Free Access
Table 2
The main module of motion planning algorithm calls this module that calculates the gradient of the DNF.
| Gradient of the DNF for the positioner i | |
|
|
|
| Inputs: | Current position of the positioner qi, |
| target position of the positioner qiT, | |
| and current position of the neighbor positioners Qneighbor ∈ Q | |
| Outputs: | The gradient of the navigation function for positioner i |
which is a vector of a two elements 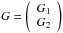 |
|
|
|
|
| G = 0 | |
| G = G + 2λ1(qi − qiT) | |
| for each neighbor positioner (j = 1:6) | |
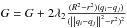
|
|
| end for | |
Notes. This function gets the current and target position of the robot as well as the current position of its adjacent positioners. The output of the function is the gradient of the DNF.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


