Fig. 1
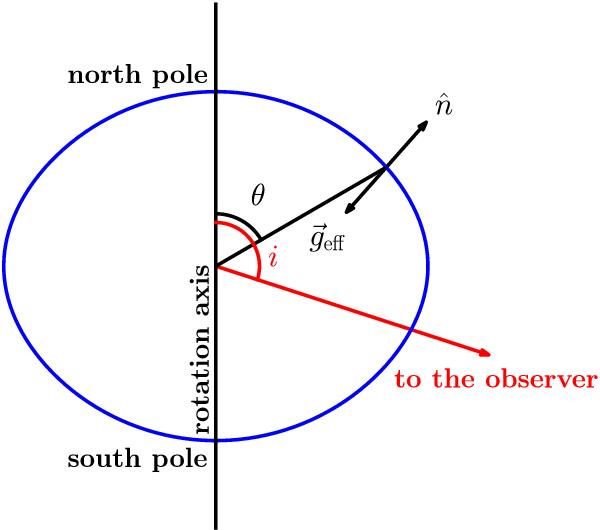
Schematic representation of a meridional cut of a rotating star. The plane shown
contains the line connecting the centre of the star to the observer and the
rotational axis. In the text, the angle i is called the inclination angle
(i =
0 when the star is seen pole-on). A given point on the surface is
defined by the angle θ that we call the colatitude in the text. Note
that in a deformed rotating star, the unit vector perpendicular to the surface
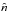 is not aligned with the direction connecting the considered position to the centre
of the star. The same is true for the effective gravity which is the classical
gravity modified by the effect of the centrifugal force.
is not aligned with the direction connecting the considered position to the centre
of the star. The same is true for the effective gravity which is the classical
gravity modified by the effect of the centrifugal force.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


