| Issue |
A&A
Volume 511, February 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A38 | |
| Number of page(s) | 15 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200811583 | |
| Published online | 04 March 2010 | |
Open clusters in the Third Galactic Quadrant
III. Alleged binary clusters![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
R. A. Vázquez1 -
A. Moitinho2 -
G. Carraro3,![]() -
W. S. Dias4
-
W. S. Dias4
1 - Facultad de Ciencias Astronómicas y Geofísicas de la
UNLP, IALP-CONICET, Paseo del Bosque s/n 1900, La Plata, Argentina
2 -
SIM/IDL, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de
Lisboa, Ed. C8, Campo Grande, 1749-016 Lisboa, Portugal
3 -
ESO, Alonso de Cordova 3107, Vitacura, Santiago, +++Chile
4 -
UNIFEI, Instituto de Ciências Exatas, Universidade Federal de Itajubá, Itajubá MG, Brazil
Received 23 December 2008 / Accepted 10 August 2009
Abstract
Aims. We aim to determine accurate distances and ages of
eight open clusters in order to: (1) assess their possible binarity (2)
provide probes to trace the structure of the Third Galactic Quadrant.
Methods. Cluster reddenings, distances, ages and metallicities
are derived from ZAMS and isochrone fits in UBVRI photometric diagrams.
Field contamination is reduced by restricting analysis to stars within
the cluster limits derived from star counts. Further membership control
is done by requiring that stars have consistent positions in several
diagrams and by using published spectral types.
Results. The derived distances, ages and metallicities have
shown that none of the analysed clusters compose binary/double systems.
Of the four candidate pairs, only NGC 2383/NGC 2384 are close
to each other, but have different metallicities and ages.
Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158 are not clusters but
fluctuations of the field stellar density. Haffner 18 is found to
be the superposition of two stellar groups at different distances:
Haffner 18(1) at 4.5 kpc and Haffner 18(2) between 9.5
and 11.4 kpc from the Sun. The derived distances and ages have
been used to situate the clusters in the Galactic context. In
particular, young stellar groups trace spiral structure at large
Galactocentric radii. At least two clusters formed during the last few
108 yr in an interstellar medium with less than solar abundances.
Conclusions. In contrast with the LMC, double clusters are
apparently rare, or even non existent, in the undisturbed environment
of the Third Galactic Quadrant. This leaves open the question of
whether binary clusters form more easily toward denser and more violent
regions of the Milky Way such as the inner Galaxy.
Key words: Galaxy: structure - open clusters and associations: general
1 Introduction
This paper continues the series of articles dedicated to analysing
the homogeneous ![]() photometry of the fields of 30 open
clusters presented in Moitinho (2001, hereafter Paper I). The
programme has been motivated by our interest in investigating the
structure of the Canis Major-Puppis-Vela region of the Galactic disc
and its interconnection with large scale star formation.
photometry of the fields of 30 open
clusters presented in Moitinho (2001, hereafter Paper I). The
programme has been motivated by our interest in investigating the
structure of the Canis Major-Puppis-Vela region of the Galactic disc
and its interconnection with large scale star formation.
The photometry described in Moitinho2001a, together with other observations collected by our group during the last decade, have resulted in new insights into the structure and stellar populations in the Third Galactic Quadrant (3GQ). Specifically, a new vision of the (stellar) spiral structure and warp has emerged in which it is seen that the Norma-Cygnus (or Outer) arm is defined over the whole 3GQ and that the Local (Orion) arm is not a small spur, but a large structure that reaches the warped outer disc (Carraro et al. 2005; Vázquez et al. 2008; Moitinho et al. 2006b). An unexpected repercussion of this scenario has been to cast considerable doubt on the existence of the highly publicised Canis Major dwarf galaxy (Martin et al. 2004). These results rely not only on the fundamental parameters derived for the clusters themselves, but also on careful analysis of the characteristics of the field population. From the sample described in Moitinho2001a, only NGC 2425, NGC 2635 (Moitinho et al. 2006a, Paper II of this series), NGC 2588 (Baume et al. 2004) and NGC 2401 (Baume et al. 2006) have been the subject of publications dedicated to their detailed photometric analysis and derivation of main physical parameters. In this paper we present a detailed analysis of the fields of four open candidate cluster pairs.
It is well known that stars tend to form in clusters rather than
in isolation. The exact mechanisms that lead from the contraction
of molecular clouds to star clusters are not well understood and
there are possibly different physical paths (gravitational
collapse; turbulence driven). One possible outcome, although
apparently rare in the Galaxy, is the emergence of binary or
double clusters (Ziyakhanovet al. 2004). From the theoretical point
of view, the formation and evolution of binary clusters poses some
challenges. Twenty years ago, it was clearly exposed by
Efremov & Sitnik (1988) that clusters tend to form part of
associations which in turn form part of complexes and
super-complexes of stars and gas. Therefore, similar chemical
composition, age and dynamical behaviour are expected for binary
clusters. Interestingly, h and ![]() Persei compose the only
confirmed true double cluster known in our Galaxy. This is in
contrast with the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), where about 10%
of the known open clusters seem to belong to pairs and probably
more than 50% of them are true binary clusters
(Dieball et al. 2002; Dieball & Grebel 2000). Following Bhatia (1990),
the lifetimes of binary clusters depend on their mutual separation
but also on the tidal force of the parental galaxy and on
encounters with giant molecular clouds. The models of
Bhatia (1990) indicate binary cluster lifetimes ranging from
a few 106 yr to
Persei compose the only
confirmed true double cluster known in our Galaxy. This is in
contrast with the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), where about 10%
of the known open clusters seem to belong to pairs and probably
more than 50% of them are true binary clusters
(Dieball et al. 2002; Dieball & Grebel 2000). Following Bhatia (1990),
the lifetimes of binary clusters depend on their mutual separation
but also on the tidal force of the parental galaxy and on
encounters with giant molecular clouds. The models of
Bhatia (1990) indicate binary cluster lifetimes ranging from
a few 106 yr to
![]() yr. Besides pairs originating
from the same star forming event (which we call ``true
binary/double clusters''), gravitational capture can also create
cluster pairs. In this case, components can have different ages
and compositions and will tend to eventually merge
(de Oliveira et al. 2000).
yr. Besides pairs originating
from the same star forming event (which we call ``true
binary/double clusters''), gravitational capture can also create
cluster pairs. In this case, components can have different ages
and compositions and will tend to eventually merge
(de Oliveira et al. 2000).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f1.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg5.png)
|
Figure 1: DSS images of the four regions investigated in this article. The squares delimit the areas covered by the photometric measurement (East is at left and North at top): 1) Czernik 29 and Haffner 10; 2) Haffner 18 and Haffner 19; 3) NGC 2383 and NGC 2384; 4) Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The rest of this article is structured as follows: Sect. 2 describes the object sample and data set; Sect. 3 discusses the strategy for determining cluster parameters. Section 4 is dedicated to an analysis of each cluster. Section 5 contextualises the clusters in the Galaxy. Some final comments and conclusions are given in Sect. 6.
2 Cluster sample
The sample of 30 open clusters presented in
Moitinho2001a was selected in the Galactic range
![]() and
and
![]() ,
with angular diameters of approximately
,
with angular diameters of approximately
![]() and with
estimated ages of less than
and with
estimated ages of less than
![]() yr (
yr (
![]() ). From that sample we found that Czernik 29 (Cz 29) and
Haffner 10 (Haff 10); Haffner 18 (Haff 18) and Haffner 19 (Haff
19); NGC 2383 and NGC 2384 and Ruprecht 72 (Rup 72) and
Ruprecht 158 (Rup 158) are potential members of cluster pairs.
). From that sample we found that Czernik 29 (Cz 29) and
Haffner 10 (Haff 10); Haffner 18 (Haff 18) and Haffner 19 (Haff
19); NGC 2383 and NGC 2384 and Ruprecht 72 (Rup 72) and
Ruprecht 158 (Rup 158) are potential members of cluster pairs.
Considering only the constraint of Galactic longitude, the open
cluster catalogue of Dias et al. (2002) lists 7 candidate cluster
pairs separated by less than
![]() .
Pairs filtered out by
the selection criteria were
Collinder 196/Collinder 198 having
.
Pairs filtered out by
the selection criteria were
Collinder 196/Collinder 198 having
![]() ;
Ruprecht 27/Alessi 18 because
Ruprecht 27 is too old and Alessi 18 is a doubtful cluster
appearing to be a random concentration in the sky;
Ruprecht 52/Ruprecht 155 also appear to be
random noise in the stellar distribution. This is also the case of
Ruprecht 72/Ruprecht 158, although still with a
slight possibility of being real entities and were thus kept. As
will be seen later in Sect. 4.4, they are indeed
fluctuations in the stellar distribution and not clusters. The
observed cluster pairs are indicated in Table 1
that shows all, except one, of the optically visible
double-cluster candidates in that region of the Milky Way.
;
Ruprecht 27/Alessi 18 because
Ruprecht 27 is too old and Alessi 18 is a doubtful cluster
appearing to be a random concentration in the sky;
Ruprecht 52/Ruprecht 155 also appear to be
random noise in the stellar distribution. This is also the case of
Ruprecht 72/Ruprecht 158, although still with a
slight possibility of being real entities and were thus kept. As
will be seen later in Sect. 4.4, they are indeed
fluctuations in the stellar distribution and not clusters. The
observed cluster pairs are indicated in Table 1
that shows all, except one, of the optically visible
double-cluster candidates in that region of the Milky Way.
Table 1: Position of cluster centres and estimated radii.
At the time of the observations presented here (1994 and 1998), no all-sky infrared surveys were available. With the advent of 2MASS (Cutri et al. 2003), systematic searches for embedded star clusters became possible. A similar search to the one performed in the optical, but now over the infrared cluster catalogues of Bica et al. (2003) and Dutra et al. (2003), only reveals two more pairs. Another exercise than can be done is to search over the merged list of optically revealed and hidden clusters. In this case 6 further candidates arise. However, the occurrence of embedded/non-embedded physical pairs is unlikely given the different environments of the prospective components.
