| Issue |
A&A
Volume 543, July 2012
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | C1 | |
| Number of page(s) | 2 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201117910e | |
| Published online | 03 July 2012 | |
A far-infrared survey of bow shocks and detached shells around AGB stars and red supergiants (Corrigendum)
1
Instituut voor Sterrenkunde, KU Leuven, Celestijnenlaan 200D,
3001
Leuven
Belgium
e-mail: nick@ster.kuleuven.be
2
University of Vienna, Department of Astronomy,
Türkenschanzstraße 17,
1180
Wien,
Austria
3
Centre for Plasma-astrophysics, K.U.Leuven, Celestijnenlaan
200B, 3001
Leuven,
Belgium
4
Sterrenkundig Instituut Anton Pannekoek, Universiteit van
Amsterdam, Science Park 904,
1098,
Amsterdam, The
Netherlands
5
Royal Observatory of Belgium, Ringlaan 3, 1180
Brussels,
Belgium
6
Institut d’Astronomie et d’Astrophysique, Université Libre de
Bruxelles, CP 226, Boulevard du
Triomphe, 1050
Bruxelles,
Belgium
7
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of
Denver, 2112 E. Wesley
Ave., Denver,
CO
80208,
USA
8
Laboratoire Univers et Théories, Observatoire de Paris, UMR 8102
du CNRS, Université Paris Diderot, 92190
Meudon,
France
Key words: stars: AGB and post-AGB / circumstellar matter / infrared: ISM / hydrodynamics / stars: mass-loss / errata, addenda
Two errors have appeared in the original published version of this article. A copy-and-paste error resulted in two subsequent LSR space motion corrections to the values for CW Leo reported in the original Table 1. The correct values are given here in Table 1. The second error resulted from the omission of the “square” term for the distance in the actual computation of the dust mass following Eq. (5) (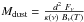 ). This correction results in a, distance dependent, increase of dust mass by approximately two orders of magnitude. The complete corrected original Table 5 is reproduced in this erratum. Only the values in Cols. 9 and 10 have changed.
). This correction results in a, distance dependent, increase of dust mass by approximately two orders of magnitude. The complete corrected original Table 5 is reproduced in this erratum. Only the values in Cols. 9 and 10 have changed.
The above corrections give total observed gas and dust masses ranging from 0.002 to 0.56 M⊙. These corrections change in part the conclusions arrived at in the final paragraph of Sect. 3.3. In particular, we note that the inferred total mass of gas and dust is significantly higher than the potential mass swept-up from interstellar medium (ISM). The estimated swept-up ISM mass, MISM, ranges from ~10-5 to 10-1 M⊙. These results indicate that on average only a few percent of the observed dust in the bow shock region originates from the surrounding medium. For individual objects, notably CW Leo and α Ori, the contribution from ISM dust could be as much as 10−25%, while for others it is estimated to be even less than one percent (Table 5). These corrections now show that the derived masses are consistent with dust emission being predominantly from stellar wind grains trapped in the wind-ISM interaction rather than from
interstellar grains, which is consistent with hydrodynamical modeling as discussed recently for α Ori by e.g. Mohamed et al. (2012) and Mackey et al. (2012). Note that the derived dust masses are sensitive not only to the adopted dust temperature, but also the dust opacity law, and the adopted gas-to-dust ratio. These uncertainties together potentially introduce an order of magnitude uncertainty to the derived total dust and gas mass. For example, an increase in dust temperature results in a decrease of the dust mass, thus increasing the relative importance of the ISM contribution.
LSR proper motion, space velocity, position angle and inclination for CW Leo.
Aperture flux of observed bow shocks (Class I and II) and detached rings (Class III).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Anthony Marston for alerting us to the error in the dust mass calculation.
References
- Harper, G. M., Brown, A., & Guinan, E. F. 2008, AJ, 135, 1430 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mackey, J., Mohamed, S., Neilson, H. R., Langer, N., & Meyer, D. M.-A. 2012, ApJ, 751, L10 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, S., Mackey, J., & Langer, N. 2012, A&A, 541, A1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
© ESO, 2012
All Tables
Aperture flux of observed bow shocks (Class I and II) and detached rings (Class III).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


