Fig. 8
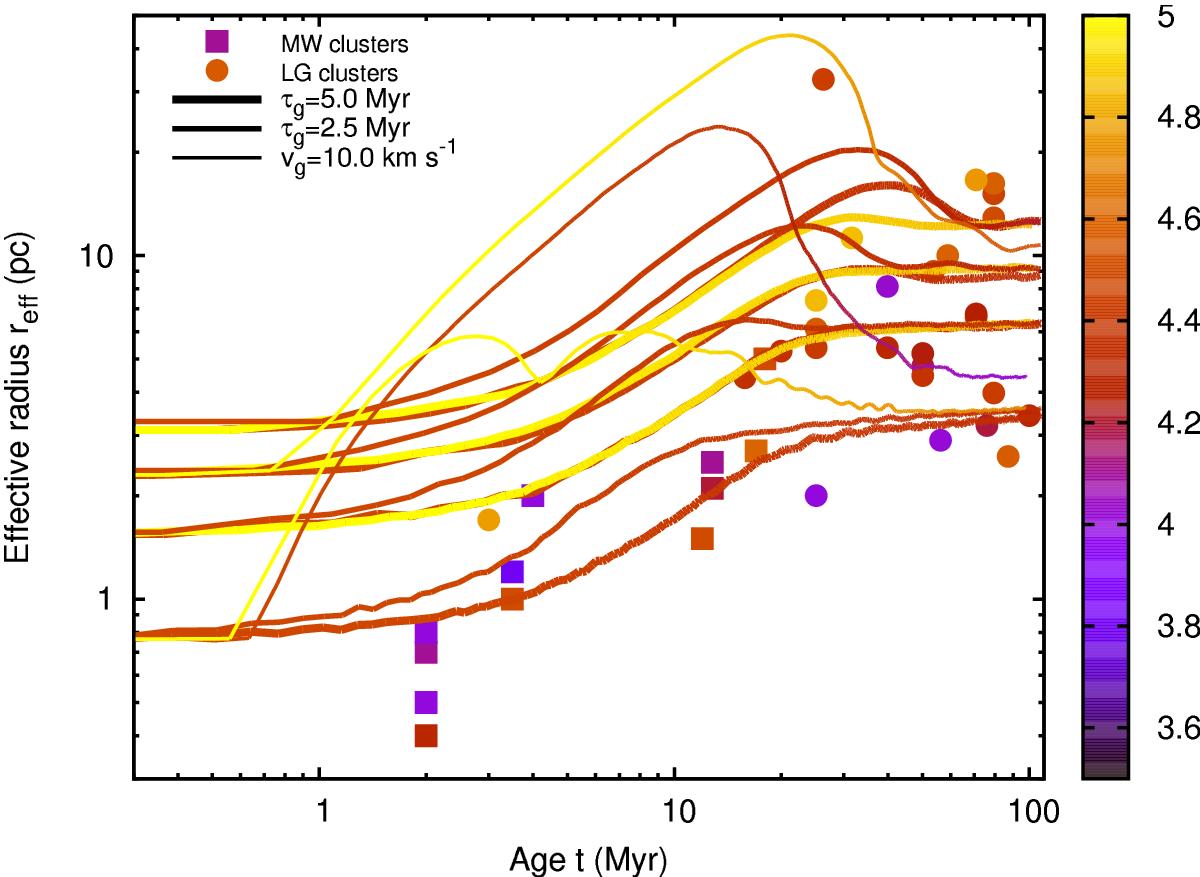
Curves representing the evolution of projected half-mass radii (or effective radii) reff(t) for computed model clusters that include a gas expulsion phase. Unlike those in the previous figures, these computed clusters initiate from much more extended stellar distributions with initial half-mass radius, rh(0) > 1 pc (see Table 4, bottom). Furthermore, the gas expulsion timescales, τg, are much longer as indicated in the legend, making the gas expulsion placid in these cases (except for vg = 10 km s-1, which causes explosive expulsion as in the previous cases). For ϵ ≈ 30% star formation efficiency, these extended model clusters expand to the observed sizes of the most extended young massive clusters in the Local Group (filled symbols), while also covering the mass ranges appropriate for them. We note that with slow or placid gas expulsion, the clusters tend to reach sizes that are nearly independent of their initial masses, unlike their explosive counterparts. As for the previous figures, the symbols and the curves are colour-coded according to the corresponding current total (photometric) mass.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


