| Issue |
A&A
Volume 520, September-October 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A59 | |
| Number of page(s) | 10 | |
| Section | Stellar atmospheres | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201014333 | |
| Published online | 04 October 2010 | |
New findings on the prototypical Of?p stars![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
Y. Nazé1,![]() - A. ud-Doula2 - M. Spano3 - G. Rauw1,
- A. ud-Doula2 - M. Spano3 - G. Rauw1,![]() - M. De Becker1,4 - N. R. Walborn5
- M. De Becker1,4 - N. R. Walborn5
1 - GAPHE, Département AGO, Université de Liège, Allée du 6 Août 17, Bât. B5C, B4000 Liège, Belgium
2 - Penn State Worthington Scranton, 120 Ridge View Drive, Dunmore, PA 18512, USA
3 - Observatoire de Genève, Université de Genève, 51 Chemin des Maillettes, 1290 Sauverny, Switzerland
4 - Observatoire de Haute-Provence, 04870 Saint-Michel l'Observatoire, France
5 - Space Telescope Science Institute![]() , 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA
, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA
Received 1 March 2010 / Accepted 7 June 2010
Abstract
Aims. In recent years several in-depth investigations of the
three prototypical Of?p stars were undertaken. These multiwavelength
studies revealed the peculiar properties of these objects (in the
X-rays as well as in the optical): magnetic fields, periodic line
profile variations, recurrent photometric changes. However, many
questions remain unsolved.
Methods. To clarify some of the properties of the Of?p stars, we have continued their monitoring. A new XMM-Newton observation and two new optical datasets were obtained.
Results. Additional information about the prototypical Of?p trio
has been found. HD 108 has now reached its quiescent,
minimum-emission state for the first time in 50-60 yr. The échelle
spectra of HD 148937 confirm the presence of the 7d variations in
the Balmer lines and reveal similar periodic variations (though of
lower amplitudes) in the He I ![]() 5876 and He II
5876 and He II ![]() 4686 lines, underlining its similarities with the other two prototypical Of?p stars. The new XMM-Newton
observation of HD 191612 was taken at the same phase in the line
modulation cycle, but at a different orbital phase from previous data.
It clearly shows that the X-ray emission of HD 191612 is modulated
by the 538d period and not by the orbital period of 1542d - it is thus
not of colliding-wind origin. The phenomenon responsible for the
optical changes appears also at work in the high-energy domain. There
are problems however: our MHD simulations of the wind magnetic
confinement predict both a harder X-ray flux of a much larger strength
than what is observed (the modelled differential emission measure peaks
at 30-40 MK, whereas the observed one peaks at 2 MK) and
narrow lines (hot gas moving with velocities of 100-200 km s-1, whereas the observed full width at half maximum is
4686 lines, underlining its similarities with the other two prototypical Of?p stars. The new XMM-Newton
observation of HD 191612 was taken at the same phase in the line
modulation cycle, but at a different orbital phase from previous data.
It clearly shows that the X-ray emission of HD 191612 is modulated
by the 538d period and not by the orbital period of 1542d - it is thus
not of colliding-wind origin. The phenomenon responsible for the
optical changes appears also at work in the high-energy domain. There
are problems however: our MHD simulations of the wind magnetic
confinement predict both a harder X-ray flux of a much larger strength
than what is observed (the modelled differential emission measure peaks
at 30-40 MK, whereas the observed one peaks at 2 MK) and
narrow lines (hot gas moving with velocities of 100-200 km s-1, whereas the observed full width at half maximum is ![]() 2000 km s-1).
2000 km s-1).
Key words: X-rays: stars - stars: individual: HD 108 - stars: individual: HD 148937 - stars: individual: HD 191612 - stars: emission-line, Be
1 Introduction
The presence of C IIIThe three prototypical Of?p stars are HD 108, HD 148937, and HD 191612. They are the most studied objects of that category, though some open questions still remain.
HD 108 displays correlated photometric, Balmer, and He I line profile variations: the star is brighter when the emission lines are stronger (Nazé et al. 2008b,2001). The variations appear in a recurrent mode, with a probable time scale of about 55 years (Nazé et al. 2006). The minimum emission state was not yet reached in 2004 (Nazé et al. 2004), which prevented a precise evaluation of the recurrence time. Recently, an additional observational result enriched the picture of HD 108: the detection of a strong magnetic field (observed strength is 100-150 G, corresponding to a potential dipolar field of 0.5-2 kG Martins et al. 2010).
The behaviour of HD 191612 appears very similar to that of HD 108, but with a shorter, well-defined period of 537.6d (Howarth et al. 2007, and references therein). A strong magnetic field (-220 ![]() 38 G) was detected for this star by Donati et al. (2006),
who further proposed an oblique magnetic rotator model for the star.
Following these authors, the long period would result from magnetic
braking of the stellar rotation (for an analysis of these effects see ud-Doula et al. 2009).
Studies are now under way to check the exact geometry of the magnetic
field (Wade, private communication). Finally, it should be noted that
this star has a lower-mass companion in a 1542d orbit (Howarth et al. 2007).
38 G) was detected for this star by Donati et al. (2006),
who further proposed an oblique magnetic rotator model for the star.
Following these authors, the long period would result from magnetic
braking of the stellar rotation (for an analysis of these effects see ud-Doula et al. 2009).
Studies are now under way to check the exact geometry of the magnetic
field (Wade, private communication). Finally, it should be noted that
this star has a lower-mass companion in a 1542d orbit (Howarth et al. 2007).
HD 148937 does not display the large photometric changes and line
profile variations like the two other objects of this study. Instead,
changes of limited amplitude (the peak's amplitude varyies by a few
percents vs several 100% for the other prototypical Of?p stars)
were observed for the H![]() line, with a possible period of about 7d, during a long-term monitoring campaign (Nazé et al. 2008a),
but the temporal sampling of the optical dataset was not optimized for
finding such a short period and the resultant value may therefore be
subject to large errors. In addition, no change was detected in the
low-resolution data for other spectral lines, which differs from what
is observed in HD 108 and HD 191612. Finally, a tentative
detection of a magnetic field was reported for this star by Hubrig et al. (2008,
line, with a possible period of about 7d, during a long-term monitoring campaign (Nazé et al. 2008a),
but the temporal sampling of the optical dataset was not optimized for
finding such a short period and the resultant value may therefore be
subject to large errors. In addition, no change was detected in the
low-resolution data for other spectral lines, which differs from what
is observed in HD 108 and HD 191612. Finally, a tentative
detection of a magnetic field was reported for this star by Hubrig et al. (2008, ![]() G#,
but a spectro-polarimetric monitoring throughout the 7d cycle is
clearly needed to ascertain the strength and geometry of the field (it
is currently under way, Wade, private communication).
