Fig. 1
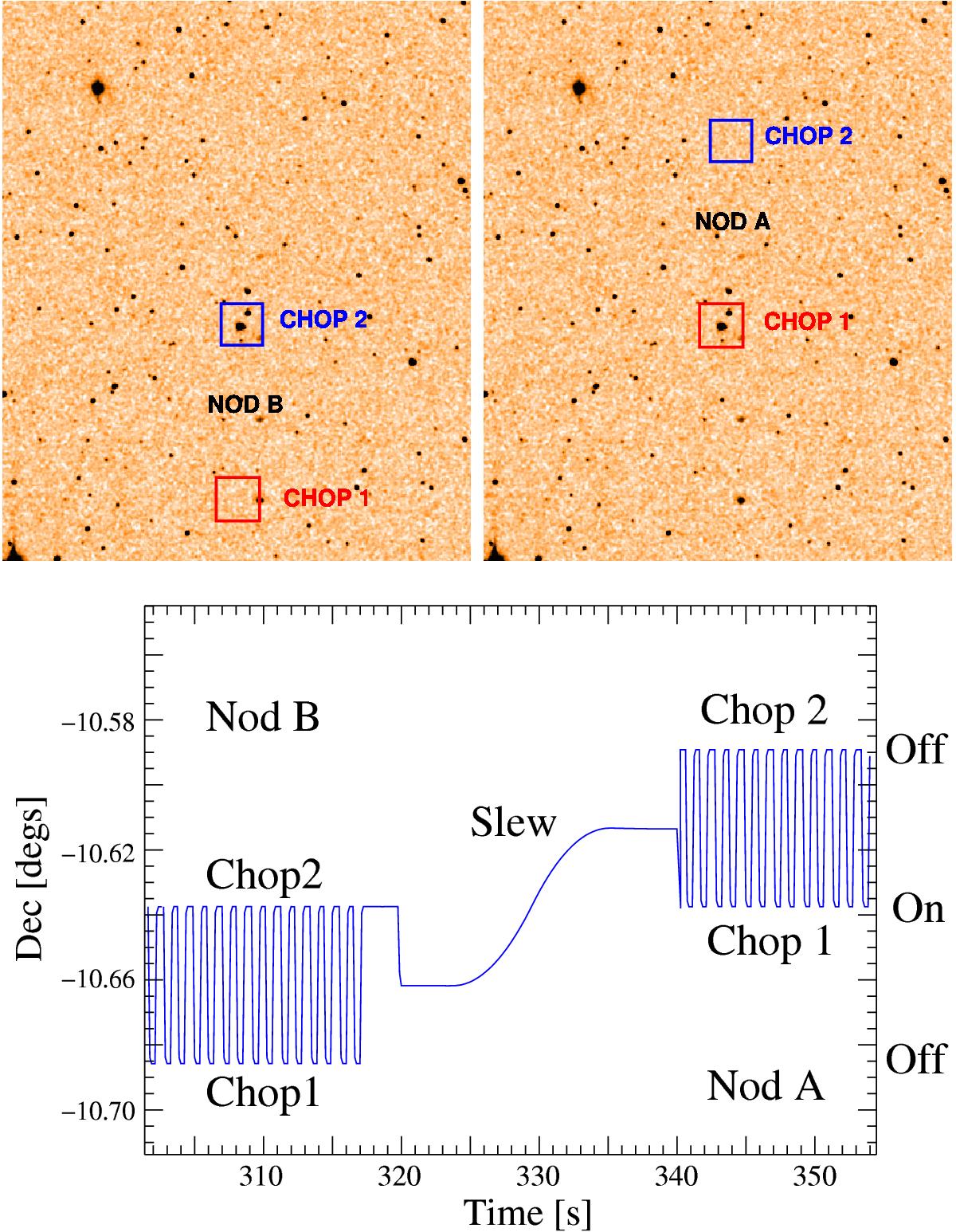
Example of chop-nod observation footprints (top), and observed position projected on the sky (bottom). In the first nod, the detector alternates between two optical paths to observe the object and the background. These paths have slightly different telescope background signals. In the second nod, the optical paths are inverted after slewing the telescope. By adding the two object-background differences, it is possible to remove the effects of the different telescope background levels.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.