2.1 Observations and reductions
The observed fields superposed on the Digitized Sky Survey (DSS)
are shown in Fig. 1. Observations and data
reductions are extensively described in
Moitinho2001a. Briefly, observations were acquired in
two runs (1994 and 1998) at the CTIO 0.9m telescope. Both runs
used the same Tek
![]() CCD and the standard set of
CCD and the standard set of
![]() filters available at CTIO. Typical seeing was about
filters available at CTIO. Typical seeing was about
![]() although a few images presented higher values
(
although a few images presented higher values
(![]()
![]() ). The
). The
![]() /pixel
plate scale resulted in a total field of view of
/pixel
plate scale resulted in a total field of view of
![]() .
Due to distortions (coma) in the
the edges of the images, stars separated by less than 150 pix from
the edges were not used, which limited the useful field of view to
.
Due to distortions (coma) in the
the edges of the images, stars separated by less than 150 pix from
the edges were not used, which limited the useful field of view to
![]() .
.
Images were processed using IRAF routines for overscan, bias, and flat-field corrections. PSF photometry was performed using the IRAF/ DAOPHOT (Stetson 1987) package and calibrated with standard star measurements in Landolt (1992) fields. For further details see Moitinho2001a.
3 Strategy for the derivation of cluster parameters
3.1 Cluster sizes
The linear size is a fundamental quantity in a comprehensive characterisation of an open cluster. It is necessary to evaluate its evolutionary status through analysis of its density and other related parameters (see Kroupa et al. 2001; Aarseth 1996; de La Fuente Marcos 1997) such as the slope of the mass spectrum. It is also routinely used as criteria for separating cluster-dominated from field-dominated regions in photometric diagrams (Baume et al. 2004).
The most usual approach for estimating cluster sizes is to assume a centrally peaked spherical stellar density distribution and then to determine the the distance at which its radial density profile merges with the (flat) density of the stellar background. In practise, this determination is normally done either by visually setting the limit in a plot or by fitting King (1962) profiles to the density profile. However, both approaches assume a spherically symmetric distribution and, in the case of the King profiles, that the system is dynamically relaxed.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=13cm,clip]{11583f2.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg25.png)
|
Figure 2: Contour plots derived in each frame. The density scale - star number per square arcminute - is shown in the respective inserts. Circles are adopted cluster boundaries. North is at the top and East to the left. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Because we are interested in determining the cluster radii to
reduce field contamination in photometric diagrams, the following
approach has been adopted: contour maps were computed in each
field by choosing adequate kernel sizes and grid steps. Once a
high and extended stellar density is identified, a circle
enclosing its full range is drawn by eye. The cluster limit is
taken as that defined by the radius of this circle. The cluster
centre is considered to be the geometric centre of the cluster as
opposed to the position of the density peak. The resulting
contour maps of the four regions under study are shown in
Fig. 2. Each panel in the figure also shows an insert
indicating the number of stars per square arcminute. A clear
example of the adequacy of the approach is Haffner 10. Had we
chosen the evident peak to compute the radial density profile, we
would have largely overestimated the angular dimension of Haffner
10 and included many field stars. In the case of NGC 2384, which
is identified as a concentration of a few bright stars, the
density enhancement is irrelevant, suggesting either that the
cluster does not exist or that it lacks faint stars. Here the
cluster is assumed to be within a circle comprising the bright
stars. As for the field of Ruprecht 72 and 158, no density
enhancements or obvious conglomerates are seen. This field will be
further discussed in Sect. 4.4.
Table 1 gives the new cluster centres in galactic
longitude, latitude,
![]() ,
,
![]() and the
adopted radii. In the cases of Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158,
centres and radii are those from the Dias et al. (2002) catalogue.
and the
adopted radii. In the cases of Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158,
centres and radii are those from the Dias et al. (2002) catalogue.
3.2 Cluster membership
Except for Ruprecht 72 and 158 (see Table 1) the
regions included in this study are not far from the formal
Galactic plane
![]() .
Under this circumstance,
interstellar absorption and field interlopers may make membership
assignment of faint stars a difficult task. Although an extensive
discussion of this can be found in Vázquez et al. (2008), here we
outline a few essential points: First, cluster parameters are
determined using only stars within the determined cluster limits.
This eliminates avoidable field contamination, enhancing the
contrast between cluster and field distributions in photometric
diagrams. Second, the location of each star is checked for
consistency in different photometric diagrams, taking into account
consistent reddening solutions, up to the magnitude limits where
they become immersed in the field star distribution.
.
Under this circumstance,
interstellar absorption and field interlopers may make membership
assignment of faint stars a difficult task. Although an extensive
discussion of this can be found in Vázquez et al. (2008), here we
outline a few essential points: First, cluster parameters are
determined using only stars within the determined cluster limits.
This eliminates avoidable field contamination, enhancing the
contrast between cluster and field distributions in photometric
diagrams. Second, the location of each star is checked for
consistency in different photometric diagrams, taking into account
consistent reddening solutions, up to the magnitude limits where
they become immersed in the field star distribution.
Third, for young clusters, the
![]() diagram can be
particularly useful for eliminating most A-F type foreground stars
that usually contaminate the vertical part (early type) of cluster
sequences in the V/B-V plane. This is due to the greater
sensitivity of the U-B index to changes in stellar temperature
compared to B-V (Meynet et al. 1993). Further membership control
is done when spectral types are available. Nevertheless,
membership assignments for stars later than A0 may remain
uncertain. However, except for distance, determining the other
basic cluster parameters, reddening and age, does not require
identification of the fainter members.
diagram can be
particularly useful for eliminating most A-F type foreground stars
that usually contaminate the vertical part (early type) of cluster
sequences in the V/B-V plane. This is due to the greater
sensitivity of the U-B index to changes in stellar temperature
compared to B-V (Meynet et al. 1993). Further membership control
is done when spectral types are available. Nevertheless,
membership assignments for stars later than A0 may remain
uncertain. However, except for distance, determining the other
basic cluster parameters, reddening and age, does not require
identification of the fainter members.
3.3 Reddenings, distances and ages of the clusters
Mean colour excesses, E(B-V) and E(U-B), were computed
in each cluster through the zero age main sequence (ZAMS) fitting
method. The position along the reddening-free ZAMS of several
spectral types earlier than A0 is indicated to help visual
inspection of the two-colour diagram (TCD). The solar content
(Z=0.019) Schmidt-Kaler (1982) ZAMS (hereinafter SKZ) has
been shifted along the reddening line given by the standard
relation
![]() to fit the cluster sequence. The E(B-V)uncertainties
quoted in Table 4 (in advance) reflects the range of
ZAMS displacement to bracket cluster members. In a few cases
(Cz 29, Haffner 10 and NGC 2383) the SKZ line does not follow
the
shape of the cluster sequence beyond the location of A-type stars
(the ZAMS knee). Since the morphology of the ZAMS in this portion
of the TCD strongly depends on the metal content, we made several
trials with intrinsic colour-colour lines of different
metallicities (Girardi et al. (2000) -hereafter G00) to find the
interval that best approaches the cluster sequence shape. A mean
value of the metal content was then assumed and also of
E(B-V) -with an acceptable level of departure- representing
the uncertainty of these parameters (as shown in Table 4).
to fit the cluster sequence. The E(B-V)uncertainties
quoted in Table 4 (in advance) reflects the range of
ZAMS displacement to bracket cluster members. In a few cases
(Cz 29, Haffner 10 and NGC 2383) the SKZ line does not follow
the
shape of the cluster sequence beyond the location of A-type stars
(the ZAMS knee). Since the morphology of the ZAMS in this portion
of the TCD strongly depends on the metal content, we made several
trials with intrinsic colour-colour lines of different
metallicities (Girardi et al. (2000) -hereafter G00) to find the
interval that best approaches the cluster sequence shape. A mean
value of the metal content was then assumed and also of
E(B-V) -with an acceptable level of departure- representing
the uncertainty of these parameters (as shown in Table 4).
Wherever solar metal content is assumed, cluster apparent distance moduli were visually derived by fitting the SKZ to the observed cluster main sequence (MS) in colour-magnitude diagrams (CMDs). As said above, a different from solar metal content may become evident in some clusters from the reddening estimation. Therefore, we applied the same metal content set of isochronous lines (Girardi et al. 2000) until the best MS match is achieved in the CMD. The method is exemplified with the cluster Haffner 10 (see Sect. 4.1.1) where a simultaneous fit of the ``turn-off'', the Red Clump and MS was performed using the appropriate isochrone. Notice that in cases like this one, we can simultaneously obtain the color excess, the distance modulus and also the age of the cluster. In one case, given the large amount of internal reddening (see Sect. 4.2.1), the range of distance modulus is so large that we only indicate extreme values of the interval instead of the fitting uncertainty. Regardless of the metal content adopted, the fitting error of the apparent distance modulus for each cluster was estimated by eye as discussed below.
Cluster ages were derived by the same technique of fitting the isochrone (Girardi et al. 2000) set that reasonably matches the shape of the observed cluster sequence regarding the adopted metal content used to compute color excesses and distance moduli. Despite the special care put in fitting all the potential cluster members, some sequences are not satisfactorily reproduced by one single isochrone, as said above, and a range of them has been indicated in each cluster of Table 4. Known reasons to fail the fitting include the effect of un-resolved binaries, stellar rotation and variable reddening due to remaining material from the star formation process (in very young clusters) that broaden the cluster sequence. This point is crucial since age estimates may vary strongly (up to 100% for those younger than 107 years) if the effects mentioned above are not conveniently accounted for. If potential PMS-stars were detected in a cluster, we compared the estimated nuclear age to the one derived by fitting pre-main sequence isochrones from Siess et al. (2000) assuming a metal content similar to that adopted to compute the nuclear age.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f3.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg29.png)
|
Figure 3: Upper left panel: the TCDs for the entire region. Middle upper panel: Haffner 10 area. Right upper panel: Czernik 29. The SKZ (solid line) is shown together with the colour excess relation for O3-, B3-, B6- (dashed lines) and A0-type stars (solid). The reference intrinsic fitting line from G00 to Czernik 29 sequence, for Z = 0.004, is discussed in the text. Lower panels: the correspondent CMDs where long-dashed lines are the isochrone [log (t)] fits from G00 to Haffner 10 and Czernik 29 CMD sequences, for Z = 0.008 and Z = 0.004, respectively as discussed in the text. Some stars, pointed out using our notation, are also discussed in the text. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The removal of interstellar absorption in a cluster, AV, allows one to obtain the true distance modulus. AV has been determined from the above colour excess estimate via the ratio of total to selective absorption, R = AV/E(B-V). Though analysis in Moitinho2001a has shown that in this part of the Galaxy a normal value of R =3.1 is to be expected, an independent check of the reddening law was performed by examining the field stellar distribution in plots such as the one in Fig. 4. For guidance we show in each B-V/V-Iplanes the slopes of the reddening vectors for E(V-I)/E(B-V) = 1.244 - normal reddening law -, R =3.1, (Dean et al. 1978) and E(V-I)/E(B-V) = 1.5 for R= 3.75together with the intrinsic relation for dwarf and giant stars from Cousins (1978).