G#,
but a spectro-polarimetric monitoring throughout the 7d cycle is
clearly needed to ascertain the strength and geometry of the field (it
is currently under way, Wade, private communication).
In addition to dedicated optical campaigns, several XMM-Newton
observations of these three objects were obtained. The derived
properties are remarkably similar: overluminosities with respect to the
``canonical''
![]() = 10-7 relation, soft spectra, broad X-ray lines (Nazé et al. 2004,2007,2008a).
Monitoring HD 191612 further revealed small variations of the
X-ray flux. However, as all data were taken during the same orbital
cycle and the same 538d cycle, the exact cause for these changes
remained unclear.
= 10-7 relation, soft spectra, broad X-ray lines (Nazé et al. 2004,2007,2008a).
Monitoring HD 191612 further revealed small variations of the
X-ray flux. However, as all data were taken during the same orbital
cycle and the same 538d cycle, the exact cause for these changes
remained unclear.
Though the published studies have led to the characterization of many aspects of these Of?p stars, several questions still remain unanswered - usually, these questions are different for the different objects (e.g. on the variations of the X-rays of HD 191612, on the evolution of the optical spectra of HD 108, or on the variation timescale of HD 148937), due to the inhomogeneous datasets reported up to now. In the past few years we continued our monitoring of these three peculiar objects, with the objective of characterizing and better understanding their properties. This paper reports the results of this campaign. In Sect. 2 we present the datasets and in Sect. 3 the results, in Sect. 4 we summarize the new information.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=15cm,bb=24 470 575 690, clip]{14333fig...
...includegraphics[width=15cm, bb=18 140 550 430, clip]{14333fig1c.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg13.png)
|
Figure 1: Evolution of the line profiles in recent years for HD 108. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
2 Observations and data reduction
2.1 Aurélie data
Since 2004, when optical spectra of HD 108 were last published (Nazé et al. 2004),
we have continued the monitoring of the star with the Aurélie
spectrograph mounted on the 1.52 m telescope of the Haute-Provence
Observatory (OHP, France). The detector was a thin back-illuminated CCD
composed of
![]() pixels of size
pixels of size ![]() m2.
We used the grating #3, reaching a resolving power
between 8000 and 10 000 in the blue and red part of the
spectrum, respectively. With this instrumental setup we obtained
spectra in the 4450-4900 Å, 5480-5920 Å, and 6340-6780 Å
ranges. Exposure times were typically 20-40 min, resulting in a
signal-to-noise ratio of about 200 on average. The data were
reduced in a standard way using MIDAS. The wavelength calibration was
done using ThAr exposures taken immediately before/after the stellar
spectrum, and the spectra were normalised using low-degree polynomials.
m2.
We used the grating #3, reaching a resolving power
between 8000 and 10 000 in the blue and red part of the
spectrum, respectively. With this instrumental setup we obtained
spectra in the 4450-4900 Å, 5480-5920 Å, and 6340-6780 Å
ranges. Exposure times were typically 20-40 min, resulting in a
signal-to-noise ratio of about 200 on average. The data were
reduced in a standard way using MIDAS. The wavelength calibration was
done using ThAr exposures taken immediately before/after the stellar
spectrum, and the spectra were normalised using low-degree polynomials.
An additional échelle spectrum obtained in June 2009 at San Pedro Mártir with the Espresso spectrograph was also made available to us by P. Eenens and L. Mahy. This dataset has been added to the analysis and discussion.
2.2 Coralie échelle spectra
Twenty échelle spectra of HD 148937 were obtained in 2008 May
8-21 with the 1.2 m Euler Swiss telescope at La Silla (Chile),
equipped with the Coralie spectrograph and an EEV 2k ![]() 2k CCD with pixel size
2k CCD with pixel size ![]() m2. The Coralie instrument is an improved version of the Élodie spectrograph (Baranne et al. 1996).
These observations covered the spectral range 3850-6890 Å with a
resolving power of 55 000. During the first week, two spectra per
night were taken; during the second week, one spectrum per night was
taken. The integration times were fixed to 30 min (except for the
first two exposures, which were each 20 min long) and the typical S/N
ratio at 5000 Å was 150. The data were first reduced with the
Coralie pipeline and then normalised using low-degree polynomials. A
telluric correction was applied for H
m2. The Coralie instrument is an improved version of the Élodie spectrograph (Baranne et al. 1996).
These observations covered the spectral range 3850-6890 Å with a
resolving power of 55 000. During the first week, two spectra per
night were taken; during the second week, one spectrum per night was
taken. The integration times were fixed to 30 min (except for the
first two exposures, which were each 20 min long) and the typical S/N
ratio at 5000 Å was 150. The data were first reduced with the
Coralie pipeline and then normalised using low-degree polynomials. A
telluric correction was applied for H![]() and He I
and He I ![]() 5876 using the telluric spectrum of Hinkle et al. (2000) and the task telluric within IRAF.
5876 using the telluric spectrum of Hinkle et al. (2000) and the task telluric within IRAF.
2.3 XMM-Newton observation
HD 191612 was observed anew by XMM-Newton on 2008 April 2 (Rev. 1523, ObsID 050068201, PI Nazé), for a total exposure time of 24 ks. The instrumental configuration, processing, and extraction regions were identical to the first four observations of the source (Nazé et al. 2007). We processed the data with the Science Analysis System (SAS) software, version 8.0; further analysis was performed using the FTOOLS tasks and the XSPEC software v 11.2.0. No high background episode (due to soft protons) was detected at high-energies during this exposure.
In addition to European Photon Imaging Camera (EPIC) data, XMM-Newton provides high-resolution spectra thanks to the Reflection Grating Spectrometer (RGS) instruments. The RGS data were reduced with the SAS and then combined with the previous observations following the procedure outlined in Nazé et al. (2007). However, the improvement in signal-to-noise of the combined spectrum is not important because all observations are of similar duration. We therefore have no new results to report on the high-resolution spectrum of HD 191612, a quantitative leap in quality awaiting the advent of more sensitive observatories.
3 New results on Of?p stars
3.1 HD 108
The spectrum of HD 108 has been followed intensively since 1986 (Nazé et al. 2004,2001). While some (purely photospheric) lines such as He II ![]() 4542 remain constant, the strength of the Balmer, He I (e.g. at
4542 remain constant, the strength of the Balmer, He I (e.g. at
![]() 4471, 4713, 6678), Si III (e.g. at
4471, 4713, 6678), Si III (e.g. at ![]() 4552) and C III
4552) and C III
![]() 4650 lines
have decreased with time, with profiles changing from pure emissions or
P Cygni profiles to strong absorptions or greatly reduced emissions, as
illustrated by Fig. 1. These
lines thus appear as a blend of a constant photospheric absorption and
a varying emission component. A similar change was observed about
55 years ago (Nazé et al. 2006,2001),
but due to the lack of detailed monitoring in the past - often, only a
global idea of the profile (emission vs absorption) was recorded - the
timescale of the variations could not be precisely assessed and some
even questioned the recurrence of the phenomenon. It is therefore of
the utmost importance to see how the lines evolve and if quiescence is
reached.
