Table 3
Physical properties of GN20, GN20.2a and GN20.2b.
| Source | M ⋆ | sSFR |
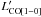
|
SFE | Z PP04 | δ GDR | αCO(GDR) | M dyn | αCO(dyn.) | ⟨ αCO ⟩ | M gas | f gas | q |
| (1010 M⊙) | (Gyr-1) | (1010 K km s-1 pc2) | (l0) | (1011 M⊙) | (1011 M⊙) | ||||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) |
|
|
|||||||||||||
| GN20 | 11 | 16.9 | 16 ± 0.4 | 116 | 8.8(9.2) | 77(27) | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 0.66 ± 0.12 | 2.41 ± 0.05 |
| GN20.2a | 3.8 | 20.9 | 9.0 ± 1.1 | 90 | 8.6(9.0) | 106(42) | 2.0 ± 1.1 | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 2.8 ± 1.6 | 2.4 ± 1.3 | 2.2 ± 1.2 | 0.85 ± 0.09 | 1.72 ± 0.04 |
| GN20.2b | 11 | 6.3 | 2.9 ± 0.6 | 238 | 8.9(9.2) | 53(27) | 2.8 ± 1.5 | ... | ... | 2.8 ± 1.5 | 0.8 ± 0.5 | 0.42 ± 0.18 | 2.60 ± 0.13 |
Notes. Column 1: name of the object. Column 2: stellar mass
determined from synthetic template fitting of the U- to IRAC 4.5
μm-band photometry (without 3.6 μm-band), assuming
a constant SFH and a Chabrier (2003) IMF. The typical uncertainties are 0.2 dex.
For GN20.2b, the stellar mass is estimated by taking an average of the results
from SED fitting with and without 4.5 μm-band. Column 3: specific star formation
rate. sSFR =
SFR/M⋆,
with SFR derived from the bolometric IR luminosity. Column 4: for GN20, the
CO(1–0) luminosity is measured by Carilli et al.
(2010). For GN20.2a and GN20.2b, we convert the CO(2–1) luminosity
measured by Carilli et al. (2011) to
CO(1–0) luminosities by assuming r21 = 0.84 (Bothwell et al. 2013). Column 5: SFE =
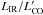 in
units of l0
= L⊙ (K km s-1 pc2)-1. Column 6: metallicity
estimated based on the FMR (values outside the parenthesis) and mass-metallicity
(values in the parenthesis) relation applied to the present-day elliptical
galaxies. We have corrected for the metallicity scale from KD02 to PP04 for the
FMR by adopting the prescriptions in Kewley
& Ellison (2008). Column 7: gas-to-dust ratio derived from the
relation of Magdis et al. (2012a) which
relates the δGDR to metallicity. The values
in the parenthesis are inferred assuming a metallicity estimated from the
mass-metallicity relation of present-day elliptical galaxies, while the values
outside the parenthesis are from the FMR relation. Column 8:
CO-to-H2
conversion factor in units of M⊙ (K km s-1 pc2)-1, inferred from
in
units of l0
= L⊙ (K km s-1 pc2)-1. Column 6: metallicity
estimated based on the FMR (values outside the parenthesis) and mass-metallicity
(values in the parenthesis) relation applied to the present-day elliptical
galaxies. We have corrected for the metallicity scale from KD02 to PP04 for the
FMR by adopting the prescriptions in Kewley
& Ellison (2008). Column 7: gas-to-dust ratio derived from the
relation of Magdis et al. (2012a) which
relates the δGDR to metallicity. The values
in the parenthesis are inferred assuming a metallicity estimated from the
mass-metallicity relation of present-day elliptical galaxies, while the values
outside the parenthesis are from the FMR relation. Column 8:
CO-to-H2
conversion factor in units of M⊙ (K km s-1 pc2)-1, inferred from
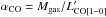 , with
Mgas =
Mdust ×
δGDR. Column 9: dynamical masses
within the half-light radius. For GN20.2b, we do not derive an estimate of
dynamical mass, as the dynamical mass estimated in this way is found to be smaller
than stellar mass. Column 10: CO-to-H2 conversion factor estimated based on the
dynamical method. Column 11: the average of CO-to-H2 conversion factor
derived from gas-to-dust ratio method and dynamical modeling. Column 12: molecular
gas mass measured from
, with
Mgas =
Mdust ×
δGDR. Column 9: dynamical masses
within the half-light radius. For GN20.2b, we do not derive an estimate of
dynamical mass, as the dynamical mass estimated in this way is found to be smaller
than stellar mass. Column 10: CO-to-H2 conversion factor estimated based on the
dynamical method. Column 11: the average of CO-to-H2 conversion factor
derived from gas-to-dust ratio method and dynamical modeling. Column 12: molecular
gas mass measured from 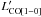 and
⟨ αCO
⟩. Column 13: molecular gas fraction: fgas =
Mgas/
(Mgas +
M⋆). The
uncertainties are mainly dominated by the uncertainties in molecular gas
estimates. Column 14: IR-radio correlation parameter.
and
⟨ αCO
⟩. Column 13: molecular gas fraction: fgas =
Mgas/
(Mgas +
M⋆). The
uncertainties are mainly dominated by the uncertainties in molecular gas
estimates. Column 14: IR-radio correlation parameter.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


