Fig. 6
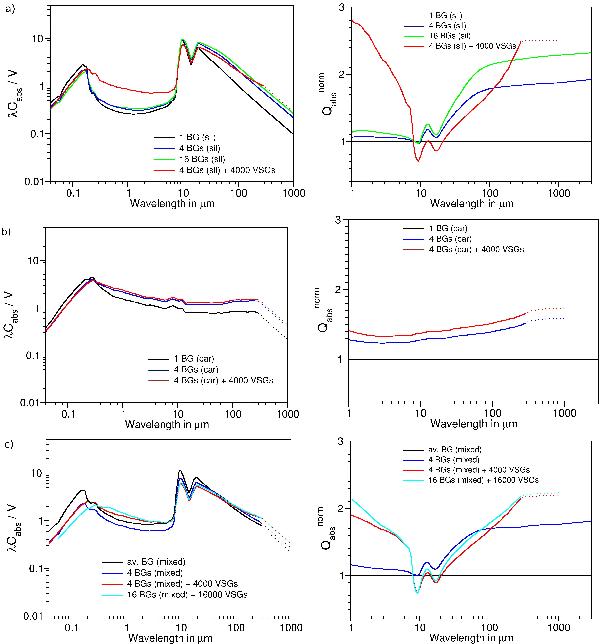
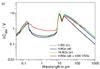
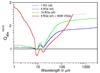
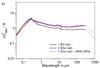
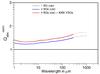
λCabs/V (left) and 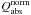 (right) plotted versus the wavelengths in μm. Aggregates consist of BGs of astronomical silicate a), of BGs of amorphous carbon b) and of a mixture of both c). Results are shown for 1 BG only and for aggregates consisting of 4 BGs and of 16 BGs. We consider bare BGs and BGs with 1000 VSGs per BG (40% of the volume of a BG); “car” indicates amorphous carbon, “sil” astronomical silicate and “mixed” aggregates consisting of 4 BGs, where 1 BG is of amorphous carbon and 3 BGs of astronomical silicate, and of 16 BGs, where 4 BGs are of amorphous carbon and 12 BGs of astronomical silicate. For case c) the black curves show the result for isolated grains of 1 BG of amorphous carbon and 3 BGs of astronomical silicate. The bend occurring at 300 μm is due to the optical constants of amorphous carbon that are assumed to have a power-law at wavelengths longward 300 μm. The results at wavelengths longer than 300 μm are therefore uncertain and shown as dotted lines here.
(right) plotted versus the wavelengths in μm. Aggregates consist of BGs of astronomical silicate a), of BGs of amorphous carbon b) and of a mixture of both c). Results are shown for 1 BG only and for aggregates consisting of 4 BGs and of 16 BGs. We consider bare BGs and BGs with 1000 VSGs per BG (40% of the volume of a BG); “car” indicates amorphous carbon, “sil” astronomical silicate and “mixed” aggregates consisting of 4 BGs, where 1 BG is of amorphous carbon and 3 BGs of astronomical silicate, and of 16 BGs, where 4 BGs are of amorphous carbon and 12 BGs of astronomical silicate. For case c) the black curves show the result for isolated grains of 1 BG of amorphous carbon and 3 BGs of astronomical silicate. The bend occurring at 300 μm is due to the optical constants of amorphous carbon that are assumed to have a power-law at wavelengths longward 300 μm. The results at wavelengths longer than 300 μm are therefore uncertain and shown as dotted lines here.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.