Fig. A.1
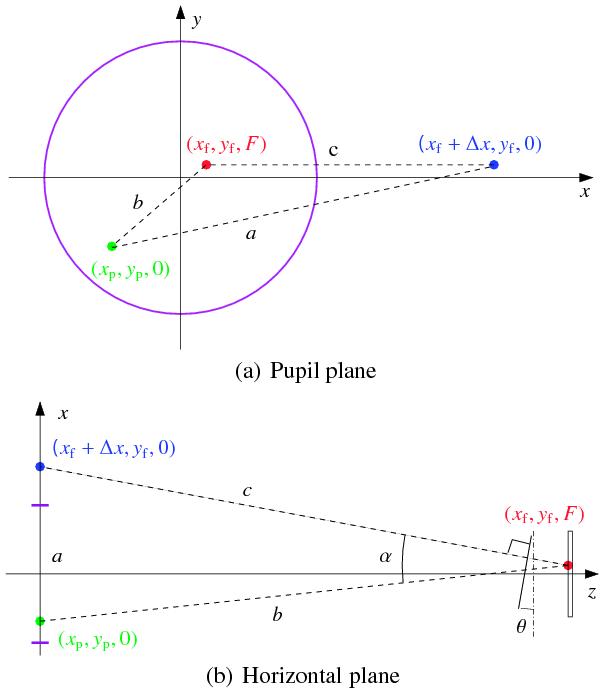
Filter tilt geometry. a) Projected on the pupil plane. b) Top view, projection on the horizontal plane. The pupil with diameter D = 1 is indicated by the circle in a) and by the two tick marks on the x axis in b). The focal length is f. In (x,y,z) space (z is the optical axis), a ray leaves the pupil plane at (xp,yp,0) and hits the detector in the focal plane at (xf,yf,F). The filter surface normal from (xf,yf,F) intersects with the pupil plane at an x-coordinate increased by an amount Δx given by Eq. (A.5). The angle θ is in a horizontal plane but α is in general not.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.