Fig. 1

Illustration of notations. The z axis is chosen perpendicular to
the surface, and the (xz) plane is chosen parallel to the
magnetic field lines, which make an
angle θB with the normal to the
surface. The direction of the reflected beam with wave vector
kr is determined by the polar
angle θk and the azimuthal
angle ϕ, and αr is the angle
between the reflected beam and the field lines. Thick solid lines show the
reflected beam and magnetic field directions, thin solid lines illustrate the
coordinates, and dashed lines show the incident photon wave vector
ki and its quadrant. The lines marked
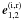 illustrate the basic polarizations adopted for the description of reflectivities:
illustrate the basic polarizations adopted for the description of reflectivities:
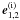 and
and 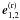 are perpendicular to the wave vectors ki
and ki, respectively;
are perpendicular to the wave vectors ki
and ki, respectively;
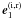 are parallel to the surface, and
are parallel to the surface, and 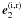 lie in the perpendicular plane. The axes x′ and
y′ lie in the plane made by
lie in the perpendicular plane. The axes x′ and
y′ lie in the plane made by
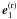 and
and 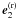 ,
x′ being aligned in the plane made by
B and
kr.
,
x′ being aligned in the plane made by
B and
kr.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


