Fig. 1.
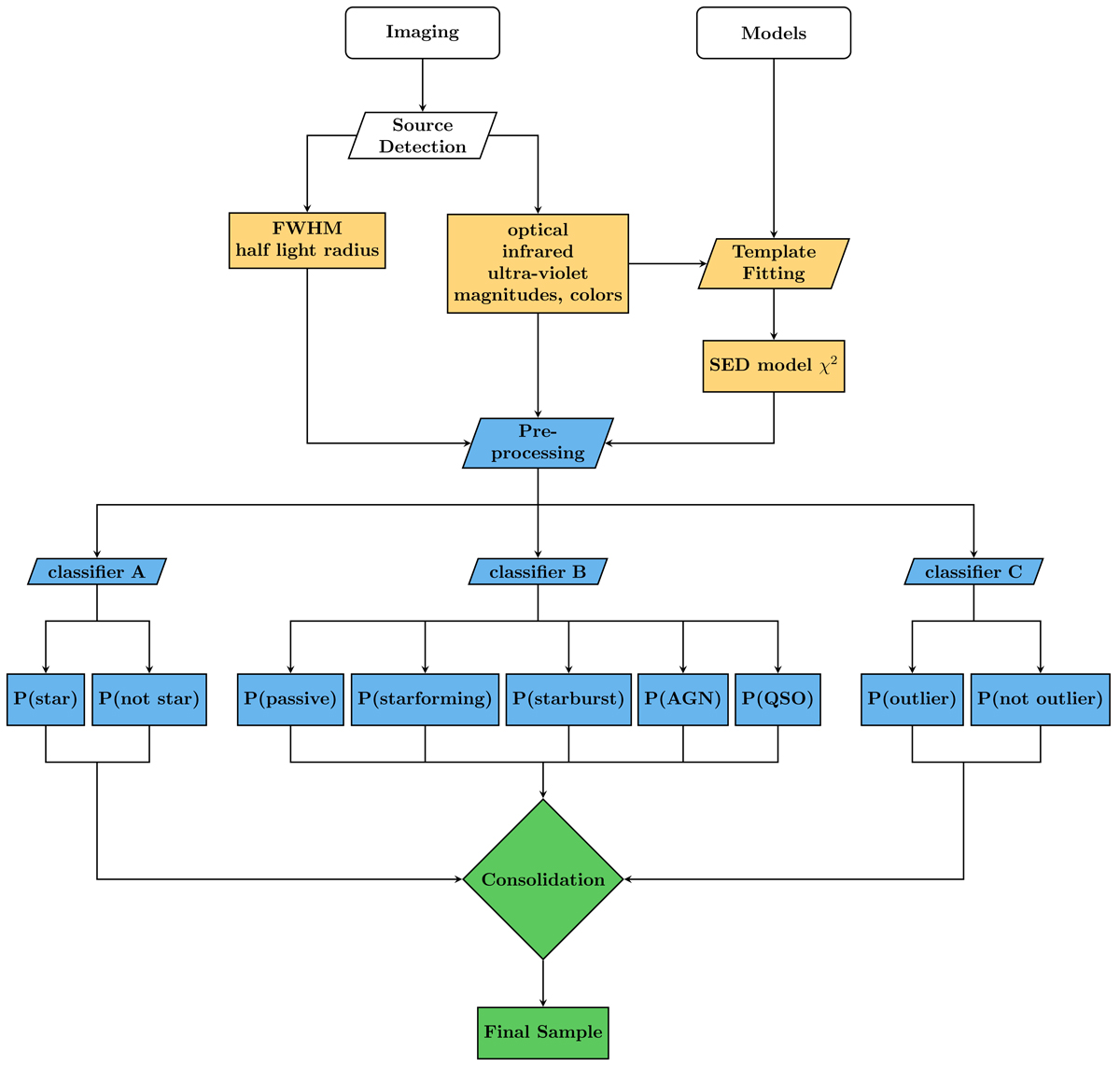
Components of the classification aided photometric redshift estimation method (CPz). Photometric and morphometric parameters are extracted from the observed images. Magnitudes, colors and an estimation of the source shape (e.g., half light radius) make up the input attributes. The spectral energy distributions are fitted with model templates of star, galaxy and active galactic nuclei populations, the χ2 value of the best fitting model per library is added to the input attribute set. The pre-processing of the data consists of normalization and whitening of the attribute distributions (zero mean and variance of one) and the sample is split into training, testing and validation subsamples. The training sample is presented to three distinct classifiers, producing a probability for each source to A) be a star B) have an optimal photometric redshift from a collection of distinct libraries C) be a photometric redshift outlier. The final phase of CPz is the consolidation of the results, during which the test sample is used to decide on the thresholds adopted for each classifier and the assessment of the final accuracy on the classification and the photometric redshift performance using the validation sample.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


