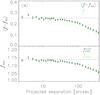
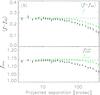
Fig. 9
a) Anisotropy of the lensing signal in the simulations using the observed positions of the “red” lens sample in the RCS2. The filled black diamonds (open green diamonds) show the shear anisotropy estimators (not) corrected for systematic shear. The ellipticities of the lenses have been randomly assigned. The lensing anisotropy declines slightly at scales >20 arcsec, which is expected as clustering of lenses with random position angles leads to an isotropic signal at large scales. In panel b), we add an additional ellipticity of 0.03 to the e1 component of the lenses to mimic intrinsic alignments. This increases the shear anisotropy, but also induces cross shear, so that the systematic shear corrected shear anisotropy estimators are unchanged.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.