4650 lines
have decreased with time, with profiles changing from pure emissions or
P Cygni profiles to strong absorptions or greatly reduced emissions, as
illustrated by Fig. 1. These
lines thus appear as a blend of a constant photospheric absorption and
a varying emission component. A similar change was observed about
55 years ago (Nazé et al. 2006,2001),
but due to the lack of detailed monitoring in the past - often, only a
global idea of the profile (emission vs absorption) was recorded - the
timescale of the variations could not be precisely assessed and some
even questioned the recurrence of the phenomenon. It is therefore of
the utmost importance to see how the lines evolve and if quiescence is
reached.
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{2mm}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig2.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg19.png)
|
Figure 2:
Evolution as a function of time of a few quantities related to HD 108. Upper panel: EW (in Å, in the range 4845-4870 Å) of H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Though the emission component had nearly disappeared these last years (Nazé et al. 2004),
the emissions continued to decline until 2004. Now, HD 108 has
finally reached its quiescent state because the data taken between 2005
and 2009 are very similar (Figs. 1 and 2). Based on past behaviour (Nazé et al. 2001),
it is expected that the emission will get stronger again in the future,
as is seen in HD 191612. Note however that for HD 191612 the
quiescent state occurs during one-third of the cycle, which would
correspond to about 18 years for HD 108. Assuming that the
variations are due to an oblique magnetic rotator configuration, this
quiescence timescale would depend on the exact geometry of the system
though, which may be different for the two objects despite their
obvious similarities. From the literature it is only known that H![]() remained in absorption during about 10 years, while He I
remained in absorption during about 10 years, while He I ![]() 4471 did so during several decades (Nazé et al. 2001).
However, the exact evolution was not recorded and it cannot be
concluded from the older data how long the lines remained constant,
i.e. in a quiescent state.
4471 did so during several decades (Nazé et al. 2001).
However, the exact evolution was not recorded and it cannot be
concluded from the older data how long the lines remained constant,
i.e. in a quiescent state.
3.2 HD 148937
Previously, a long-term monitoring (three years, with monthly
observations) provided an extensive set of low-resolution spectra.
These data revealed the variability of three lines: H![]() ,
H
,
H![]() ,
and He II
,
and He II ![]() 4686 (Nazé et al. 2008a). However, this variability was of low amplitude: the equivalent widths (EWs) measured for H
4686 (Nazé et al. 2008a). However, this variability was of low amplitude: the equivalent widths (EWs) measured for H![]() ,
the most variable line, display a dispersion which, though it was 10
times larger than that observed for the neighbouring narrow diffuse
interstellar band (DIB), correspond to a change of only 20% in EW
(it also corresponds to a variation in the peak's amplitude of
only 7% between the two extreme profiles), whereas the other
prototypical Of?p stars have H
,
the most variable line, display a dispersion which, though it was 10
times larger than that observed for the neighbouring narrow diffuse
interstellar band (DIB), correspond to a change of only 20% in EW
(it also corresponds to a variation in the peak's amplitude of
only 7% between the two extreme profiles), whereas the other
prototypical Of?p stars have H![]() lines varying from absorption to emission, with EWs and peak amplitudes varying by
lines varying from absorption to emission, with EWs and peak amplitudes varying by ![]() 100%. Moreover, the He I and C III
lines seemed relatively constant, a behaviour different from that of
HD 108 and HD 191612 - though subtle changes may have
remained hidden in such low-resolution data. A period search further
revealed a period of 7.031
100%. Moreover, the He I and C III
lines seemed relatively constant, a behaviour different from that of
HD 108 and HD 191612 - though subtle changes may have
remained hidden in such low-resolution data. A period search further
revealed a period of 7.031 ![]() 0.003d when we studied the line profile variations of H
0.003d when we studied the line profile variations of H![]() closely. However, the data sampling, aimed at studying
monthly-to-yearly variations, was not adequate for detecting such a
short period, which thus required confirmation with a more intense
temporal sampling. A new, short-term monitoring was therefore
undertaken, yielding 20 high-resolution spectra over two weeks.
closely. However, the data sampling, aimed at studying
monthly-to-yearly variations, was not adequate for detecting such a
short period, which thus required confirmation with a more intense
temporal sampling. A new, short-term monitoring was therefore
undertaken, yielding 20 high-resolution spectra over two weeks.
For consistency, the radial velocities and EWs were estimated as in Nazé et al. (2008a); they are given in Table 1. While the C IV and DIBs display constant EWs, the Balmer, He II ![]() 4686, and He I
4686, and He I ![]() 5876 lines show a larger dispersion. When plotted against time (Fig. 3), obvious modulations are detected. H
5876 lines show a larger dispersion. When plotted against time (Fig. 3), obvious modulations are detected. H![]() and He II
and He II ![]() 4686 lines display maximum emission when H
4686 lines display maximum emission when H![]() ,
H
,
H![]() ,
and He I
,
and He I ![]() 5876 present a minimum absorption.
5876 present a minimum absorption.
The variability detected when looking at EWs is confirmed by the temporal variance spectrum (TVS, see Fullerton et al. 1996, and Fig. 4),
which compares the variations between spectra with the scatter expected
from random noise in each wavelength bin. Note that the variability has
not the same amplitude for all lines of a given element: for the Balmer
lines, the TVS is very significant for H![]() ,
significant for H
,
significant for H![]() ,
and barely significant for H
,
and barely significant for H![]() .
This might explain why the variability of, e.g., He I
.
This might explain why the variability of, e.g., He I ![]() 4471 is not detected - its amplitude, expected to be lower than for He I
4471 is not detected - its amplitude, expected to be lower than for He I ![]() 5876, is certainly hidden by the noise. Note that no significant variation of the C III
5876, is certainly hidden by the noise. Note that no significant variation of the C III ![]() 4650 lines is detected.
4650 lines is detected.
