Fig. 1
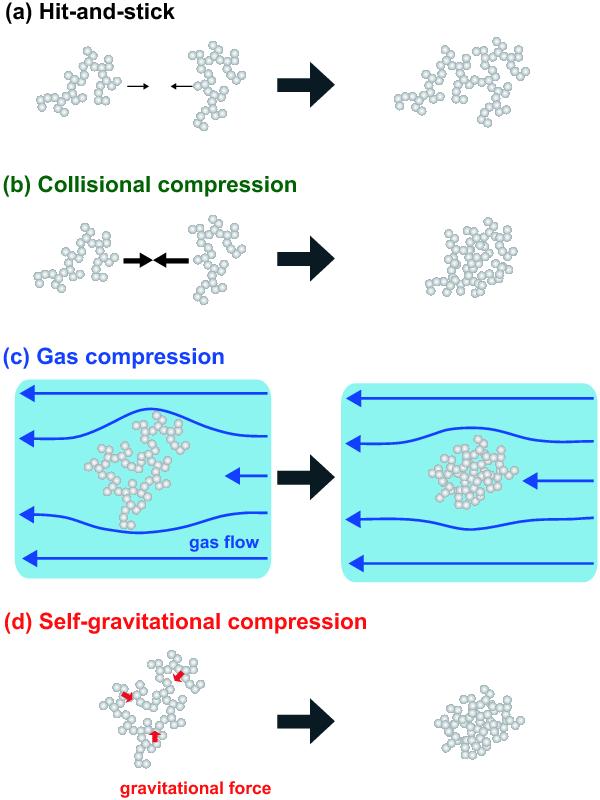
Schematic drawing to illustrate dust growth via fluffy aggregates. a) The dust aggregate hits another aggregate to be stick. This reduces dust density and occurs in a very early stage of dust growth. b) When the collisional speed is high enough to disrupt the dust aggregates, they are compressed. c) Dust aggregates have a velocity difference against gas, and they feel the ram pressure by the gas. The ram pressure statically compresses the dust aggregates. d) When the dust aggregates become so massive that they do not support their structure, they are compressed by their own self-gravity.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


