Fig. 8
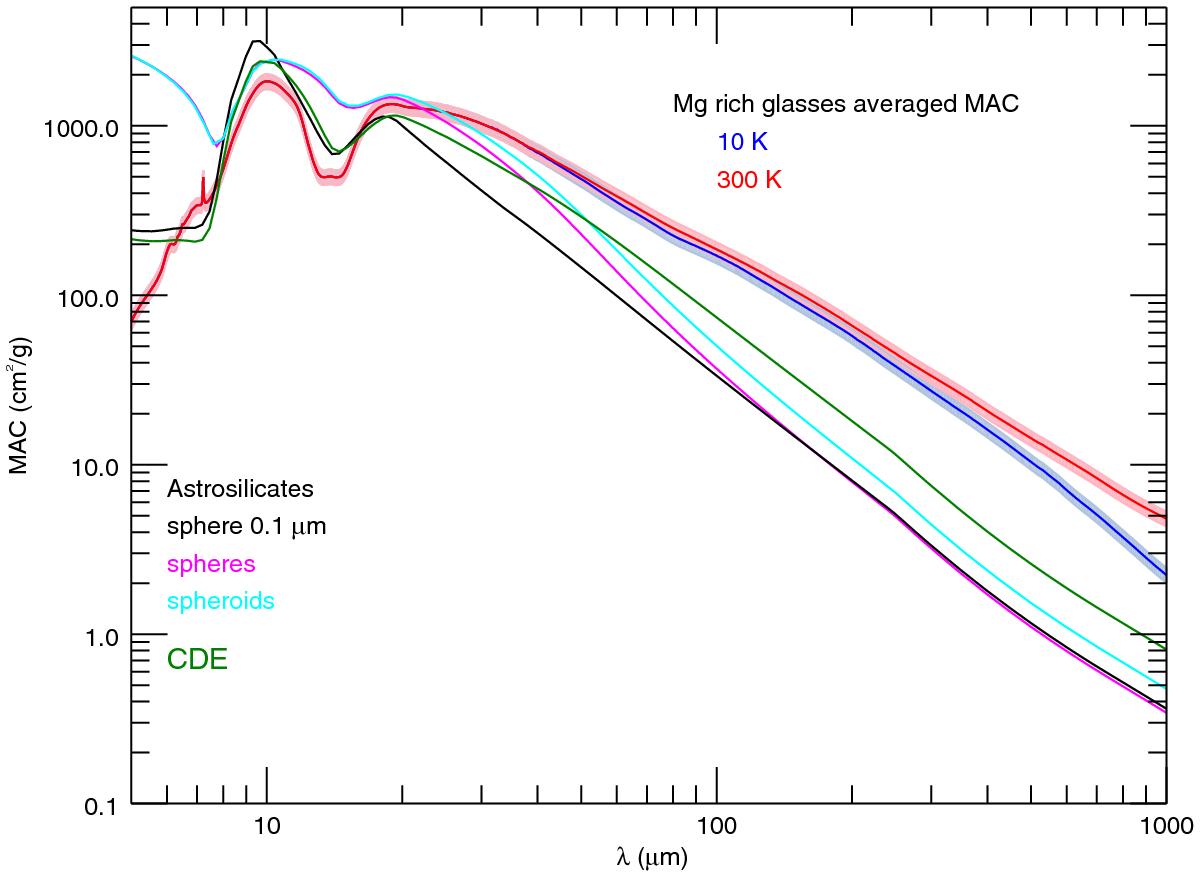
Comparison of averaged experimental mass absorption coefficients with the MAC calculated from cosmic dust model. The solid line curves with the uncertainty represent the MAC averaged on the four samples X35, X40, X50A and X50B: (red) MAC at 300 K, (blue) MAC at 10 K. The MAC of the “astrosilicates” from (Li & Draine 2001) are calculated using Mie Theory for a 0.1 μm size grain (black), for a log-normal grain size distribution with a mean diameter of 1 μm for spherical grains (magenta) and for prolate grains (cyan) and for a CDE model (green). See text for more details.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