Our strategy of visually fitting the SKZ (or other intrinsic lines) to the observed cluster sequence has been extensively treated in the literature; see, e.g., Blaauw (1963), Phelps & Janes (1994) and Kassis et al. (1997), for a quantitative approach to the many factors (photometric errors, binaries, double stars, metal content, etc.) that reduce the accuracy of the parameters in a typical cluster. Aware of these effects, we decided that the best way to minimize their influence and to obtain a reasonably good parameter estimation of a cluster is by fitting the ZAMS to the remaining envelope of the MS (as stated by Turner 1973 and Turner 1976). The same holds for the isochrone fitting in the next subsection.
4 Analysis
This section presents the photometric analysis of each cluster field. An error cut-off of 0.10 mag was applied to all data plotted in the photometric diagrams. This is done to minimise artifacts introduced by high noise and low completeness.
4.1 Haffner 10 and Czernik 29
These two objects, located in Puppis, were the subject of an early
![]() photographic study by FitzGerald & Moffat (1980) who
concluded that they form a physical pair of relatively young
objects at 2.9 kpc. Pietrukowicz et al. (2006) published a BVI CCD
study of these two clusters together with NGC 2425. They derived
no reddening, distance or age for Czernik 29 and suggested that it
is not related to Haffner 10, which they determined to be a 2.5 Gyr cluster at 3.1-4.3 kpc.
photographic study by FitzGerald & Moffat (1980) who
concluded that they form a physical pair of relatively young
objects at 2.9 kpc. Pietrukowicz et al. (2006) published a BVI CCD
study of these two clusters together with NGC 2425. They derived
no reddening, distance or age for Czernik 29 and suggested that it
is not related to Haffner 10, which they determined to be a 2.5 Gyr cluster at 3.1-4.3 kpc.
Figure 3 shows the TCD and CMD (upper and lower left panels respectively) of the CCD field including both clusters. The TCD looks peculiar as at least three star sequences are seen: first, a hook-like structure appears at 0.1 < U-B < 0.5 and 0.7 < B-V; second, a dense clump of stars at 0.0 < U-B <0.5 and 0.5 < B-V < 1.2 that accumulate below V > 16 and is followed by a tail probably composed of giants and/or subgiants/dwarfs. A third sequence appears at B-V > 1.3 which is mostly composed of field giants. Only a few bright hot stars appear, spread out in the field.
The diagrams become simpler when only stars within cluster limits (Table 1) are plotted.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{11583f4.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg31.png)
|
Figure 4: Upper panels: the V/V-I CMD for Haffner 10 ( left) and Czernik 29 ( right). Dashed lines are the isochrone [log (t)] fitting from G00 at the indicated metal content Z. Lower panels: the corresponding B-V/V-I TCDs. Straight lines show the colour excess relation for R = 3.1 and 3.7 (Dean et al. 1978). The curved lines are the mean intrinsic colours for stars of Luminosity Class V and III from Cousins (1978). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
4.1.1 Haffner 10
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14cm,clip]{11583f5.eps}
\vspace*{2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg32.png)
|
Figure 5: Left: enlargement of the TCD of Czernik 29 in Fig. 3. The fitting of the SKZ (solid line) and the mean intrinsic curve for Z = 0.004 (short-dashed line) from G00 are indicated. The colour excess relation for A0-type stars is also shown. Middle: the same in the V/B-V CMD; the two best isochrones [log (t)] fittings at Z = 0.004 are pointed out. Right: same as in middle in the V/U-B CMD |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The TCD of Haffner 10 (Fig. 3, middle upper panel) displays an absence of late type dwarfs. The well separated concentration of late type stars corresponds to the red clump and a few field giants, as supported by inspection of the the V/B-VCMD (Fig. 3, middle lower panel). The presence of the cluster is clearly seen in this CMD as well as in the V/V-I CMD (Fig. 4,upper panel), showing a clear main sequence, turn-off (TO) and red clump.
There is a number of blue stars stars above the TO which could qualify as blue-straggler candidates. However, Haffner 10 as well as Czernik 29 are seen in projection against the Local arm and to the less populated (in this region of the Galaxy) Perseus arm (Vázquez et al. 2008; Moitinho et al. 2006a). The extensive discussion in Carraro et al. (2008) has shown that under these circumstances some blue-straggler candidates are likely young field A-type stars not far from their birthplaces in the spiral arms. As will be seen later on, both clusters are at almost the same distance as the Local and Perseus arms in this this direction.
The extinction law toward Haffner 10 is checked in the B-V and V-I diagram of Fig. 4 (left lower panel). The stellar distribution is consistent with a normal extinction law, R = 3.1, supporting the results from Moitinho2001a.
A simple quick inspection of the TCDs and CMDs of Haffner 10 shows
that it is an old cluster. In the absence of early type stars to
constrain reddening alone, the cluster reddening, distance and age
were determined by finding the isochrones and parameters that best fit
simultaneously the main sequence, TO and the red-clump in different
CMDs. The best match was found for a mean age of 2.5 Gyr (log(t) = 9.2-9.4) with
metal content
![]() (the same one found by
Pietrukowicz et al. (2006)), reddened by
(the same one found by
Pietrukowicz et al. (2006)), reddened by
![]() and
with a distance
modulus
and
with a distance
modulus
![]() .
This locates Haffner 10 at
.
This locates Haffner 10 at
![]() kpc
from the Sun, in agreement with Pietrukowicz et al. (2006).
kpc
from the Sun, in agreement with Pietrukowicz et al. (2006).
Finally, we discuss the apparent thickness of the main sequence seen in both CMDs. Indeed, the strip occupied from the MS to about 1 mag brighter (or 0.2 mag bluer) is completely populated by stars. The immediate explanation would be field star contamination, since field stars are expected to be present in the photometric diagrams and in this case there are not many found outside the strip. However, both, the blue and red envelopes of the strip have the same curved shape, and do not define the typical triangular/wedge shape found for most fields star distributions.
This same strip morphology is also seen in the data of Pietrukowicz et al. (2006) covering a smaller area, so it is not likely be a selection artifact. It is likely due to one of two factors, or a combination of both: a) Haffner 10 is the remainder of an initially well populated cluster with many binary stars. b) the cluster is seen projected against a stellar field with similar properties of reddening and distance. Although there are undoubtedly binaries in the cluster, we are inclined to consider the second possibility. If binaries were to dominate, then why no/few MS field stars are observed would be very hard to justify. If there was an originally very populated cluster, we would see significant signatures of it over larger areas, which we do not.
Under the similar-field scenario, we notice that:
- a)
- the maps of Moitinho et al. (2006a), Vázquez et al. (2008) and Fig. 15 in Sect. 5 situate Haffner 10 on the far side of the Local arm or the inner side of Perseus (both arms cross at about this Galactic longitude). Approximately 1kpc after Haffner 10, there is a complex of CO clouds which can block most background stellar contamination, thus leaving the blue/faint side of the MS unpopulated. This would cut the left side of the typical field triangle/wedge.
- b)
- As for the bright/red side, which is the populated side, both
the shape (MS like) and thickness (
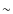 1 in the magnitude
axis) mag are compatible with a stellar distribution affected by a
similar amount of reddening as is Haffner 10 and distributed from
the distance to the cluster to about 1 kpc closer. Given that the
location of Haffner 10 and that the Local arm is about 1 kpc wide,
this is the expected distribution of Local arm stars in the CMDs.
1 in the magnitude
axis) mag are compatible with a stellar distribution affected by a
similar amount of reddening as is Haffner 10 and distributed from
the distance to the cluster to about 1 kpc closer. Given that the
location of Haffner 10 and that the Local arm is about 1 kpc wide,
this is the expected distribution of Local arm stars in the CMDs.
4.1.2 Czernik 29
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f6.eps}
\vspace*{2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg39.png)
|
Figure 6: Upper panels show the TCDs for the entire region ( left); Haffner 18 area (Haffner 18(1), filled squares, and Haffner 18(2), open squares) ( middle); and Haffner 19 ( right). The SKZ (solid line) is shown in its normal position and shifted to fit the respective cluster sequences. The colour excess relations for an O3-, B3-, B6- and A0-type stars are as in Fig. 3. Lower panels show the corresponding CMDs. Long-dashed lines in Haffner 18 area -Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2)- and in Haffner 19 are the isochrone fittings from G00, labeled log(t). The right lower panel shows the fitting to Haffner 19 of pre-main sequence isochrones (grey lines, solar metal content) from Siess et al. (2000) for 4 ( upper) and 5 ( lower) Myr (see text). A number of relevant stars is pointed out in Haffner 19 for a better judgement of their positions in both diagrams. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The field of Czernik 29 (upper and lower right panels in Fig. 3) is simpler to interpret. Since field contamination is not strong, the cluster sequence is easily distinguishable, slightly reddened and composed of late B- and A-type stars. The V/V-I CMD (right upper panel of Fig. 4) exhibits a well defined MS down to V = 19. The two brightest blue stars (11 and 12), as well as the others labelled 52, 54 and 152 in Fig. 3, are not cluster members but foreground stars given their locations in the CMD and TCD.
