Fig. 6
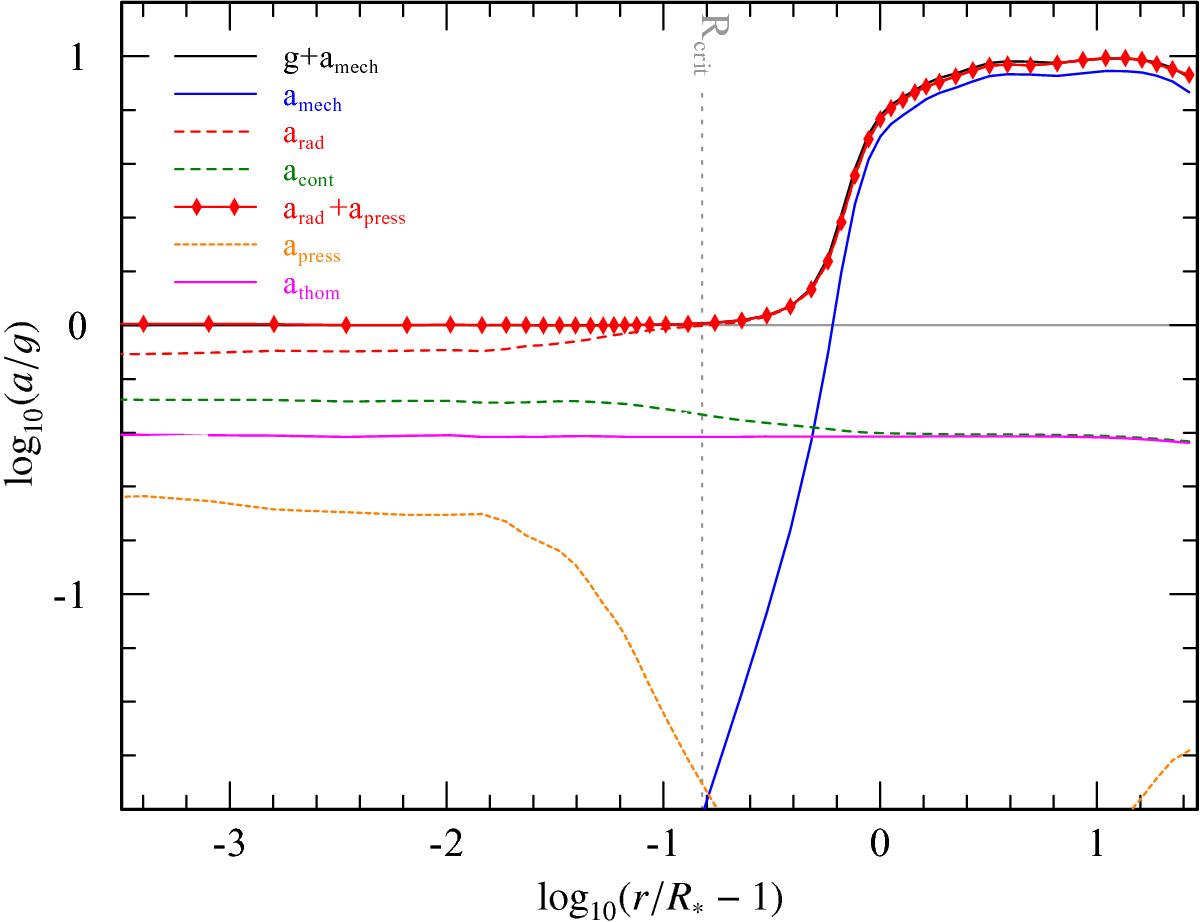
Acceleration stratification for a hydrodynamically consistent model. The wind acceleration (thick red diamond line) is compared to the repulsive sum of inertia and gravitational acceleration g(r) (black line). The fact that these two curves are (almost) identical illustrates that the hydrodynamic equation is fulfilled throughout the stellar atmosphere. For a more convenient illustration, all terms are normalized to g(r). The input parameters of the model are compiled in Table 1 while the resulting quantities can be found in Table 3.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