Periodograms were calculated for the 20-exposures dataset using the techniques of Heck et al. (1985, see remarks in Gosset et al. 2001# in the wavelength interval where lines vary significantly (for details about the method see Rauw et al. 2001). The results are shown in Fig. 5: the highest peak is located at a frequency of 0.1315d-1, 0.1353d-1, 0.1373d-1, and 0.1397d-1 for He II ![]() 4686, H
4686, H![]() ,
He I
,
He I ![]() 5876, and H
5876, and H![]() ,
respectively. These frequencies translate into a period of 7.16-7.60
,
respectively. These frequencies translate into a period of 7.16-7.60 ![]() 0.40d.
The relatively large error compared to the old dataset simply stems
from the different observational timespans (two weeks vs.
2.5 years), while the period differences from one line to the
other have two origins: the noise, which more affects the fainter lines
such as He I
0.40d.
The relatively large error compared to the old dataset simply stems
from the different observational timespans (two weeks vs.
2.5 years), while the period differences from one line to the
other have two origins: the noise, which more affects the fainter lines
such as He I ![]() 5876,
and the different amplitudes of the variations (the signal is indeed
more difficult to catch for low amplitude changes, e.g. for He I
5876,
and the different amplitudes of the variations (the signal is indeed
more difficult to catch for low amplitude changes, e.g. for He I ![]() 5876). The H
5876). The H![]() line, which is both strong and the most variable line, yields the most reliable period, i.e. 7.16
line, which is both strong and the most variable line, yields the most reliable period, i.e. 7.16 ![]() 0.40d from the new dataset only. Taking the errors into account
0.40d from the new dataset only. Taking the errors into account![]() , this agrees with the results reported by Nazé et al. (2008a).
The 7d period was thus not an artefact from our inadequate time
sampling. HD 148937 therefore appears quite similar to the two
other Galactic Of?p stars, though with a shorter period, a smaller
amplitude of the variations, and with the sole exception of the
apparent constancy in the C III lines. A
spectropolarimetric monitoring should be undertaken to see if this
could be related to e.g. a low inclination of the star's rotation axis.
, this agrees with the results reported by Nazé et al. (2008a).
The 7d period was thus not an artefact from our inadequate time
sampling. HD 148937 therefore appears quite similar to the two
other Galactic Of?p stars, though with a shorter period, a smaller
amplitude of the variations, and with the sole exception of the
apparent constancy in the C III lines. A
spectropolarimetric monitoring should be undertaken to see if this
could be related to e.g. a low inclination of the star's rotation axis.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig3a.ps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig3b.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg22.png)
|
Figure 3:
Evolution with time of the EWs (expressed in Å) for some lines of HD 148937. Left: the strongest emission lines (Balmer line of H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=10.5cm]{14333fig4a.ps}\includegraphics[width=7.5cm]{14333fig4b.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg23.png)
|
Figure 4:
Left: average spectra and TVS of He II |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9.2cm]{14333fig5a.ps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig5b.ps}
\vspace*{7mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg24.png)
|
Figure 5:
Left, from top to bottom: raw periodogram of H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Table 1: Mean and dispersion of the measured RVs and EWs for HD 148937.
3.3 HD 191612
3.3.1 X-ray data
The previous observations of HD 191612 (Nazé et al. 2007)
revealed changes in the X-ray flux, but the origin of this variability
was unclear. To get a better understanding of this phenomenon, we
undertook a new XMM-Newton observation, whose scheduling was carefully chosen. While the previous observations were taken at orbital phases
![]() -0.96 and at phases
-0.96 and at phases
![]() -0.44 in the 538d cycle, the new exposure corresponds to a phase
-0.44 in the 538d cycle, the new exposure corresponds to a phase
![]() in the line-profile/photometric cycle of 538d and a phase
in the line-profile/photometric cycle of 538d and a phase
![]() in the orbital cycle (Fig. 6, ephemeris taken from Howarth et al. 2007).
The new data thus enable us to check whether the flux variations are
linked to the circumstellar, possibly magnetic, structures surrounding
the star or to colliding winds in a binary. In the former case, the new
data should be nearly identical to the previous observation taken at a
similar phase
in the orbital cycle (Fig. 6, ephemeris taken from Howarth et al. 2007).
The new data thus enable us to check whether the flux variations are
linked to the circumstellar, possibly magnetic, structures surrounding
the star or to colliding winds in a binary. In the former case, the new
data should be nearly identical to the previous observation taken at a
similar phase
![]() .
For the other case, a dramatic variation is expected though. In a
colliding wind binary, variations of the flux, correlated with orbital
phase, are expected to arise from changes in the separation (in
eccentric systems) and/or in the absorbing column (when the winds are
different). Indeed, such variations have been observed in several
systems (for a review, see Güdel & Nazé 2009).
In HD 191612, the previous observations, taken before periastron,
revealed a 20% change in reddening-corrected flux (see Table 2) for a phase difference
.
For the other case, a dramatic variation is expected though. In a
colliding wind binary, variations of the flux, correlated with orbital
phase, are expected to arise from changes in the separation (in
eccentric systems) and/or in the absorbing column (when the winds are
different). Indeed, such variations have been observed in several
systems (for a review, see Güdel & Nazé 2009).
In HD 191612, the previous observations, taken before periastron,
revealed a 20% change in reddening-corrected flux (see Table 2) for a phase difference
![]() of only 0.12, corresponding to a change in separation of 36%.
The new observation was taken two-thirds of the orbit later, near
apastron: the change in separation compared to previous data has thus
increased (up to 60%), and so should the difference in flux, if it
is truly linked to the colliding wind emission.
of only 0.12, corresponding to a change in separation of 36%.
The new observation was taken two-thirds of the orbit later, near
apastron: the change in separation compared to previous data has thus
increased (up to 60%), and so should the difference in flux, if it
is truly linked to the colliding wind emission.
The new data were processed following the same procedure as for the previous data, but using a newer XMM-Newton reduction software. The count rates derived from a run of the task
![]() amount to 0.122
amount to 0.122 ![]() 0.002 cts s-1 for EPIC MOS1, 0.119
0.002 cts s-1 for EPIC MOS1, 0.119 ![]() 0.002 cts s-1 for EPIC MOS2, and 0.392
0.002 cts s-1 for EPIC MOS2, and 0.392 ![]() 0.005 cts s-1 for EPIC pn. The evolution of the count rates and hardness ratio is shown in Fig. 6.
The new data agree very well with previous observations taken at the
same phase of the 538 d cycle, both in strength (similar count
rates) and in hardness (similar hardness ratios); they are in addition
clearly different from the results of previous observations obtained at
the latest phase (where the count rates are
0.005 cts s-1 for EPIC pn. The evolution of the count rates and hardness ratio is shown in Fig. 6.
