Fig. 3
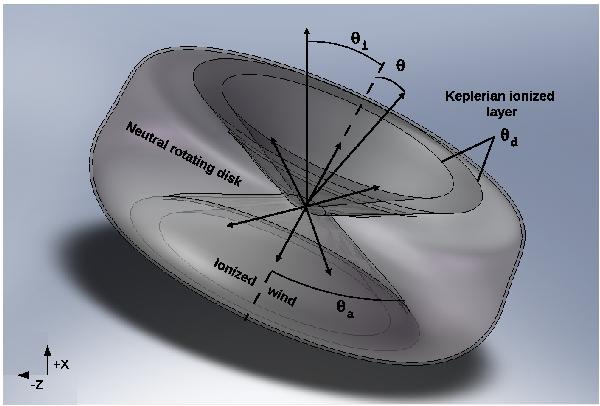
Sketch of the double-cone geometry used for the modelling of MWC349A. The ionized gas is contained in a double cone with its revolution axis perpendicular to the plane of the neutral disk. Each cone has a semi-opening angle of θa and is made up of two ionized regions with different kinematics: i) a rotating and expanding ionized wind contained within the double-cone with semi-opening angle θa − θd; and ii) a Keplerian rotating ionized layer comprised between the ionized wind and the neutral disk with an opening angle relative to the conical surface of the double cone of θd. The observer is located toward the negative z-axis. The derived inclination angle θi is such that the source is tipped up in front.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


