Fig. 1
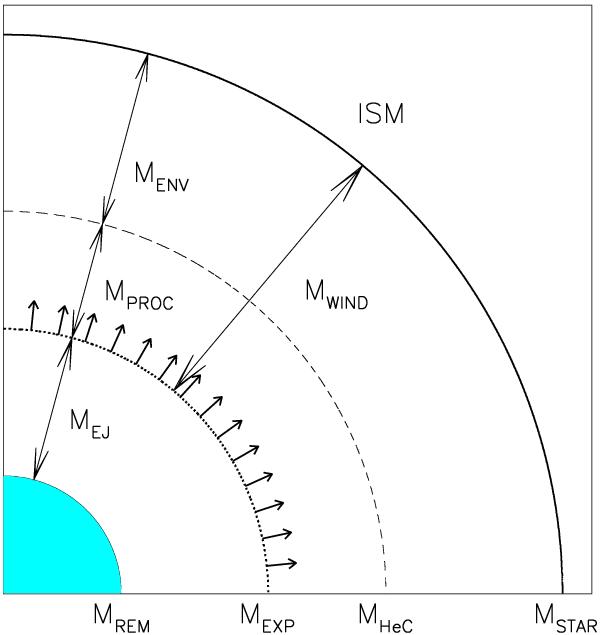
Schematic representation of a supernova exploding in the wind of its parent star. The star of initial mass M∗ explodes with a mass MExp, i.e. it has lost a mass Mwind = M∗ − MExp. The most massive stars become WR stars and their wind expels not only the H-envelope (of mass MEnv, with composition similar to that of the ISM) but also nuclearly processed layers, of mass MProc, i.e. MWind = MEnv + MProc, where MProc = MHeC − MExp and MHeC is the mass of the (H-exhausted) He-core. The star leaves a remnant (neutron star or black hole) of mass MRem; the mass ejected in the SN explosion is MEj = MExp − MRem. Efficient GCR acceleration presumably starts at the beginning of the ST phase, when a mass MS1 ~ MEj is swept up in front of the SN shock wave (which is indicated by arrows).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


