Fig. 1.
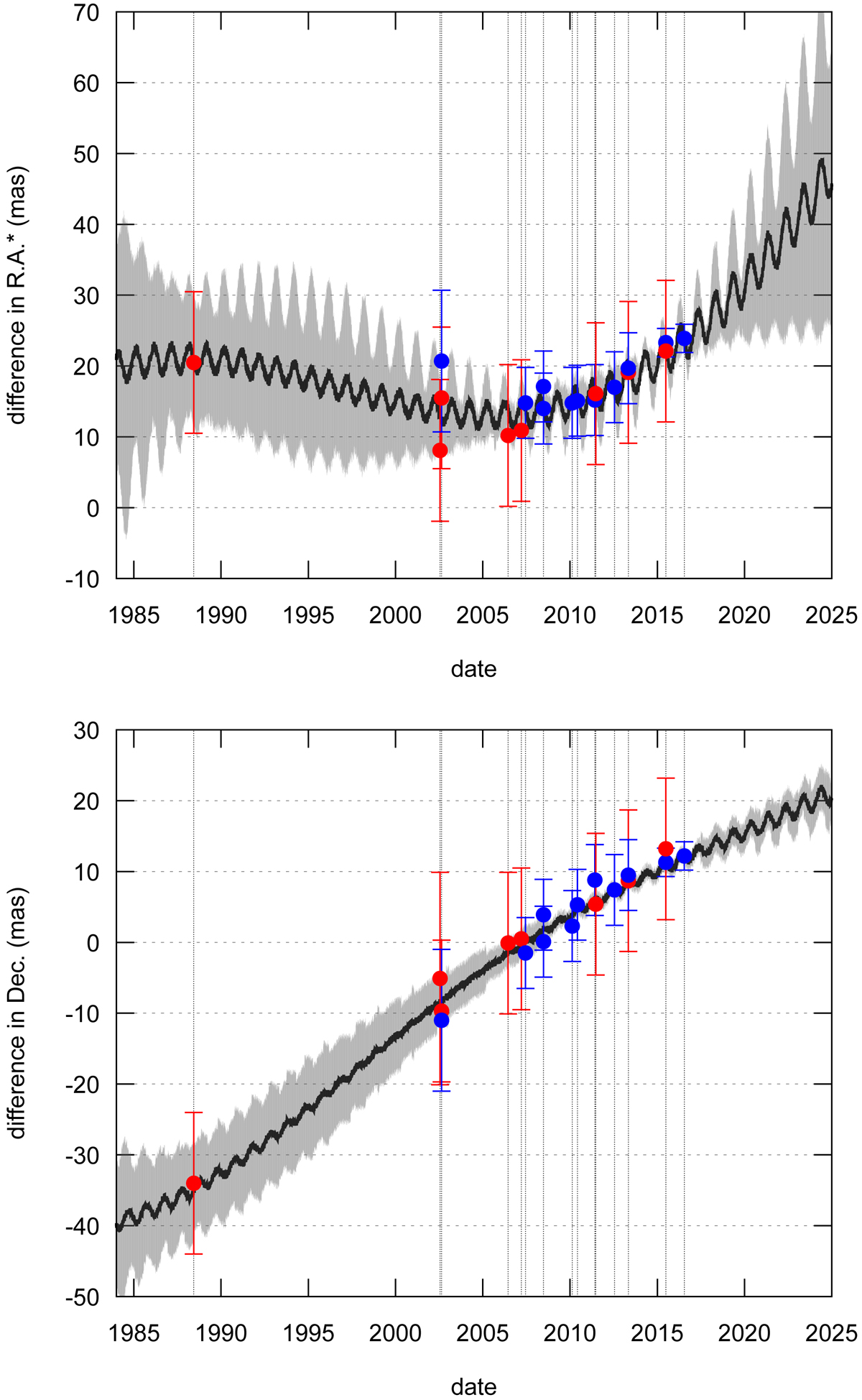
Difference between NIMAv8 and JPL DE436 ephemeris of Pluto’s system barycentre (black line) in right ascension (weighted by cos δ) and in declination. Blue bullets and their estimated precision in error bar represent the positions coming from the occultations studied in this work and red bullets represent the positions deduced from other publications. The grey area represents the 1σ uncertainty of the NIMA orbit. Vertical grey lines indicate the date of the position for a better reading on the x-axis. The angular diameter of Pluto, as seen from Earth, is about 115 mas, while the atmosphere detectable using ground-based stellar occultations subtends about 150 mas on the sky.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