The new data agree very well with previous observations taken at the
same phase of the 538 d cycle, both in strength (similar count
rates) and in hardness (similar hardness ratios); they are in addition
clearly different from the results of previous observations obtained at
the latest phase (where the count rates are ![]() 35% smaller, corresponding to a
35% smaller, corresponding to a ![]() 20
20![]() difference, and the hardness ratio HR1 measured on pn data is lower by 7
difference, and the hardness ratio HR1 measured on pn data is lower by 7![]() ).
).
The best spectral fit is provided in Table 2, together with the previous results for comparison (reproduced from Nazé et al. 2007). The fitted model has the form
wabs(
![]() )*[wabs(
)*[wabs(
![]() )*mekal(kT1) + wabs (
)*mekal(kT1) + wabs (
![]() )*mekal(kT2)], with wabs(
)*mekal(kT2)], with wabs(
![]() ) =
) =
![]() cm-2 (Diplas & Savage 1994) and using solar abundances for both absorptions and optically-thin plasma emissions - i.e. the same model as used in Nazé et al. (2007) for consistency reasons
cm-2 (Diplas & Savage 1994) and using solar abundances for both absorptions and optically-thin plasma emissions - i.e. the same model as used in Nazé et al. (2007) for consistency reasons![]() . Quoted fluxes are in the 0.4-10.0 keV energy range, and the unabsorbed fluxes
. Quoted fluxes are in the 0.4-10.0 keV energy range, and the unabsorbed fluxes
![]() are corrected only for the interstellar absorbing column. For each
parameter, the lower and upper limits of the 90% confidence interval
(derived from the ERROR command under XSPEC) are noted as indices and exponents, respectively. The normalisation factors are defined as
are corrected only for the interstellar absorbing column. For each
parameter, the lower and upper limits of the 90% confidence interval
(derived from the ERROR command under XSPEC) are noted as indices and exponents, respectively. The normalisation factors are defined as
![]() ,
where D,
,
where D, ![]() and
and ![]() are respectively the distance to the source, the electron and proton density of the emitting plasma. The phases
are respectively the distance to the source, the electron and proton density of the emitting plasma. The phases
![]() and
and
![]() correspond to the phases in the orbital cycle and the 538 d line profile/photometric cycle, respectively (ephemeris of Howarth et al. 2007).
Again, the spectral fits to the 2008 data agree very well with the
previous observations taken at the same phase of the 538 d cycle,
yielding the same X-ray luminosity, 9
correspond to the phases in the orbital cycle and the 538 d line profile/photometric cycle, respectively (ephemeris of Howarth et al. 2007).
Again, the spectral fits to the 2008 data agree very well with the
previous observations taken at the same phase of the 538 d cycle,
yielding the same X-ray luminosity, 9
![]() erg s-1 (for a distance of 2.29 kpc), and same
erg s-1 (for a distance of 2.29 kpc), and same
![]() ,
-6.1.
,
-6.1.
The conclusions are obvious: despite the very different orbital
phases, the new data are nearly identical to those taken three years
before at a similar phase in the 538d cycle. The modulation of the
X-ray emission thus appears directly correlated with the optical
line-profile variations, a situation very similar to that observed for ![]() Ori C (Gagné et al. 2005; Nazé et al. 2008b).
Ori C (Gagné et al. 2005; Nazé et al. 2008b).
Table 2: Best-fitting models and X-ray fluxes at Earth for each XMM -Newton observation of HD 191612.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig6a.ps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig6b.ps}
\vspace*{3mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg104.png)
|
Figure 6: Left: position of the new XMM -Newton observation in the cycles of HD 191612. The orbital cycle, calculated using orbital parameters of Howarth et al. (2007) and with the primary (resp. secondary) curve drawn in solid (resp. dotted) line, is shown on top while the bottom panel shows the line profile variation cycle of 538d from the analytical approximation of Howarth et al. (2007). The phases of the previous observations are shown by the thin short-dashed lines and the phase of the new observation by the thick long-dashed line. Right: evolution of the count rate in the 0.4-10.0 keV band ( top) and of two hardness ratios ( middle, bottom) with phase from the 538d cycle. Open symbols refer to the old observations, filled red symbols to the new dataset; triangles and squares were used for the EPIC MOS data (note that the MOS count rates are multiplied by a factor of 3 in this figure) and circles for the EPIC pn data. The hardness ratio HR1 and HR2 are defined as (M-S)/(M+S) and (H-M)/(H+M), respectively, where S is the count rate in the 0.4-1.0 keV band, M in 1-2 keV, and H in 2-10 keV. The coloured version of the figure is available on-line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
3.3.2 MHD modelling
To better understand the properties of HD 191612, a fully-dynamic numerical magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) model is needed that takes into account the impact on the wind of the magnetic field detection. We used the publically available ZEUS-3D code (Stone & Norman 1992) to evolve a consistent dynamical solution for a line-driven stellar wind from the star with a dipolar surface field. The stellar parameters of HD 191612, adopted mostly from Nazé et al. (2008b, and references therein), are listed in Table 3.
HD 191612 is a rather slow rotator with a surface rotation speed <50 km s-1 (Howarth et al. 2007; Nazé et al. 2008b).
This slow rotation probably has no significant dynamical effects on the
stellar wind. Therefore, the wind was assumed to be azimuthally
symmetric with the magnetic field axis aligned with the rotation axis![]() . This is essentially a ``2.5-D'' formulation allowing for non-zero azimuthal components of both the magnetic field
. This is essentially a ``2.5-D'' formulation allowing for non-zero azimuthal components of both the magnetic field ![]() and velocity
and velocity ![]() ,
while still assuming that all quantities are constant in the azimuthal coordinate angle
,
while still assuming that all quantities are constant in the azimuthal coordinate angle ![]() .
.
Much of the numerical procedures in this simulation follows ud-Doula et al. (2008).
The models thus include rotational effects, but for the first time we
also use the full energy equation, with an adiabatic index
![]() and a radiative cooling of MacDonald & Bailey (1981, who assumed solar abundance)
and a radiative cooling of MacDonald & Bailey (1981, who assumed solar abundance)![]() . At the initial time t=0,
the wind is represented by a relaxed non-magnetic and non-rotating
model, but we then simultaneously introduce a dipole magnetic field and
a surface rotation at the lower boundary, both defined relative to a
common polar axis. The wind and magnetic field are then let free to
compete with each other. To ensure that there are no numerical
artefacts arising from the initial conditions, we run our model for
about 1.5 Msec, which is at least 50 fluid crossing times.
. At the initial time t=0,
the wind is represented by a relaxed non-magnetic and non-rotating
model, but we then simultaneously introduce a dipole magnetic field and
a surface rotation at the lower boundary, both defined relative to a
common polar axis. The wind and magnetic field are then let free to
compete with each other. To ensure that there are no numerical
artefacts arising from the initial conditions, we run our model for
about 1.5 Msec, which is at least 50 fluid crossing times.
