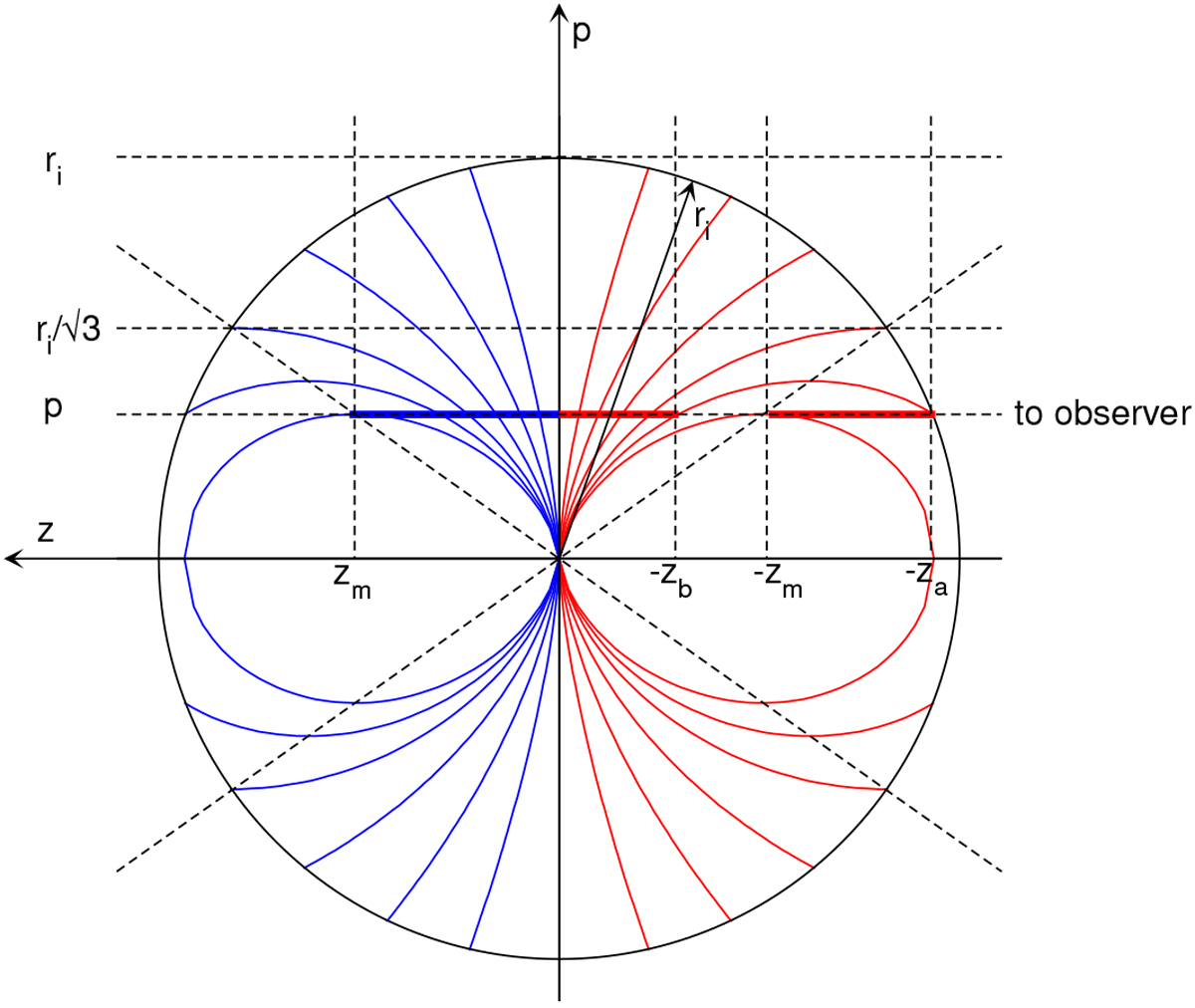
For a given projected distance ![]() the wing emission comes from the thick part of the line of sight, for radii less than ri. The emission from the thin part of the line of sight is hidden to the observer.For the blue wing, the observer can observe the emission coming from z = 0 (with vz = 0) to z = zm (with vz = −vm). For the red wing, the observer can observe the emission coming from z = −za (with r = ri, vz = va) to z = −zm (with vz = +vm), and, since the corresponding part of the equal-LOS-velocity surface facing the observer is missing (it would be outside the infall radius), from z = 0 (with vz = 0) to z = −zb (with vz = va). The velocity va is the LOS velocity of the equal-LOS-velocity surface that intersects the sphere r = ri at a projected distance p, i.e. va = vz(p, −za) = vz(p, −zb).
the wing emission comes from the thick part of the line of sight, for radii less than ri. The emission from the thin part of the line of sight is hidden to the observer.For the blue wing, the observer can observe the emission coming from z = 0 (with vz = 0) to z = zm (with vz = −vm). For the red wing, the observer can observe the emission coming from z = −za (with r = ri, vz = va) to z = −zm (with vz = +vm), and, since the corresponding part of the equal-LOS-velocity surface facing the observer is missing (it would be outside the infall radius), from z = 0 (with vz = 0) to z = −zb (with vz = va). The velocity va is the LOS velocity of the equal-LOS-velocity surface that intersects the sphere r = ri at a projected distance p, i.e. va = vz(p, −za) = vz(p, −zb).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