The TCD in Fig. 5 of Czernik 29 shows two tentative
ZAMS fits to the cluster sequence. On one side, the shape of the
SKZ (shifted solid line) does not fit the whole sequence. On the
other, it is well fitted by the metal poor
![]() reference curve (short-dashed line). Therefore, adopting this
value, the fit yields colour excesses
reference curve (short-dashed line). Therefore, adopting this
value, the fit yields colour excesses
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
The internal precision and accuracy of our photometry
[see][]Moitinho2001a leaves us confident of the
moderately metal poor nature assigned to the cluster. The best
simultaneous fits in all the CMDs (Figs. 3-5) were obtained for 250
and 320 Myr isochrones (log(t) = 8.4-8.5 and
![]() )
at
)
at
![]() ,
corresponding to a distance of
,
corresponding to a distance of
![]() kpc after correcting for visual absorption. This
makes Czernik 29 not only metal poor but also relatively young. We
draw attention to star #18. It is well fitted by the red giant
loop in the V vs. B-V CMD and is in the giant region of the
TCD, making it a possible cluster giant.
kpc after correcting for visual absorption. This
makes Czernik 29 not only metal poor but also relatively young. We
draw attention to star #18. It is well fitted by the red giant
loop in the V vs. B-V CMD and is in the giant region of the
TCD, making it a possible cluster giant.
The main sequence of Czernik 29 does not shows the broadening seen in Haffner 10 even though their separation is small. However, we note that the field of Haffner 10 is somewhat larger and that variations in the field close to the crossing of two spiral arms are expected.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f7.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg46.png)
|
Figure 7: Left: enlargement of the upper middle panel, U-B/B-V, in Fig. 6. Right: enlargement of the lower middle panel, V/B-VCMD, from Fig. 6. Some relevant stars are pointed out for a simultaneous judgement of their positions in both diagrams. Symbols and lines have the same meaning as in Fig. 6. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
As previously mentioned, Pietrukowicz et al. (2006) performed a BVI study of Haffner 10 and Czernik 29. In the case of Haffner 10, our values of EB-V, abundance, and age agree with theirs and our distance determination is not far from their distance lower limit. Regarding Czernik 29, the analysis of Pietrukowicz et al. (2006) casts some doubt on its reality as a cluster and except for angular size, no other parameter is determined. The analysis (and deeper photometry) presented here confirms that Czernik 29 is a real cluster. Yet, the large difference in distances and the different metal content of Haffner 10 and Czernik 29 exclude their physical association. They are simply randomly aligned.
4.2 Haffner 18 and Haffner 19
Haffner 18 and Haffner 19, as the previous clusters, are located in Puppis and form part of the most complex spatial structure analysed in this article. The interaction between stars and gas, the abrupt change of visual absorption (due to the Puppis window) and the proximity to the nearby emission nebulosity associated to NGC 2467 create a confusing panorama. Far and nearby stellar groups with low and high extinction call into question membership assignments (see Moreno-Corral et al. 2005, for further discussion) and parameter determinations. The strong and variable presence of dust is clearly seen in the maps of Schlegel et al. (1998).
To the best of our knowledge, the most detailed attempt to explain
these two clusters is that of FitzGerald & Moffat (1974). From their
analysis of photoelectric and photographic ![]() photometry and
spectral types they found that Haffner 18 and Haffner 19 are young
and situate both clusters at a similar distance of about 6.9 kpc
(allowing for an error of almost 1 kpc). Furthermore,
FitzGerald & Moffat (1974) argue that at such a distance both clusters
should be part of what they called the 15 kpc spiral arm, now
identified as the Norma-Cygnus arm.
photometry and
spectral types they found that Haffner 18 and Haffner 19 are young
and situate both clusters at a similar distance of about 6.9 kpc
(allowing for an error of almost 1 kpc). Furthermore,
FitzGerald & Moffat (1974) argue that at such a distance both clusters
should be part of what they called the 15 kpc spiral arm, now
identified as the Norma-Cygnus arm.
Munari & Carraro (1996) carried out ![]() CCD photometry in the
field of Haffner 19 and spectroscopy of four bright stars in the
field. They measured a variable colour excess, spanning
approximately 0.5 mag, with a mean value of
E(B-V)= 0.44 and
derived a distance of 5.1 kpc. Moreno-Corral et al. (2002) acquired
CCD photometry in the
field of Haffner 19 and spectroscopy of four bright stars in the
field. They measured a variable colour excess, spanning
approximately 0.5 mag, with a mean value of
E(B-V)= 0.44 and
derived a distance of 5.1 kpc. Moreno-Corral et al. (2002) acquired
![]() and
and ![]() photometry in the region of Haffner 19
and confirmed the distance reported by Munari & Carraro (1996).
photometry in the region of Haffner 19
and confirmed the distance reported by Munari & Carraro (1996).
Munari et al. (1998) obtained spectroscopy of 7 stars and
![]() CCD photometry of the field of Haffner 18, deriving a
mean colour excess
E(B-V) = 0.62, an age of
CCD photometry of the field of Haffner 18, deriving a
mean colour excess
E(B-V) = 0.62, an age of
![]() yr
and a distance of 6.3 kpc from the Sun. Moreno-Corral et al. (2005)
reported spectral classification for some tens of stars in the
field of Haffner 18 and located this object at a distance of
d=8.4 kpc with an error of 1.2 kpc. Such differences in the
parameters derived for the same object and using similar
techniques illustrate the complexity of the analysis and highlight
the need for deeper observations.
yr
and a distance of 6.3 kpc from the Sun. Moreno-Corral et al. (2005)
reported spectral classification for some tens of stars in the
field of Haffner 18 and located this object at a distance of
d=8.4 kpc with an error of 1.2 kpc. Such differences in the
parameters derived for the same object and using similar
techniques illustrate the complexity of the analysis and highlight
the need for deeper observations.
Figure 6, left upper and lower panels, depicts the
overall TCD and CMD of the entire Haffner 18 and 19 area surveyed
in this work. The TCD shows a large number of non-uniformly
reddened blue bright OB stars, as expected from the presence of a
strong emission complex [probably belonging to the Puppis OB2
association (Havlen 1972)] and dust clouds in this Galactic
location. In addition, the bulk of the stars appear as a dense
clump within the colour ranges
-0.1< U-B< 0.4 and
0.5 < B-V <
1.0. The overall CMD shows two clear star sequences well
separated for magnitudes brighter than
![]() .
.
Besides our photometry we also make use of available spectral types of stars in the field of Haffner 18/19. The spectral classifications and their sources are listed in Table 2.
4.2.1 Haffner 18
The TCD and CMD of the Haffner 18 area (upper and lower middle panels in Fig. 6) display two well defined stellar groups. The TCD shows both groups being affected by distinctive amounts of reddening, resulting in an unambiguous identification of their members.
The less reddened sequence (filled squares) in the TCD and CMD is
mainly defined by stars with (photometric) types later than B3.
The sequence can be followed down to A-F-types, which corresponds
to B-V < 0.5 and
![]() .
We will refer to this group as
Haffner 18(1). The best superposition of the SKZ was achieved for
a mean colour excess
.
We will refer to this group as
Haffner 18(1). The best superposition of the SKZ was achieved for
a mean colour excess
![]() ,
with a little
dispersion around the mean. Both the V/B-V CMD in
Fig. 6, as well as the V/V-I CMD in Fig. 8, show
a broadening of the upper part of this group that may be due to
unresolved visual pairs. For a better interpretation of our
assertions, we show in Fig. 7 an enlargement of the TCD and CMD of
Haffner 18 area, where several stars labeled in our id system
allow the reader to verify the coherence between their positions
in the TCD and CMD.
,
with a little
dispersion around the mean. Both the V/B-V CMD in
Fig. 6, as well as the V/V-I CMD in Fig. 8, show
a broadening of the upper part of this group that may be due to
unresolved visual pairs. For a better interpretation of our
assertions, we show in Fig. 7 an enlargement of the TCD and CMD of
Haffner 18 area, where several stars labeled in our id system
allow the reader to verify the coherence between their positions
in the TCD and CMD.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{11583f8.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg52.png)
|
Figure 8: Left and right upper panels show the V/V-I CMD for Haffner 18 area [Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2)], and Haffner 19 respectively. Symbols and lines have the same meaning as in Fig. 6. Grey lines are the best pre-main sequence fitting from Siess et al. (2000). Left and right lower panels are the respective TCDs, B-V/V-I. Symbols have the same meaning as in Fig. 6. Solid lines as in Fig. 4. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The second stellar group, which we call Haffner 18(2), is clearly
separated from the first one. Open squares are used to indicate
its most discernible elements. Haffner 18(2) is mostly composed of
very reddened blue stars that can be traced down to approximately
the locus of B3 stars. Afterwards, they merge into the stellar
background (also mixing with components of Haffner 18(1))
precluding further analysis. In agreement with earlier works,
differential reddening is strong, ranging from
![]() to 1.0. Except for a few of the stars,
E(B-V)= 0.60is the colour excess of the front-line stars composing this group.
This colour excess and range are similar to the ones derived by
Munari et al. (1998). As with the previous group, some of the
Haffner 18(2) have published spectral types.
to 1.0. Except for a few of the stars,
E(B-V)= 0.60is the colour excess of the front-line stars composing this group.
This colour excess and range are similar to the ones derived by
Munari et al. (1998). As with the previous group, some of the
Haffner 18(2) have published spectral types.
Moreno-Corral et al. (2005) affirm that the extinction law in the direction to Haffner 18 could be assumed to be normal but that NIR photometry would help to settle the issue. The V-I vs. B-Vdiagrams of both sequences are shown in the lower panels of Fig. 8. The diagram suggests that the extinction law may vary from the normal R = 3.1 value to the anomalous value of R = 3.7(dashed line). Similarly to other regions with anomalous extinction laws (eg. Trumpler 16 or Trumpler 14 Vazquez et al. 1996), we find stars belonging to both groups and to the field affected by normal and anomalous extinction, as if some of them were strongly affected by the denser interstellar medium while others were not. For some sources, the anomalies will be the result of circum-stellar envelopes, as is the case of star FM3060a -No 14 in our notation- which is surrounded by a ionized hydrogen veil (Moreno-Corral et al. 2005). For others, it will be a result of the recent star forming dust unevenly distributed along the line-of-sight to the region. Despite the evidence of stars affected by anomalous extinction, they are a small fraction. In general terms, reddening toward most stars in the region is characterised by the normal value R=3.1.
