Table 1
Characteristics of the dynamic atmospheric model for a pulsating and mass-losing C-rich AGB star that was used for computing synthetic photometry.
| Model | S | ||
|
|
|||
| (i) | L ⋆ | [L⊙] | 10 000 |
| M ⋆ | [M⊙] | 1.0 | |
| T ⋆ | [K] | 2600 | |
| [Fe/H] | [dex] | 0.0 | |
| C/O ratio | by number | 1.4 | |
|
|
|||
| (ii) | R ⋆ | [R⊙] | 493 |
| [AU] | 2.29 | ||
| log (g ⋆ [cm s-2]) | –0.94 | ||
|
|
|||
| (iii) | P | [d] | 490 |
| Δup | [km s-1] | 4 | |
| fL | 2.0 | ||
| Δmbol | [mag] | 0.86 | |
|
|
|||
| (iv) | Ṁ | [M⊙ yr-1] | 2.0–6.5 × 10-6 |
| u | [km s-1] | 13–15.5 | |
| ⟨ fc ⟩ | 0.28 | ||
Notes. Listed are (i) parameters of the hydrostatic initial model; (ii) quantities derivable from these parameters; (iii) attributes of the inner boundary (piston) used to simulate the pulsating stellar interior as well as the resulting bolometric amplitude Δmbol; and (iv) properties of the resulting wind. The notation was adopted from previous papers (DMA3, NHA10): P, Δup – period and velocity amplitude of the piston at the inner boundary; fL – free parameter to adjust the luminosity amplitude at the inner boundary; Ṁ, u – mass loss rate and outflow velocity at the outer boundary; ⟨ fc ⟩ – mean degree of condensation of carbon into dust at the outer boundary. The radial coordinates in Figs. A.1 and A.2 are plotted in units of the corresponding stellar radius R ⋆ of the hydrostatic initial model, calculated from the luminosity L ⋆ and temperature T ⋆ via the relation L ⋆ = 4π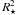 σ
σ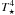 .
.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


