Fig. 5
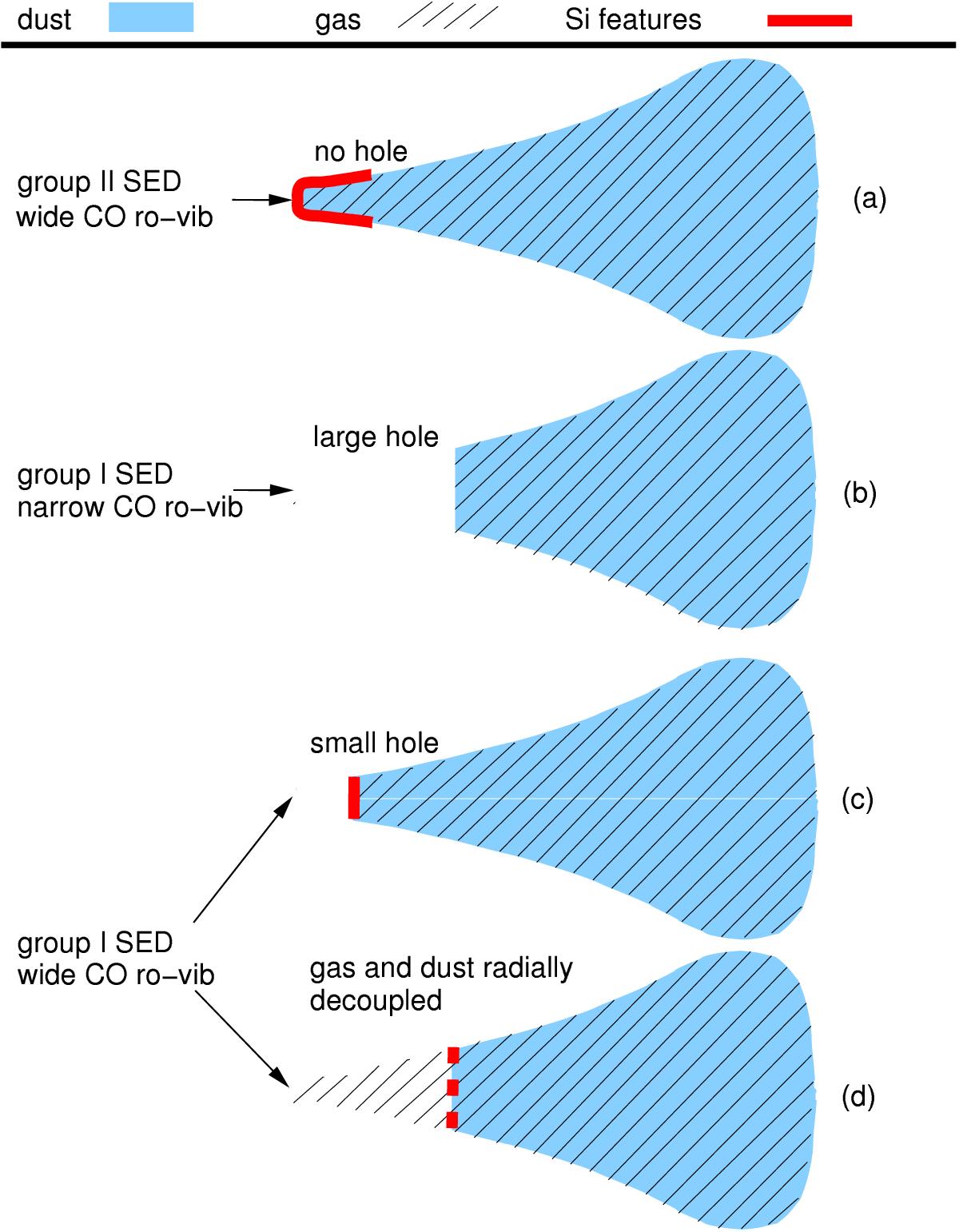
Possible disc geometries: a) a continuous disc without a hole/gap, resulting in a group II SED with silicate features and broad CO ro-vibrational lines emitted from close to the star; b) a disc with a large hole, resulting in a group I SED without silicate feature (group Ib) and with narrow CO ro-vibrational lines emitted from the outer disc wall; c) a disc with a small hole, resulting in a group I SED with silicate feature (group Ia) and with broad CO ro-vibrational lines emitted from the outer disc wall (in this case close to the star); and d) a disc with a small or large dust hole, resulting in a group I SED (with or without silicate features) and broad CO lines. The radial gas distribution differs from that of the dust and the CO lines are thus emitted from within the hole.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


