Fig. 11.
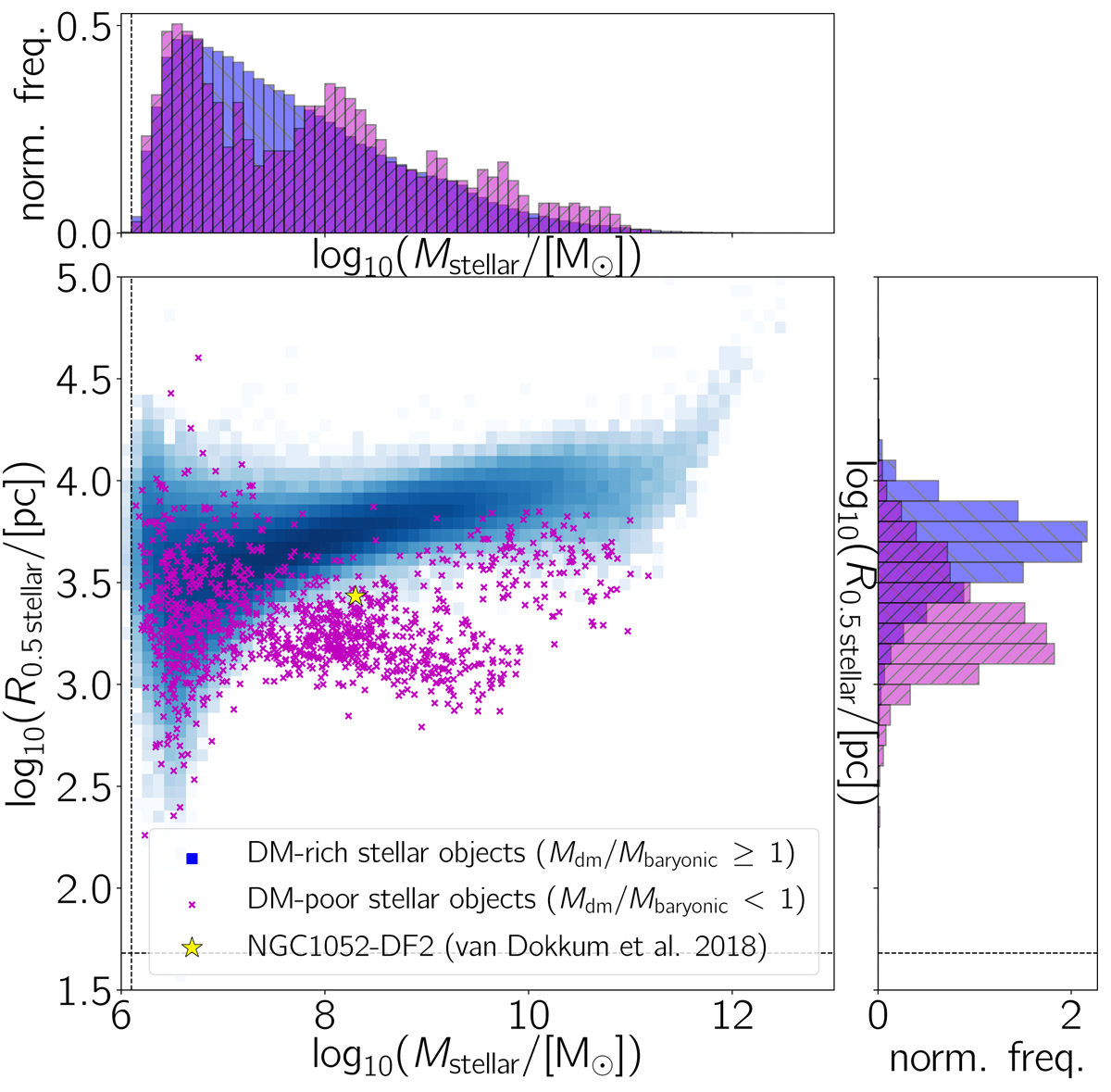
Proper radius containing half of the stellar mass, R0.5 stellar, as a function of the stellar mass, Mstellar, of simulated DMC stellar objects at redshift z = 0. Dark matter-containing stellar objects are separated in dark matter-rich (Mdm/Mbaryonic ≥ 1; blue bins) and dark matter-poor (Mdm/Mbaryonic < 1; purple crosses) types. The yellow star shows the position of NGC 1052-DF2 with Mstellar = 2 × 108 M⊙ and a 3D deprojected half-light radius of 2.7 kpc (van Dokkum et al. 2018a). The dashed vertical and horizontal lines indicate the initial baryonic matter mass of a particle (1.26 × 106 M⊙) and the smallest fiducial cell size (48 pc). Subhalos with a stellar half-mass radius below the cell resolution are not shown in the plots. The histograms are normalized such that the total area is equal to 1.0 and such that they have bin widths of log10(ΔMstellar/[M⊙]) = 0.10 and log10(ΔR0.5 stellar/[pc]) = 0.10.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