Adopting R=3.1 and
E(B-V)=0.30, the SKZ CMD fit of
Haffner 18(1) yields a distance modulus of
![]() ,
which corresponds to a distance of
,
which corresponds to a distance of
![]() kpc, after
correcting for absorption. The solar composition isochrones
(dashed lines) indicate a cluster age between 160 and 200 Myr
(log(t) = 8.2-8.3).
kpc, after
correcting for absorption. The solar composition isochrones
(dashed lines) indicate a cluster age between 160 and 200 Myr
(log(t) = 8.2-8.3).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6cm,clip]{11583f9.eps}
\vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg56.png)
|
Figure 9: The V/U-B CMD of Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2); long-dashed lines represent the best isochrone [log (t)] fittings. Grey lines are the solar content pre-main sequence isochrones of 4 ( upper) and 5 ( lower) Myr from Siess et al. (2000). Symbols as in Fig. 6. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Again, R = 3.1 was adopted for Haffner 18(2) and a colour excess E(B-V)=0.68 was deemed representative of the group's reddening. Variable extinction and the youth of the cluster (it contains many early type stars) produce a nearly vertical and fuzzy sequence in the CMD which results in higher than usual ZAMS fitting errors. Therefore, the distance modulus is in the range 17.0 < V-MV < 17.40 corresponding to a distance from 9.5 to 11.4 kpc from the Sun. The isochrones best describing the cluster sequence point to an age near 4 Myr (log(t) = 6.6-6.7) which is of the same order as the age reported by Munari et al. (1998). Given the strong internal reddening and the usual change in effective wavelength of the U filter for increasing absorption, the fitting in the V/U-B is not as good as seen in the other CMDs (V/B-V, V/V-I) of Haffner 18(2). However, the fitting goodness in these latter planes secures us a good distance estimate.
Despite this, it is illustrative to see how U-B separates stars of different temperatures as shown in Fig. 9. Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2) appear remarkably well defined and detached from each other. The stars above the isochrone of Haffner 18(2) likely include pre-main sequence objects (PMS; expected at this age) and MS stars scattered by intracluster reddening and by the presence of unresolved sources.
The colour excess range for Haffner 18(2) from
0.60 < E(B-V)<
1.0 implies a mean visual absorption of
![]() to
to
![]() mag, quite low for an object located in the distance
range 9.5 to 11.4 kpc along the Galactic plane as shown by the bar
joining the two points (see Fig. 15). As discussed in
Sect. 5 this is
consistent with the fact that the
HI layer is not coincident with the formal,
mag, quite low for an object located in the distance
range 9.5 to 11.4 kpc along the Galactic plane as shown by the bar
joining the two points (see Fig. 15). As discussed in
Sect. 5 this is
consistent with the fact that the
HI layer is not coincident with the formal,
![]() ,
Galactic plane.
,
Galactic plane.
Table 2: Spectral types of stars in Haffer 18/19.
4.2.2 Some stars in the field of Haffner 18
A simple inspection of spectral types in Table 2 shows that one spectral sub-type and/or one luminosity class is a normal difference when comparing observations from different authors for the same star. This is in addition to the internal uncertainty stated by the symbol ``:'' given by a single researcher. A few stars in Table 2 deserve some words:
- # 14: It has been classified B1Vk, O9.5V or B0.5III (see Table 2)
and is surrounded by a compact veil of H
 emission
(Moreno-Corral et al. 2005). Like Moreno-Corral et al. (2005) we agree that this is
a clear sign of a very young object, consistent with the age of
Haffner 18(2). This veil affects its colour indices and moves the
stars ``leftward'' in the U-B/B-V plane as if it had
E(B-V)
= 0.45. If we remove this value from the observed B-V=0.14 and
V= 11.94 we get
(B-V)0 = -0.31, consistent with any of its
possible spectral types. Accepting a very anomalous R-value of
4.5, the above mentioned reddening and assuming a mean absolute
magnitude MV=-5 (in view of its spectral type uncertainty), its
distance from the Sun is about 9.5 kpc in agreement with the
distance range of Haffner 18(2). The conclusions do not change if
we adopt
E(B-V) = 0.68 and R=3.1.
emission
(Moreno-Corral et al. 2005). Like Moreno-Corral et al. (2005) we agree that this is
a clear sign of a very young object, consistent with the age of
Haffner 18(2). This veil affects its colour indices and moves the
stars ``leftward'' in the U-B/B-V plane as if it had
E(B-V)
= 0.45. If we remove this value from the observed B-V=0.14 and
V= 11.94 we get
(B-V)0 = -0.31, consistent with any of its
possible spectral types. Accepting a very anomalous R-value of
4.5, the above mentioned reddening and assuming a mean absolute
magnitude MV=-5 (in view of its spectral type uncertainty), its
distance from the Sun is about 9.5 kpc in agreement with the
distance range of Haffner 18(2). The conclusions do not change if
we adopt
E(B-V) = 0.68 and R=3.1.
- # 28: In Fig. 7 this star (A4V) is not associated with any of the clusters. It is thus a field star.
- # 375: This star has been classified as B3V. However, the colours
are not consistent with this classification but indicate a later
type (
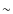 B6). Given its location and reddening in the TCD, it
is a field star not related to the clusters.
B6). Given its location and reddening in the TCD, it
is a field star not related to the clusters.
- #136: According to Moreno-Corral et al. (2005) it is a B1V star. A photometric spectral type b1 was given by FM74. However, the position in the U-B/B-V plane is not entirely consistent with the spectral classification. Our photometry gives B-V = 1.09 and U-B = 0.66 that, after excess removal, E(B-V) = 0.30 [if it were in the Haffner 18(1) field] or 0.6 [if it were in Haffner 18(2)] becoming (B-V)0=0.79, (U-B)0=0.40 or (B-V)0= 0.49 and (U-B)0=-0.05, respectively. Neither solution corresponds to a B1V-type star. The photoelectric U-B photometry from FM 74 and ours differs by more than 0.6 mag and by 0.05 and 0.07 in B-V and V respectively. Munari et al. (1998) photometry did not measure the U-B index but for the rest of indices, B-V, V-R, V-I and V, the differences are always below 0.07. We assume that the nearby star 3067 (an O8V-type star) and the small aperture telescope used by FM74 (the 61cm at La Silla) may have contributed to contaminating the U-B index. From the position in the TCD, where it looks like a late type star, and the CMD where it is as bright as some other less reddened young objects in Haffner 18(2), we conclude that the spectral type is probably wrong and it is a foreground object.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f10.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg60.png)
|
Figure 10: Upper panels show the TCDs for the entire region ( left), NGC 2383 ( middle) and NGC 2384 ( right). The SKZ is shown in its normal position and shifted to fit the respective cluster sequences. The colour excess relations for O3-, B3-, B6- and A0-type stars are indicated. Lower panels indicate the correspondent CMDs; long-dashed lines show two isochrone [log (t)] fittings from G00 at Z= 0.008 for NGC 2383 and at solar metal content in NGC 2384. Some stars in both clusters are pointed out using our notation -see text. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
4.2.3 Haffner 19
For Haffner 19 (Fig. 6, right upper and lower panels for the TCD and CMD respectively), only one group of moderately reddened blue stars is noticed in the area. Only a few bright interlopers are present within the established cluster limits.
Although simpler than in the case of Haffner 18, the CMDs (lower
panel of Fig. 6, and upper right panel of Fig. 8)
easily can be incorrectly interpreted. For example, the brightest
stars in these diagrams are not cluster members. Indeed, stars 22
and 23 may be part of Haffner 19 while stars 2, 4, 33 and 24 are
field stars. The same applies to stars 53, 60 and 61. Taking
special care with the memberships, the SKZ fits yield a colour
excess
![]() and a distance modulus of
and a distance modulus of
![]() ,
corresponding to a distance of
,
corresponding to a distance of
![]() kpc
after correction for visual absorption. This distance is within
the limits given by FitzGerald & Moffat (1974). It is however 1 kpc
closer than the distances obtained by Moreno-Corral et al. (2002) and
Munari & Carraro (1996). As with most very young clusters, the age is
not well constrained by post-MS isochrones. Taking into account
the lack of any evolved members and the consistency of the
isochrone fit (plotted in all CMDs), an age of 4 Myr (log(t)=
6.6-6.7) is estimated.
kpc
after correction for visual absorption. This distance is within
the limits given by FitzGerald & Moffat (1974). It is however 1 kpc
closer than the distances obtained by Moreno-Corral et al. (2002) and
Munari & Carraro (1996). As with most very young clusters, the age is
not well constrained by post-MS isochrones. Taking into account
the lack of any evolved members and the consistency of the
isochrone fit (plotted in all CMDs), an age of 4 Myr (log(t)=
6.6-6.7) is estimated.
Another relevant feature in Haffner 19 is the absence of main
sequence stars fainter than
![]() .
Given the youth of the
cluster, it is interpreted as being due to lower mass members
being on the PMS phase. The absolute magnitude at which the MS
ends,
.
Given the youth of the
cluster, it is interpreted as being due to lower mass members
being on the PMS phase. The absolute magnitude at which the MS
ends,
![]() ,
corresponds to early A-type stars, which is
consistent with the estimated age for the cluster. Scaled to the
reddening and distance modulus, pre-main sequence isochrones of 4
and 5 Myr, from Siess et al. (2000), have been superimposed in the
B/B-V and V/V-I planes showing good agreement with the nuclear
age derived from Girardi et al. (2000). Later type cluster
members are thus redder and brighter than their ZAMS counterparts
and are hidden among the field stars in the CMDs. The faint end of
the MS is seen in both CMDs, although much more clearly in the
V/V-I plane (see Lyra et al. 2006, for a detailed comparison of the use of
different colour-magnitude combinations in PMS
characterisation). Given the youth of the cluster with
objects in the contraction phase it is expected that we will
detect anomalies in the extinction law as seen in Fig. 8 (lower
panel).
,
corresponds to early A-type stars, which is
consistent with the estimated age for the cluster. Scaled to the
reddening and distance modulus, pre-main sequence isochrones of 4
and 5 Myr, from Siess et al. (2000), have been superimposed in the
B/B-V and V/V-I planes showing good agreement with the nuclear
age derived from Girardi et al. (2000). Later type cluster
members are thus redder and brighter than their ZAMS counterparts
and are hidden among the field stars in the CMDs. The faint end of
the MS is seen in both CMDs, although much more clearly in the
V/V-I plane (see Lyra et al. 2006, for a detailed comparison of the use of
different colour-magnitude combinations in PMS
characterisation). Given the youth of the cluster with
objects in the contraction phase it is expected that we will
detect anomalies in the extinction law as seen in Fig. 8 (lower
panel).
