Fig. 13
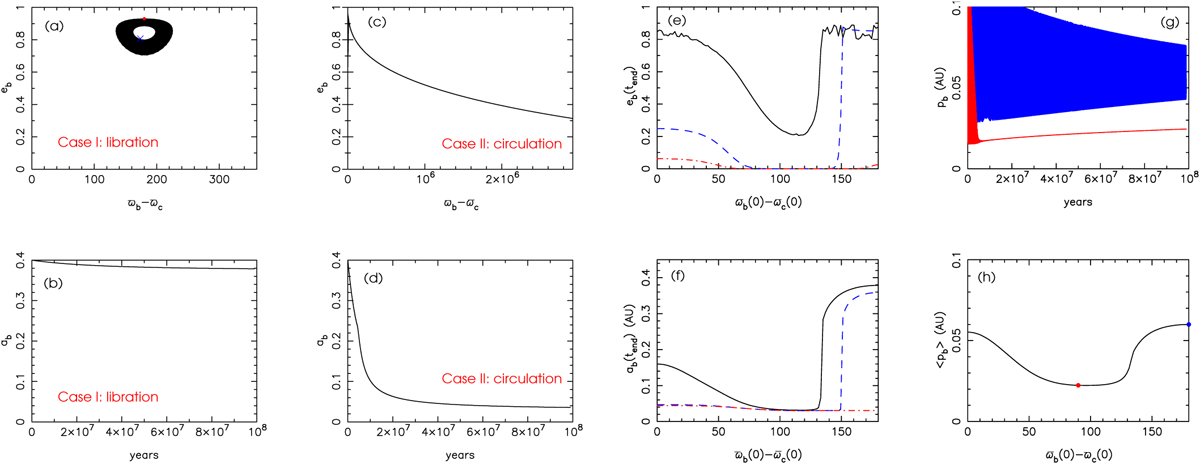
Effect of the initial value of ϖb − ϖc on the subsequent tidal evolution of a system. Panels a and b: ϖb(0) − ϖc(0) = 180° (Case I); panels c and d: ϖb(0) − ϖc(0) = 90° (Case II). The red dot and blue cross in panel a indicate the initial and current state, respectively, of Kepler-419. Panels e and f: valuesof ab and eb at tend = 108 yr (solid black curves), tend = 109 yr (dashed blue curves), and tend = 2.3 × 109 yr (the estimated age of the system; dot-dashed red curves) as functions of the initial value of ϖb − ϖc, which show that for a range of initial relative orientations, planet b can sustain a high value of eb because it spends most of its time with a periastron distance which is too high for significant circularisation to occur. Panel g: evolution of planet b’s periastron distance, pb, for Case I (blue) and Case II (red), the latter showing escape from libration and hence a permanently low value of pb. Panel h: average value of pb, ⟨pb ⟩, as a functionof ϖb(0) − ϖc(0). Angles are in degrees.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


