Fig. 2
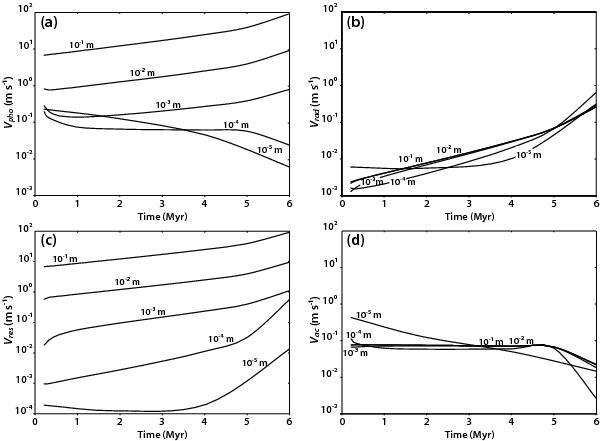
Velocities of particles due to photophoresis a); radiation pressure b); residual gravity c); and accretion flow d) represented as a function of time and size in the midplane of the disk characterized by a mass of 0.03 M⊙ and a lifetime of 6 Myr. The density of particles is 500 kg m-3 and the radius of the inner gap is 2 AU. Position of larger particles essentially corresponds to the balance between photophoresis and residual gravity velocities. When the disk opacity is prominent, i.e., at early epochs, the position of smaller particles is mainly driven by the balance between photophoresis and accretion flow velocities. At later epochs, the position of these particles becomes ruled by the balance between all velocities.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