4.2.4 Haffner 18ab and Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2)
FitzGerald & Moffat (1974) consider Haffner 18 as an elongated stellar
structure, almost parallel to the galactic plane, composed of two
adjacent and indistinguishable clusters which they label Haffner
18a and Haffner 18b. However, they suggest caution by saying that
their data did not allow then to decide whether absorbing dust
clouds could be responsible for this peculiar elongated
morphology. The contour map shown in Fig. 2 reveals a more
spherical structure only detectable when all stars down to ![]() are taken into account, thus indicating that the influence of
dust clouds is important amongst the faintest objects. Our
photometry reveals two groups superposed along the line of sight.
However, contrarily to FitzGerald & Moffat (1974), we find them to be
at different distances. The closest one, Haffner 18(1), is less
concentrated than the farther Haffner 18(2).
are taken into account, thus indicating that the influence of
dust clouds is important amongst the faintest objects. Our
photometry reveals two groups superposed along the line of sight.
However, contrarily to FitzGerald & Moffat (1974), we find them to be
at different distances. The closest one, Haffner 18(1), is less
concentrated than the farther Haffner 18(2).
4.3 NGC 2383 and NGC 2384
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=11cm,clip]{11583f11.eps}
\vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg66.png)
|
Figure 11: Left: enlargement of the TCD of Fig. 10 The SKZ and the mean intrinsic line for Z = 0.008 from G00 (short-dashed). The colour excess relations as in Fig. 3. Right: long-dashed lines depict the two isochrone [log (t)] fittings at Z = 0.008 in the V/U-B CMD. Grey-solid line is the SKZ fitted to the distance modulus of NGC 2384 (see text). Stars -our notation- discussed in the text are pointed out. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
These objects belong to the constellation of Canis Major at the
extreme of an elephant trunk-like structure in the maps of
Schlegel et al. (1998). NGC 2383 is a compact cluster as seen in
Fig. 1. Approximately 6' southeast, a handful
of bright blue stars appear as a cigar-shaped structure that has
been historically identified as the open cluster NGC 2384 (see
Fig. 1). Both objects were observed by
Vogt & Moffat (1972) who found them to be separated by more than 1 kpc
thus excluding their physical association and later
FitzGerald et al. (1979) performed spectral classification for ten
star in the fields of both clusters. Subramaniam & Sagar (1999)
obtained ![]() photometry and spectroscopy of both clusters
finding that they are very close, only 9 pc from each other. They
did however discard a common origin based on the very different
ages estimated for both aggregates.
photometry and spectroscopy of both clusters
finding that they are very close, only 9 pc from each other. They
did however discard a common origin based on the very different
ages estimated for both aggregates.
The global TCD and CMD of the surveyed region (upper and lower left panels respectively in Fig. 10) show the presence of a sequence comprising very blue hot stars with U-B < 0.5 and B-V < 0.54. The bulk of the stellar distribution is noticeable as a clump in the TCD within 0.5 < B-V < 1.3 and 0.0 < U-B < 0.5. Its counterpart in the CMD is represented by the notorious stellar distribution that broadens at V > 16.
The density contour plot (Fig. 2) only reveals the presence of NGC 2383. In all trials using different kernel sizes, NGC 2384 always appeared as a marginal handful of bright and hot stars without a faint counterpart adding to the stellar density. As discussed in Sect. 3.1, further analysis assumes that NGC 2384 is contained within a circle comprising the bright stars. The TCDs and CMDs of NGC 2383 and NGC 2384 are shown in Fig. 10 (middle and right panels, respectively).
4.3.1 NGC 2383
The sequence of NGC 2383 is very well defined in the photometric
diagrams (Fig. 10 middle panels). At a first
glance, one is tempted to consider the few dispersed hot B-type
stars with U-B < 0.0 as members of NGC 2383. However, the
cluster is only seen from late B- and A-type stars with U-B >
0.0 to later types. The TCD of the cluster members is
characterised by a slight internal scatter that broadens the
sequence and is identifiable down to
![]() .
In the
CMD, NGC 2383 is well detached from the field exhibiting a tight
sequence from
.
In the
CMD, NGC 2383 is well detached from the field exhibiting a tight
sequence from
![]() .
The few hot B-type stars
with U-B < 0.0 that could be taken as members of NGC 2383 in the
TCD are all above V = 14 and are not related to the cluster.
Some of these stars (labelled in our figures) are hot according to
their location in the TCD, but too faint in the CMD, suggesting no
connection with NGC 2383: they are stars 33, 42, 57, 62 and 78 to
which we return later.
.
The few hot B-type stars
with U-B < 0.0 that could be taken as members of NGC 2383 in the
TCD are all above V = 14 and are not related to the cluster.
Some of these stars (labelled in our figures) are hot according to
their location in the TCD, but too faint in the CMD, suggesting no
connection with NGC 2383: they are stars 33, 42, 57, 62 and 78 to
which we return later.
We notice that the SKZ does not fit well all the stars of NGC 2383
in the TCD. Indeed, as seen in Fig. 10 - upper
middle panel -, as in the case of Czernik 29, a close inspection
reveals that the solar SKZ does not follow the A-F-type stellar
sequence, which appears to be metal deficient. The G00 relation
with metallicity
![]() produces a much better match to
the data for
produces a much better match to
the data for
![]() as shown in the left panel
of Fig. 11. In the right panel of
Fig. 11, some stars are indicated for the reader�s
guidance: Nos. 22, 25, 30, 47, 48, 45 and 51 belong to the upper
main sequence of NGC 2383 whereas Nos. 4, 5, 44, 49, 77 and 82 are
obvious field stars. It is interesting to note that stars 33, 42,
57, 62 and 78 do not follow the cluster isochrones and may have no
relation to NGC 2383. Star 33, in particular, was given a spectral
type of A3V by Subramaniam & Sagar (1999), although we note that its
observed colours suggest an earlier spectral type of around B3.
as shown in the left panel
of Fig. 11. In the right panel of
Fig. 11, some stars are indicated for the reader�s
guidance: Nos. 22, 25, 30, 47, 48, 45 and 51 belong to the upper
main sequence of NGC 2383 whereas Nos. 4, 5, 44, 49, 77 and 82 are
obvious field stars. It is interesting to note that stars 33, 42,
57, 62 and 78 do not follow the cluster isochrones and may have no
relation to NGC 2383. Star 33, in particular, was given a spectral
type of A3V by Subramaniam & Sagar (1999), although we note that its
observed colours suggest an earlier spectral type of around B3.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{11583f12.eps} \vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg71.png)
|
Figure 12: Upper and lower panels have the same meaning as in Figs. 4 and 8 for the indicated Z content. Lower panels as in Figs. 4 and 8. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Considering the V/B-V, the V/U-B and the V/V-I CMDs simultaneously (Figs. 10-12) we see that the cluster sequence is contaminated by a few interlopers, which only start introducing some spread in the stellar distribution for 15 > V.
As for the extinction law, Fig. 12, lower panel shows that with
the exception of a few stars with possible anomalous colours, it
is a completely R=3.1 law. Adopting a colour excess of
E(B-V)=0.30, the best simultaneous data fit in all the CMDs
yields
![]() ,
which corresponds to a distance
,
which corresponds to a distance
![]() kpc. The best isochrone matches indicate
a cluster age between 250 and 310 Myr (log(t) = 8.4-8.5). These
results agree with those of Subramaniam & Sagar (1999).
kpc. The best isochrone matches indicate
a cluster age between 250 and 310 Myr (log(t) = 8.4-8.5). These
results agree with those of Subramaniam & Sagar (1999).
4.3.2 NGC 2384
NGC 2384 is an peculiar object visible in the hot region of the TCD in Fig. 10 (upper right panel) and in the brightest region of the CMD in the same figure. The right panels of Fig. 12 show the V/V-I and the B-V/V-I diagrams of the cluster. All diagrams show that NGC 2384 is well defined in the bright sector.
As seen in the lower panel of Fig. 12, the absorption law does not
show any signs of anomaly. Adopting R = 3.1, the SKZ fit to
NGC 2384 yields
![]() ,
with no clues to the
cluster's metal content. The distance modulus is determined to be
,
with no clues to the
cluster's metal content. The distance modulus is determined to be
![]() ,
corresponding to a distance of
,
corresponding to a distance of
![]() kpc. The age is estimated to be between 12 and 16 Myr
(log(t) = 7.1-7.2), not far from the 20 Myr found by
Subramaniam & Sagar (1999).
kpc. The age is estimated to be between 12 and 16 Myr
(log(t) = 7.1-7.2), not far from the 20 Myr found by
Subramaniam & Sagar (1999).
As noticed in Sect. 3.2, the U-B index is useful
for separating different groups. Returning to the V/U-B CMD of
NGC 2383 in Fig. 11, we can re-interpret the nature
of the few hot stars seen in Fig. 10 (upper
panel) and which we have already seen are not connected to
NGC 2383. Indeed, as discussed in the previous section, the area
of NGC 2383 contains two different groups that separate from each
other for U-B < 0.0. The group defined by the broadened sequence
starting at
![]() is NGC 2383. The other, defined by
the hottest stars 33, 42, 57, 62 and 78, not only do not follow
the sequence of NGC 2383 but also coincide with the colour excess,
distance and age of the stars in NGC 2384. To test this idea we
have superposed in Fig. 11 (right panel) the SKZ
(grey solid line) corrected for the distance modulus and colour
excess of NGC 2384. The remarkably good fit achieved for the
bluest stars with U-B < 0.0 seen together with NGC 2383 members
indicates that stars belonging to/or connected with NGC 2384 are
distributed in a larger area including not only the south-east
side of NGC 2383 but also partially the region occupied by
NGC 2383 itself. Therefore, NGC 2384 appears thus as a sparse
group of bright stars projected against (and slightly closer than)
the older cluster NGC 2383. In the light of the results obtained
for the handful of stars composing NGC 2384 and summarising, this
cluster seems more like a sparse young remnant group of a recent
star formation episode in front of NGC 2383.
is NGC 2383. The other, defined by
the hottest stars 33, 42, 57, 62 and 78, not only do not follow
the sequence of NGC 2383 but also coincide with the colour excess,
distance and age of the stars in NGC 2384. To test this idea we
have superposed in Fig. 11 (right panel) the SKZ
(grey solid line) corrected for the distance modulus and colour
excess of NGC 2384. The remarkably good fit achieved for the
bluest stars with U-B < 0.0 seen together with NGC 2383 members
indicates that stars belonging to/or connected with NGC 2384 are
distributed in a larger area including not only the south-east
side of NGC 2383 but also partially the region occupied by
NGC 2383 itself. Therefore, NGC 2384 appears thus as a sparse
group of bright stars projected against (and slightly closer than)
the older cluster NGC 2383. In the light of the results obtained
for the handful of stars composing NGC 2384 and summarising, this
cluster seems more like a sparse young remnant group of a recent
star formation episode in front of NGC 2383.
