Fig. 10
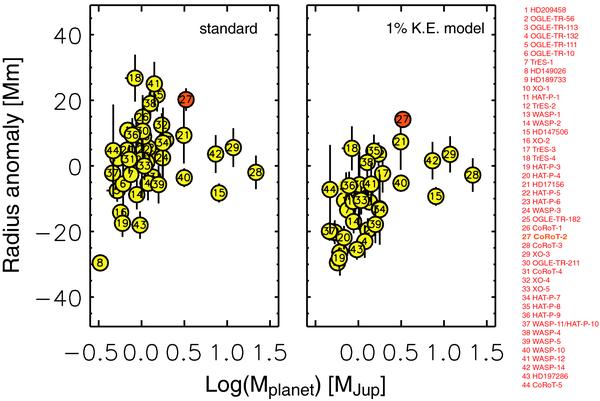
Radius anomaly (difference between observed and modeled radius – see text –) as a function of planetary mass (in log) for a selection of known transiting giant planets. Left panel: standard models (including stellar irradiation but no extra heat source) are used for the comparison. Right panel: models assume an extra heat source at the planet’s center equivalent to 1% of the incoming stellar heat flux (see Guillot & Showman 2002). CoRoT-2b is labeled “27”. It is the most anomalously large planet on the right panel.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


