Fig. 6
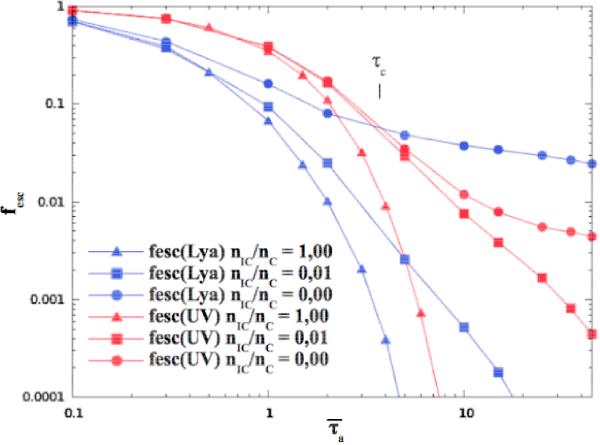
Evolution of the Lyα (blue lines) and UV continuum (red) escape
fraction as a function of the dust optical depth
(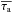 )
for a homogeneous (triangles), a weakly clumpy (squares), and an extremely clumpy
(spheres) medium. In these simulations, we adopt FF = 0.23, CF = 0.997
(Rmin = 49 and Rmax = 64
cells),
)
for a homogeneous (triangles), a weakly clumpy (squares), and an extremely clumpy
(spheres) medium. In these simulations, we adopt FF = 0.23, CF = 0.997
(Rmin = 49 and Rmax = 64
cells), 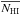 = 1019 cm-2, vexp = 0
km s-1, and b = 40 km s-1. For
comparison, the UV escape fractions (Fig. 4) are overlaid (red lines). For the
extremely clumpy medium we note that for
= 1019 cm-2, vexp = 0
km s-1, and b = 40 km s-1. For
comparison, the UV escape fractions (Fig. 4) are overlaid (red lines). For the
extremely clumpy medium we note that for 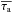 larger than a certain limit τc (here roughly equal to
3.5), fesc(UV) drops below
fesc(Lyα).
larger than a certain limit τc (here roughly equal to
3.5), fesc(UV) drops below
fesc(Lyα).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