Table 3: Spectral types in NGC 2383 and NGC 2384.
4.3.3 Some specific stars in both clusters
As mentioned earlier, Subramaniam & Sagar (1999) performed spectral classification of 6 stars in NGC 2383 (listed in Table 3). They concluded that star S1 (No. 5 in our notation) is of type A3I. Our photometry (see the TCD in Fig. 10) indicates it is of an early spectral type, more consistent with the B0III classification given by FitzGerald et al. (1979). Star S2 (4 in our notation) has been classified as A6III by Subramaniam & Sagar (1999) and A3V by FitzGerald et al. (1979). Our diagrams do not allow us to decide on its most probable luminosity class, only that it is related to NGC 2383.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f13.eps} \vspace*{-1.5mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg78.png)
|
Figure 13: Upper panels show the TCDs for the entire region ( left), Ruprecht 72 ( middle) and Ruprecht 158 ( right). The SKZ is shown in its normal position. The colour excess relations are indicated. Lower panels have the same meaning as in Figs. 3, 6 and 10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
A special case is that of star S8 (No 3 in our list, indicated in
Fig. 10, left panels). Following
Subramaniam & Sagar (1999), it is a background M1I supergiant. We
agree that this star is not a member of NGC 2383 but it becomes
interesting to analyse its location in the Galaxy: Adopting a mean
![]() for an M1I-type star and correcting its visual
magnitude, V=9.74, for the mean of the colour excesses of
NGC 2383,
E(B-V) = 0.30, the corrected distance modulus
V0-MV is between 13.51 and 14.50, corresponding to distances
from 5 to 8 kpc, which makes it a distant background object.
Unless the spectral classification from Subramaniam & Sagar (1999) is
wrong, this is a very young object that should not be far from its
birthplace, somewhere between the Perseus and Outer arms, as
discussed in Sect. 5.
for an M1I-type star and correcting its visual
magnitude, V=9.74, for the mean of the colour excesses of
NGC 2383,
E(B-V) = 0.30, the corrected distance modulus
V0-MV is between 13.51 and 14.50, corresponding to distances
from 5 to 8 kpc, which makes it a distant background object.
Unless the spectral classification from Subramaniam & Sagar (1999) is
wrong, this is a very young object that should not be far from its
birthplace, somewhere between the Perseus and Outer arms, as
discussed in Sect. 5.
4.4 Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158.
The last objects of our study are Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158, located in Puppis. Analysis of the star density (contour plots in Fig. 2) in the area of these supposed open clusters does not reveal any significant stellar enhancement. Visual inspection of the maps in Fig. 1, combined with the density study, suggest that these putative clusters result from a visual impression created by a slight random concentration of a few moderately bright field stars. Nevertheless, an investigation of the parameters listed in the Dias et al. (2002) catalogue was carried out by adopting several radii around the reported cluster centres.
Figure 13 shows the TCD and CMD of the entire field
(upper and lower left panels, respectively). It is a typical
diagram of a moderately high latitude field containing a
significant population of dwarf stars across a range of
metallicity together with traces of a moderately young population.
This last population is easily seen at 0.6 < B-V where a knee of
late B- and A-type stars appears. Most of these stars are of
average brightness and appear mostly above ![]() .
Still,
some of them can be tracked down to the faintest magnitudes,
indicating that a moderately young population is intercepted all
along the line of sight.
.
Still,
some of them can be tracked down to the faintest magnitudes,
indicating that a moderately young population is intercepted all
along the line of sight.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{11583f14.eps} \vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg81.png)
|
Figure 14: Upper and lower panels as in Figs. 4, 8 and 12. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
If TCDs and CMDs for Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158 (Fig. 13, middle
and right panels, respectively) are built assuming a common
radius, e.g., 2.5![]() around the centres given in the
Dias et al. (2002) catalogue, we obtain sparse diagrams
resembling those in the left panels representing the total
surveyed area. Again, the V/V-I CMDs in the upper panels of
Fig. 14 are almost identical. The extinction law checked in the
B-V/V-I diagrams, lower panels in Fig. 14, confirms its
normality as asserted in Moitinho2001a.
around the centres given in the
Dias et al. (2002) catalogue, we obtain sparse diagrams
resembling those in the left panels representing the total
surveyed area. Again, the V/V-I CMDs in the upper panels of
Fig. 14 are almost identical. The extinction law checked in the
B-V/V-I diagrams, lower panels in Fig. 14, confirms its
normality as asserted in Moitinho2001a.
5 The clusters and spiral structure
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{11583f15.eps}\vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg82.png)
|
Figure 15:
Upper panel: the X-Y plane with the Sun at 0,0. Open
squares are CO clouds (the largest mean the most massive clouds)
in units of 105 |
| Open with DEXTER | |
We will now see how the studied clusters fit in the Galactic
context. Figure 15, upper panel, is an X-Y projection of
the Galactic plane (X-axis is negative towards
![]() and the Y-axis is positive towards the Galaxy anti-centre). The
Outer and Perseus arms from Vallée (2005) are drawn for the
reader's guidance. In order to compare cluster locations with
those of potential star formation complexes, CO clouds (open
squares) with masses higher than
and the Y-axis is positive towards the Galaxy anti-centre). The
Outer and Perseus arms from Vallée (2005) are drawn for the
reader's guidance. In order to compare cluster locations with
those of potential star formation complexes, CO clouds (open
squares) with masses higher than
![]()
![]() (May et al. 2008,1997) have been plotted.
(May et al. 2008,1997) have been plotted.
Only three clusters have ages that enable them to be potential arm tracers. They are Haffner 18(2), at less than 10 Myr it is a secure component of the Outer arm; NGC 2384, around 15 Myr is at the intersection of the Local arm with Perseus, while Haffner 19, 4 Myr, could be part of the Local arm beyond the crossing of the Perseus arm. The other older clusters, Haffner 18(1), NGC 2383 and Czernik 29 have ages that suggest they are not too far from their birthplaces. In particular, Haffner 18(1) is not far beyond Perseus and may be tracing the Local arm extension out in the Third Galactic Quadrant. Haffner 10 is seen at the position of Perseus but it is probably just passing across given its large age.
The metallicities of NGC 2383 and Czernik 29, Z = 0.008 and Z = 0.004,
respectively, their similar ages (from 250 to 300 Myr) and
distances (
![]() kpc) indicate a relatively recent star
formation event in the last 300 Myr and that this process took
place in a less metallic and localised environment. These metallic
abundances agree with the expected [Fe/H] at such a distance,
i.e.,
kpc) indicate a relatively recent star
formation event in the last 300 Myr and that this process took
place in a less metallic and localised environment. These metallic
abundances agree with the expected [Fe/H] at such a distance,
i.e.,
![]() dex to
dex to
![]() dex and
this puts these two clusters on the plateau already devised
through analysis of other objects such as isolated hot stars
(Cayrel de Strobel et al. 1997; Daflon & Cunha 2004), planetary nebula
(Costa et al. 2004), Cepheids (Fry & Carney 1997), etc., though more
limited in distance. We cannot argue against or in favour of the
existence of a radial metallicity gradient (see Koen & Lombard 2007; Chen et al. 2003).
dex and
this puts these two clusters on the plateau already devised
through analysis of other objects such as isolated hot stars
(Cayrel de Strobel et al. 1997; Daflon & Cunha 2004), planetary nebula
(Costa et al. 2004), Cepheids (Fry & Carney 1997), etc., though more
limited in distance. We cannot argue against or in favour of the
existence of a radial metallicity gradient (see Koen & Lombard 2007; Chen et al. 2003).
Figure 15 also indicates the probable location of the S8
star (No. 3 in our notation) according to the findings of
Sect. 4.3.3. Whatever the true distance
(based on the single spectral classification estimate
from Subramaniam & Sagar 1999), this is a young star which, at both
estimated distance limits, is close to CO cloud complexes (that
is, between the innermost part of the Outer arm and the outermost
part of the Perseus arm). It is also possible that S8 is a member
of the extension of the Local arm outward the Third Galactic
Quadrant, after its crossing of Perseus. It is remarkable that S8
suffers so little absorption (
![]() )
at such a
large distance. Inspecting the maps of Schlegel et al. (1998),
NGC 2383 and NGC 2384 are both located near a vast hole in the
dust distribution which facilitates observation of distant objects
like this star. Such low reddening is also measured toward
Haffner 18(2), at
)
at such a
large distance. Inspecting the maps of Schlegel et al. (1998),
NGC 2383 and NGC 2384 are both located near a vast hole in the
dust distribution which facilitates observation of distant objects
like this star. Such low reddening is also measured toward
Haffner 18(2), at ![]() 11 kpc, although Haffner 18(2) is almost
coincident with the formal Galactic plane and S8 is below it.
11 kpc, although Haffner 18(2) is almost
coincident with the formal Galactic plane and S8 is below it.
Regarding the clusters, only Haffner 18(2) is a plausible member
of the Outer arm. According to its Z-height, it is on the northern
rim of the HI layer of the Galactic plane: In fact, when looking
at Figs. 3, 4 and 9 of Voskes & Burton (2006), the HI layer at 14 and
16 kpc from the Galactic centre shows evidence of the warp down to
1.5 kpc below the formal Galactic plane and that the northern part
of the layer tends to be located at
![]() .
The warp
could thus partially explain the low visual absorption toward
Haffner 18(2) in spite of its distance.
.
The warp
could thus partially explain the low visual absorption toward
Haffner 18(2) in spite of its distance.
6 Comments and conclusions
Table 4: Results obtained for the eight clusters.