Immediately after t=0, the magnetic field channels wind material towards the tops of closed loops near the equator. There the collision with the opposite stream leads to strong shocks, like in ``magnetically confined wind shocks'' (MCWS) presented by Babel & Montmerle (1997). Denser material then cools radiatively very quickly, leading to a dense disc-like structure (Fig. 7). Some of the less dense post-shock material within the closed magetic loops remain very hot (ca. 80MK) for a long period of time. In this model, the Alfvén radius or magnetosphere extends about 3-4 stellar radii above the stellar surface.
Initially mass builds up in the equatorial region below the Keplerian radius estimated to be about 4.5 R*, but then there appear repeated episodes of infall of inner disc material back onto the stellar surface. Over a longer timescale, there appears another, somewhat different kind of disruption, one that starts higher up, closer to the Alfvén radius. This is characterized by outward ejections of the upper disc mass, leading to ``centrifugally driven mass ejections''. These ejections can lead to X-ray flares (see ud-Doula et al. 2006), but these short-term variations cannot be detected in the observations of HD 191612, since they lack the required sensitivity to analyse the lightcurve on very short timescales.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig7a.eps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig7b.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg109.png)
|
Figure 7:
Snapshots of density ( left) and temperature ( right), in cgs units on a logarithmic colour-scale, shown with field lines (solid lines) at arbitrarily chosen time t=1300 ks for the 2D MHD simulation of HD 191612. The x and y axes
are labelled in units of the stellar radius. Note the unsteady nature
of the dense equatorial region, which undergoes episodic emptyings and
refills. Within the magnetosphere (i.e. the closed loop region), the
opacity at 10 Å or 1.2 keV may reach high values ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig8a.eps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig8b.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg110.png)
|
Figure 8: Volume emission-measure distribution (DEM) per log T= 0.1 bin for our MHD simulations of HD 191612. The MHD simulation is used to compute the emission measure per unit volume per logarithmic temperature bin, then integrated over three-dimensional space assuming azimuthal symmetry about the magnetic dipole axis. Left: DEM as a function of time and temperature; the periodic variations due to build-ups and infalls are clearly seen. The coloured version of this figure is available on-line. Right: time-averaged DEM as a function of temperature. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Figure 8 shows the differential emission measure (DEM, or the relative amount of material in a given temperature bin) calculated in the MHD simulation. The DEM peaks at very high temperatures (about 10 MK and larger), suggesting that the very hot gas dominates the X-ray emission of the system. Of course, the material in the unshocked regions remains at the effective temperature of the star due to the intense UV radiation from the parent star that keeps the wind nearly isothermal.
Table 3: Stellar parameters used for the MHD simulation of HD 191612, adopted mostly from Nazé et al. (2008b, and references therein).
3.3.3 Comparison of models and observations
Applying a magnetically-confined wind model to HD 191612 yields
four clues. First, the X-ray emission should clearly be dominated by
very hot plasma, as was the case for ![]() Ori C (see Fig. 6 of Gagné et al. 2005). Second, on average, the total EM calculated for HD191612 in the 1-100 MK range amounts to
Ori C (see Fig. 6 of Gagné et al. 2005). Second, on average, the total EM calculated for HD191612 in the 1-100 MK range amounts to
![]() cm-3. This agrees well with the MHD simulation of
cm-3. This agrees well with the MHD simulation of ![]() Ori C,
considering the difference in the stellar parameters and modelling.
Indeed, the simulated EM for this star in the same temperature range
reached
Ori C,
considering the difference in the stellar parameters and modelling.
Indeed, the simulated EM for this star in the same temperature range
reached
![]() cm-3 (Gagné et al. 2005),
i.e. a factor 6.5 lower than for HD 191612, which is close to
the factor of 4 expected from the EMs scaling with the third power
of the radius. Considering an average cooling factor
cm-3 (Gagné et al. 2005),
i.e. a factor 6.5 lower than for HD 191612, which is close to
the factor of 4 expected from the EMs scaling with the third power
of the radius. Considering an average cooling factor
![]() of
of ![]()
![]() erg cm3 s-1 (Raymond et al. 1976), this yields a totally unabsorbed X-ray luminosity of
erg cm3 s-1 (Raymond et al. 1976), this yields a totally unabsorbed X-ray luminosity of ![]()
![]() erg s-1 in the 0.5-10. keV range. Third, the hot gas generally moves with velocities of about 100-200 km s-1 in the MHD models and only very few hot plasma reach 400 km s-1,
whatever the viewing angle on the equatorially-confined region. This is
unsurprising because the hot gas always remains close to the star: the
associated X-ray lines are thus expected to be narrow, again a similar
result to that found for
erg s-1 in the 0.5-10. keV range. Third, the hot gas generally moves with velocities of about 100-200 km s-1 in the MHD models and only very few hot plasma reach 400 km s-1,
whatever the viewing angle on the equatorially-confined region. This is
unsurprising because the hot gas always remains close to the star: the
associated X-ray lines are thus expected to be narrow, again a similar
result to that found for ![]() Ori C.
Finally, the X-ray emission should be modulated throughout the cycle
of 538d, because the viewing angle on the disc-like structure
changes.
Ori C.
Finally, the X-ray emission should be modulated throughout the cycle
of 538d, because the viewing angle on the disc-like structure
changes.
The observations (both old and new) do not fully agree with
this picture. On the one hand, the emission is modulated with the 538d
cycle, as expected for MCWS. The observed X-ray emission is indeed
bright (LX=7-
![]() erg s-1
when corrected for the interstellar absorption), it is on the luminous
edge compared to ``normal'' O-type stars (for O stars observed
with XMM-Newton,
erg s-1
when corrected for the interstellar absorption), it is on the luminous
edge compared to ``normal'' O-type stars (for O stars observed
with XMM-Newton,
![]() = -6.45 with a dispersion of 0.51 dex, see Nazé 2009). Considering the uncertainty in the spectral models (see Table 2), the observations yield a totally unabsorbed X-ray luminosity of
= -6.45 with a dispersion of 0.51 dex, see Nazé 2009). Considering the uncertainty in the spectral models (see Table 2), the observations yield a totally unabsorbed X-ray luminosity of ![]() 8-
8-
![]() erg s-1, for the ``hot'' and ``cool'' model respectively. Total emission measures, derived from the normalisation factors of Table 2 or as in Gagné et al. (2005) for a spectral fitting considering a single absorbing column for both thermal components, amount to 3-
erg s-1, for the ``hot'' and ``cool'' model respectively. Total emission measures, derived from the normalisation factors of Table 2 or as in Gagné et al. (2005) for a spectral fitting considering a single absorbing column for both thermal components, amount to 3-
![]() cm-3
for an equivalent ``cool'' model and ten times lower for an equivalent
``hot'' model. Theoretical predictions thus agree rather well with the
``cool'' model, which is also the one favored by the DEM modelling (Nazé et al. 2007).
cm-3
for an equivalent ``cool'' model and ten times lower for an equivalent
``hot'' model. Theoretical predictions thus agree rather well with the
``cool'' model, which is also the one favored by the DEM modelling (Nazé et al. 2007).
