Fig. 2
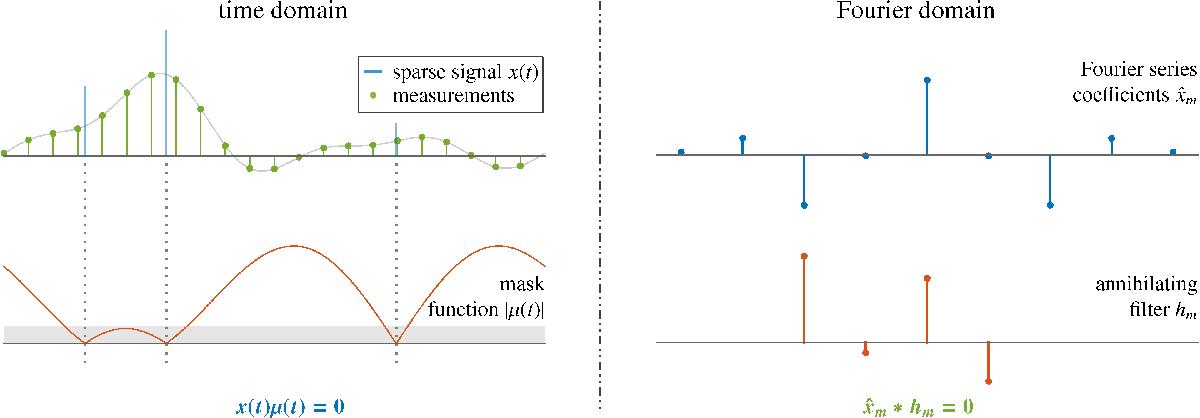
Sparse recovery with annihilating filter method. The annihilation equation that the sparse signal should satisfy x(t)μ(t) = 0 is equivalent to a set of discrete convolution equations between uniformly sinusoidal samples and a finite length discrete filter in the Fourier domain. The mask function μ(t), which can be estimated from the given lowpass filtered samples of x(t), vanishes at the position where x(t) is different from zero.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


