Table 6
Predictions of the black hole mass for the galaxy NGC 4889.
| Relation | b | m | M • | (M•)max | (M•)min |
|
|
|||||
| M• − σe/200 (McConnell et al. 2011) | 8.29 ± 0.06 | 5.12 ± 0.36 | 3.3 × 109 | 4.6 × 109 | 2.3 × 109 |
| M• − σe/200 (this work) | 8.27 ± 0.02 | 5.33 ± 0.13 | 3.5 × 109 | 3.9 × 109 | 3.1 × 109 |
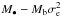 (Feoli & Mancini 2011) (Feoli & Mancini 2011) |
4.56 ± 0.10 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 1.3 × 1010 | 2.1 × 1010 | 7.5 × 109 |
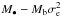 (this work) (this work) |
4.05 ± 0.15 | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 8.1 × 109 | 1.8 × 1010 | 3.7 × 109 |
| Experimental data (NGC 4889) | σe = 347 | Mb = 1.75 × 1012 | 2.1 × 1010 | 3.7 × 1010 | 5.5 × 109 |
Notes. Column (1): scaling relations. Columns (2)−(3): the regression coefficients, the intercept b and the slope m. Column (4): the predicted black hole mass. Column (5): the predicted maximal value of black hole mass. Column (6): the predicted minimal value of black hole mass. Last row: the experimental data from McConnell & Ma (2013).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