On the other hand, however, the X-ray emission of HD 191612 displays broad lines (
![]() km s-1, Nazé et al. 2007)
and is far from being as hard as predicted by the model. Indeed, a fit
of the EPIC data by a DEM model yields a strong emission peak at about
2 MK, not beyond 10 MK, as shown for example in Fig. 3
of Nazé et al. (2007). In addition, the average temperature
km s-1, Nazé et al. 2007)
and is far from being as hard as predicted by the model. Indeed, a fit
of the EPIC data by a DEM model yields a strong emission peak at about
2 MK, not beyond 10 MK, as shown for example in Fig. 3
of Nazé et al. (2007). In addition, the average temperature![]() derived in the 2XMM survey for HD 191612 amounts to
derived in the 2XMM survey for HD 191612 amounts to ![]() 0.3 keV and is thus quite normal (85% of the stars in the 2XMM have
0.3 keV and is thus quite normal (85% of the stars in the 2XMM have
![]() below 1 keV, Nazé 2009) - it does not resemble the extreme case of
below 1 keV, Nazé 2009) - it does not resemble the extreme case of ![]() Ori C for which
Ori C for which
![]() amounts to 2.5 keV in the same 2XMM survey and for which the MCWS
model works well. The relatively soft character of that emission
despite the large magnetic confinement parameter might be reminiscent
of the characteristics observed in some B-type stars (Güdel & Nazé 2009):
further investigation of the MCWS model and magnetic field geometry is
thus required to understand the high-energy properties of the Of?p
stars.
amounts to 2.5 keV in the same 2XMM survey and for which the MCWS
model works well. The relatively soft character of that emission
despite the large magnetic confinement parameter might be reminiscent
of the characteristics observed in some B-type stars (Güdel & Nazé 2009):
further investigation of the MCWS model and magnetic field geometry is
thus required to understand the high-energy properties of the Of?p
stars.
4 Conclusions
Our continued monitoring in the X-ray and optical domains of the prototypical Of?p stars has now clarified some of their observational properties.For HD 108, the Balmer, C III ![]() 4650, He I, and Si III lines
display minimum emissions since 2005: the star has thus finally reached
its quiescent state for the first time in 50-60 yr. Long-term
monitoring of this quiescence will further constrain the geometry of
the line emission region.
4650, He I, and Si III lines
display minimum emissions since 2005: the star has thus finally reached
its quiescent state for the first time in 50-60 yr. Long-term
monitoring of this quiescence will further constrain the geometry of
the line emission region.
For HD 148937, the 7d variations in the Balmer lines are
confirmed by a short-term monitoring. During this cycle, the amplitude
of the emission peak in H![]() ,
the most variable line, changes by only 7%. Thanks to the high
spectral resolution of the new data, similar periodic variations,
though of even smaller amplitude, are detected in the He I
,
the most variable line, changes by only 7%. Thanks to the high
spectral resolution of the new data, similar periodic variations,
though of even smaller amplitude, are detected in the He I ![]() 5876 and He II
5876 and He II ![]() 4686 lines. These detections underline the similarities of the star with the other two prototypical Of?p objects.
4686 lines. These detections underline the similarities of the star with the other two prototypical Of?p objects.
For HD 191612, a new XMM-Newton observation clearly shows that its X-ray emission is modulated by the 538d period and not the orbital period - it is thus not of colliding-wind origin: the phenomenon responsible for the optical changes appears also at work in the high-energy domain. Contrary to observations, our MHD simulations predict a hard spectrum, dominated by very hot plasma (>10 MK) and narrow lines. Further refinements to the modelling will be needed in order to fully explain this discrepancy.
AcknowledgementsY.N., M.D.B. and G.R. acknowledge support from the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique (Belgium), the Communauté Française de Belgique, the PRODEX XMM and Integral contracts, and the ``Action de Recherche Concertée'' (CFWB-Académie Wallonie Europe). The authors thank L. Mahy and P. Eenens for providing the 2009 échelle spectrum. ADS and CDS were used for preparing this document.
References
- Babel, J., & Montmerle, T. 1997, A&A, 323, 121 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Baranne, A., Queloz, D., Mayor, M., et al. 1996, A&AS, 119, 373 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, D. H. 2009, AIP Conf. Ser., 1161, 132 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Diplas, A., & Savage, B. D. 1994, ApJS, 93, 211 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Donati, J.-F., Howarth, I. D., Bouret, J.-C., et al. 2006, MNRAS, 365, L6 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton, A. W., Gies, D. R., & Bolton, C. T. 1996, ApJS, 103, 475 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, M., Oksala, M. E., Cohen, D. H., et al. 2005, ApJ, 628, 986 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gosset, E., Royer, P., Rauw, G., Manfroid, J., & Vreux, J.-M. 2001, MNRAS, 327, 435 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Güdel, M., & Nazé, Y. 2009, A&ARv, 17, 309 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Heck, A., Manfroid, J., & Mersch, G. 1985, A&AS, 59, 63 [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle, K., Wallace, L., Valenti, J., & Harmer, D. 2000, Visible and Near Infrared Atlas of the Arcturus Spectrum 3727-9300 A, ed. K. Hinkle, L. Wallace, J. Valenti, & D. Harmer (San Francisco: ASP) [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, I. D., Walborn, N. R., Lennon, D. J., et al. 2007, MNRAS, 381, 433 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hubrig, S., Schöller, M., Schnerr, R. S., et al. 2008, A&A, 490, 793 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, J., & Bailey, M. E. 1981, MNRAS, 197, 995 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Martins, F., Donati, J.-F., Marcolino, W. L. F., et al. 2010, MNRAS, 407, 1423 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nazé, Y. 2009, A&A, 506, 1055 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Nazé, Y., Vreux, J.-M., & Rauw, G. 2001, A&A, 372, 195 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Nazé, Y., Rauw, G., Vreux, J.-M., & De Becker, M. 2004, A&A, 417, 667 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Nazé, Y., Barbieri, C., Segafredo, A., Rauw, G., & De Becker, M. 2006, IBVS, 5693 [Google Scholar]
- Nazé, Y., Rauw, G., Pollock, A. M. T., Walborn, N. R., & Howarth, I. D. 2007, MNRAS, 375, 145 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nazé, Y., Walborn, N. R., Rauw, G., et al. 2008a, AJ, 135, 1946 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nazé, Y., Walborn, N. R., & Martins, F. 2008b, Rev. Mex. Astron. Astrofis., 44, 331 [Google Scholar]
- Rauw, G., Morrison, N. D., Vreux, J.-M., Gosset, E., & Mulliss, C. L. 2001, A&A, 366, 585 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, J. C., Cox, D. P., & Smith, B. W. 1976, ApJ, 204, 290 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Stone, J. M., & Norman, M. L. 1992, ApJS, 80, 753 [Google Scholar]
- ud-Doula, A., & Owocki, S. P. 2002, ApJ, 576, 413 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- ud-Doula, A., Townsend, R. H. D., & Owocki, S. P. 2006, ApJ, 640, L191 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- ud-Doula, A., Owocki, S. P., & Townsend, R. H. D. 2008, MNRAS, 385, 97 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- ud-Doula, A., Owocki, S. P., & Townsend, R. H. D. 2009, MNRAS, 392, 1022 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Walborn, N. R. 1972, AJ, 77, 312 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Walborn, N. R., Howarth, I. D., Herrero, A., & Lennon, D. J. 2003, ApJ, 588, 1025 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Walborn, N. R., Howarth, I. D., Rauw, G., et al. 2004, ApJ, 617, L61 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Walborn, N. R., Sota, A., Maiz-Apellaniz, J., et al. 2010, ApJ, 715, L74 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Footnotes
- ... stars
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- Based on observations collected at the Haute-Provence Observatory, at the La Silla and San Pedro Mártir Observatories, and with XMM-Newton, an ESA Science Mission with instruments and contributions directly funded by ESA Member States and the USA (NASA).
- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- Research Associate FRS-FNRS.
- ... Institute
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- Operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under NASA contract NAS5-26555.
- ... account
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- Note that combining the two datasets is not possible due to
the very different spectral resolutions (R=2300 vs.
55 000). As the best period estimate comes from the longest
time coverage, the value of 7.031
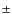 0.003d from Nazé
et al. (2008a) should be considered as the best
measurement on an absolute scale.
0.003d from Nazé
et al. (2008a) should be considered as the best
measurement on an absolute scale.
- ... reasons
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- As in Nazé et al. (2007), we noted that the two sets of parameters give a good fit, but we recall that a fit by a differential emission measure (DEM) model clearly favours the ``cool'' fit.
- ... axis
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- This simplifies the computation and makes no assumption about the true geometry of the system, i.e. an oblique rotator model is not excluded; it can easily be simulated here by changing the viewing angle on the system.
- ... abundance#
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- Note that models used by Gagné et al. (2005) made use of the full energy equation, but did not include rotation.
- ... temperature
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
-
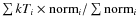 for
models using a single absorption in front of the thermal emission
components.
for
models using a single absorption in front of the thermal emission
components.
All Tables
Table 1: Mean and dispersion of the measured RVs and EWs for HD 148937.
Table 2: Best-fitting models and X-ray fluxes at Earth for each XMM -Newton observation of HD 191612.
Table 3: Stellar parameters used for the MHD simulation of HD 191612, adopted mostly from Nazé et al. (2008b, and references therein).
All Figures
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=15cm,bb=24 470 575 690, clip]{14333fig...
...includegraphics[width=15cm, bb=18 140 550 430, clip]{14333fig1c.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg13.png)
|
Figure 1: Evolution of the line profiles in recent years for HD 108. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{2mm}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig2.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg19.png)
|
Figure 2:
Evolution as a function of time of a few quantities related to HD 108. Upper panel: EW (in Å, in the range 4845-4870 Å) of H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig3a.ps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig3b.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg22.png)
|
Figure 3:
Evolution with time of the EWs (expressed in Å) for some lines of HD 148937. Left: the strongest emission lines (Balmer line of H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=10.5cm]{14333fig4a.ps}\includegraphics[width=7.5cm]{14333fig4b.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg23.png)
|
Figure 4:
Left: average spectra and TVS of He II |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9.2cm]{14333fig5a.ps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig5b.ps}
\vspace*{7mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg24.png)
|
Figure 5:
Left, from top to bottom: raw periodogram of H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig6a.ps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig6b.ps}
\vspace*{3mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg104.png)
|
Figure 6: Left: position of the new XMM -Newton observation in the cycles of HD 191612. The orbital cycle, calculated using orbital parameters of Howarth et al. (2007) and with the primary (resp. secondary) curve drawn in solid (resp. dotted) line, is shown on top while the bottom panel shows the line profile variation cycle of 538d from the analytical approximation of Howarth et al. (2007). The phases of the previous observations are shown by the thin short-dashed lines and the phase of the new observation by the thick long-dashed line. Right: evolution of the count rate in the 0.4-10.0 keV band ( top) and of two hardness ratios ( middle, bottom) with phase from the 538d cycle. Open symbols refer to the old observations, filled red symbols to the new dataset; triangles and squares were used for the EPIC MOS data (note that the MOS count rates are multiplied by a factor of 3 in this figure) and circles for the EPIC pn data. The hardness ratio HR1 and HR2 are defined as (M-S)/(M+S) and (H-M)/(H+M), respectively, where S is the count rate in the 0.4-1.0 keV band, M in 1-2 keV, and H in 2-10 keV. The coloured version of the figure is available on-line. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig7a.eps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig7b.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg109.png)
|
Figure 7:
Snapshots of density ( left) and temperature ( right), in cgs units on a logarithmic colour-scale, shown with field lines (solid lines) at arbitrarily chosen time t=1300 ks for the 2D MHD simulation of HD 191612. The x and y axes
are labelled in units of the stellar radius. Note the unsteady nature
of the dense equatorial region, which undergoes episodic emptyings and
refills. Within the magnetosphere (i.e. the closed loop region), the
opacity at 10 Å or 1.2 keV may reach high values ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig8a.eps}\includegraphics[width=9cm]{14333fig8b.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/12/aa14333-10/Timg110.png)
|
Figure 8: Volume emission-measure distribution (DEM) per log T= 0.1 bin for our MHD simulations of HD 191612. The MHD simulation is used to compute the emission measure per unit volume per logarithmic temperature bin, then integrated over three-dimensional space assuming azimuthal symmetry about the magnetic dipole axis. Left: DEM as a function of time and temperature; the periodic variations due to build-ups and infalls are clearly seen. The coloured version of this figure is available on-line. Right: time-averaged DEM as a function of temperature. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
Copyright ESO 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