The photometric data analysed in this work have allowed us to
characterise the observed clusters and to assess their alleged
binary nature. Cluster reddenings, distances, ages and in a few
cases metallicities were determined and are listed in
Table 4. We find that parameters of stellar
systems of the type studied here are more reliable when, besides
![]() photometry, U measurements are also available. In
particular, U data provide a check of spectral classification
and criteria for efficiently separating field from cluster stars.
photometry, U measurements are also available. In
particular, U data provide a check of spectral classification
and criteria for efficiently separating field from cluster stars.
Summarising the main results of this investigation:
- a)
- Czernik 29 and Haffner 10 are not a cluster pair in the sense that they do not have a common origin. Analysis of the photometric diagrams has shown that the two objects have different metallicities and ages, ruling out such a possibility.
- b)
- Haffner 18 and Haffner 19 belong to an extraordinarily complex stellar structure where several young star groups are seen along the line of sight. Our deep photometry has allowed us to disentangle two groups in the direction of Haffner 18 naming the nearest one Haffner 18(1), and the farther one Haffner 18(2). They differ in ages and distances: Haffner 18(1) is located at 4.5 kpc and is characterised by a reddening excess E(B-V) = 0.30. Haffner 18(2) at a larger distance, between 9.5 and 11.4 kpc from the Sun, is composed of young stars. Haffner 19 is relatively far from Haffner 18(1), more than 1.5 kpc away, though affected by similar reddening. This fact and the very different ages precludes a common origin.
- c)
- NGC 2383 and NGC 2384 do not seem to form a pair either. Both
groups have similar reddenings and distances but quite different
ages. It was found that NGC 2383 is considerably metal-poor with
 .
No traces of a density enhancement of faint stars
were detected around NGC 2384. Apparently, NGC 2384 is some kind
appendix of a dispersed young stellar structure slightly closer
than NGC 2383.
.
No traces of a density enhancement of faint stars
were detected around NGC 2384. Apparently, NGC 2384 is some kind
appendix of a dispersed young stellar structure slightly closer
than NGC 2383.
- d)
- Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158 are not clusters but slight random
fluctuations of the field stellar density.
Of the 5 optically visible double cluster candidates in this region of the Galaxy, we have analysed 4. For one, it has been found that its components were not clusters at all. None of the analysed pairs has qualified as a binary cluster, indicating that, as opposed to the LMC, these systems are rare in the outskirts of the Galaxy. This could mean that:
- a)
- Double cluster lifetimes are short. No significant active star forming regions are seen presently in this sector of the Galaxy, meaning that statistically they would have already decoupled or merged. However, this hypothesis does not seem to be supported by the small number of candidate pairs, 2, within the known embedded clusters in the same sector of the Galaxy.
- b)
- Double clusters form preferentially in environments different to that of the 3GQ, closer to the environment of the LMC. In that sense, it would be relevant to evaluate the frequency of binary clusters toward denser and more violent regions of the Milky Way, such as the inner Galaxy.
R.A.V. wishes to acknowledge the financial support from the IALP (UNLP-CONICET, Argentina) and the PIP No. 5970 from CONICET. A.M. acknowledges support from F.C.T. (Portugal) through grant POCI/CTE-AST/57128/2004. A.M. and R.A.V. also acknowledge support from the ESO Visiting Astronomer Programme. The authors are grateful for useful suggestions from an anonymous referee that improved the article.
References
- Aarseth, S. J. 1996, in The Origins, Evolution, and Destinies of Binary Stars in Clusters, ed. E. F. Milone, & J.-C. Mermilliod, ASP Conf. Ser., 90, 423 [Google Scholar]
- Baume, G., Moitinho, A., Giorgi, E. E., Carraro, G., & Vázquez, R. A. 2004, A&A, 417, 961 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Baume, G., Moitinho, A., Vázquez, R. A. et al. 2006, MNRAS, 367, 1441 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, R. K. 1990, PASJ, 42, 757 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Bica, E., Dutra, C. M., & Barbuy, B. 2003, A&A, 397, 177 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Blaauw, A. 1963, Baltical Astronomical Data, Univ. of Chicago, 383 [Google Scholar]
- Carraro, G., Vázquez, R. A., Moitinho, A., & Baume, G. 2005, ApJ, 630, L153 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Carraro, G., Vázquez, R. A., & Moitinho, A. 2008, A&A, 482, 777 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Cayrel de Strobel, G., Soubiran, C., Friel, E. D., Ralite, N., & Francois, P. 1997, A&AS, 124, 299 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L., Hou, J. L., & Wang, J. J. 2003, AJ, 125, 1397 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Costa, R. D. D., Uchida, M. M. M., & Maciel, W. J. 2004, A&A, 423, 199 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins, A. W. J. 1978, MNSSA, 37, 62 [Google Scholar]
- Cutri, R. M., Skrutskie, M. F., van Dyk, S. et al. 2003, explanatory Supplement to the 2MASS All Sky Data Release [Google Scholar]
- Daflon, S., & Cunha, K. 2004, ApJ, 617, 1115 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- de La Fuente Marcos, R. 1997, A&A, 322, 764 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, M. R., Bica, E., & Dottori, H. 2000, MNRAS, 311, 589 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J. F., Warren, P. R., & Cousins, A. W. J. 1978, Dean, 183, 569 [Google Scholar]
- Dias, W. S., Alessi, B. S., Moitinho, A., & Lépine, J. R. D. 2002, A&A, 389, 871 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Dieball, A., & Grebel, E. K. 2000, A&A, 358, 897 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Dieball, A., Müller, H., & Grebel, E. K. 2002, A&A, 391, 547 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Dutra, C. M., Bica, E., Soares, J., & Barbuy, B. 2003, A&A, 400, 533 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Efremov, Y. N., & Sitnik, T. G. 1988, PAZh, 14, 817 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald, M. P., & Moffat, A. F. J. 1974, AJ, 79, 873 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald, M. P., & Moffat, A. F. J. 1980, PASP, 92, 489 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald, M. P., Luiken, M., Maitzen, H. M., & Moffat, A. F. J. 1979, A&AS, 37, 345 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Fry, A. M., & Carney, B. W. 1997, AJ, 113, 1073 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Girardi, L., Bressan, A., Bertelli, G., & Chiosi, C. 2000, A&AS, 141, 371 [Google Scholar]
- Kassis, M., Janes, K. A., Friel, E. D., & Phelps, R. L. 1997, AJ113, 1723 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- King, I. 1962, AJ, 67, 471 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Koen, C., & Lombard, F. 2007, MNRAS, 382, 693 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kroupa, P., Aarseth, S., & Hurley, J. 2001, MNRAS, 321, 699 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Landolt, A. U. 1992, AJ, 104, 340 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Lyra, W., Moitinho, A., van der Bliek, N. S., & Alves, J. 2006, A&A, 453, 101 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Martin, N. F., Ibata, R. A., Bellazzini, M. et al. 2004, MNRAS, 348, 12 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- May, J., Alvarez, H., & Bronfman, L. 1997, A&A, 327, 325 [Google Scholar]
- May, J., Bronfman, L., Max-Moerbeck, W., & Olmos, F. 2008, ApJ, submitted [Google Scholar]
- Meynet, G., Mermilliod, J.-C., & Maeder, A. 1993, A&AS, 98, 477 [Google Scholar]
- Moitinho, A. 2001, A&A, 370, 436 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Moitinho, A., Carraro, G., Baume, G., & Vazquez, R. A. 2006a, A&A, 445, 493 [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Moitinho, A., Vázquez, R. A., Carraro, G. et al. 2006b, MNRAS, 368, L77 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Corral, M. A., Chavarría-K., C., & de Lara, E. 2002, Rev. Mex. Astron. Astrofis., 38, 141 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Corral, M. A., Chavarría-K, C., & de Lara, E. 2005, Rev. Mex. Astron. Astrofis., 41, 69 [Google Scholar]
- Munari, U., & Carraro, G. 1996, MNRAS, 283, 905 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Munari, U., Carraro, G., & Barbon, R. 1998, MNRAS, 297, 867 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps, R. L., & Janes, K. 1994, ApJS, 90, 31 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrukowicz, P., Kaluzny, J., & Krzeminski, W. 2006, MNRAS, 365, 110 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, D. J., Finkbeiner, D. P., & Davis, M. 1998, ApJ, 500, 525 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Kaler, T. 1982, Landolt-Börnstein, Group VI, 2b, Stars and Star Clusters (Berlin: Springer), 15 [Google Scholar]
- Siess, L., Dufour, E., & Forestini, M. 2000, A&A, 358, 593 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Stetson, P. B. 1987, PASP, 99, 181 [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam, A., & Sagar, R. 1999, AJ, 117, 937 [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D. G. 1974, AJ, 78, 597 [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D. G. 1976, AJ, 81, 97 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vallée, J. P. 2005, AJ, 130, 569 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, R. A., Baume, G., Feinstein, A., & Prado, P. 1996, A&AS, 116, 75 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, R. A., May, J., Carraro, G. et al. 2008, ApJ, 672, 930 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, N., & Moffat, A. F. J. 1972, A&AS, 7, 133 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Voskes, T., & Burton, W. B. 2006, The Warped HI Layer of the Outer Galaxy, M.Sc. Thesis, University of Leiden, under supervision of W. B. Burton. [arXiv:astro-ph/0601653] [Google Scholar]
- Ziyakhanov, R. F., Nuritdinov, S. N., Muminov, M. M., & Muslimova, Y. C. 2004, Order and Chaos in Stellar and Planetary Systems, Proceedings of the Conference held 17-24 August, 2003 at St. Petersburg State University, Russia. Edited by Gene G. Byrd, Konstantin V. Kholshevnikov, Aleksandr A. Myllri, Igor I. Nikiforov and Victor V. Orlov. (San Francisco: Astronomical Society of the Pacific), ASP Conf. Proc., 316, 192 [Google Scholar]
Footnotes
- ... clusters
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- The original photometry is only available in electronic form at CDS via anonymous ftp to cdsarc.u-strasbg.fr (130.79.128.5) or via http://cdsweb.u-strasbg.fr/cgi-bin/qcat?J/A+A/511/A38
- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- on leave from Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Padova, Vicolo Osservatorio 2, 35122 Padova, Italy
All Tables
Table 1: Position of cluster centres and estimated radii.
Table 2: Spectral types of stars in Haffer 18/19.
Table 3: Spectral types in NGC 2383 and NGC 2384.
Table 4: Results obtained for the eight clusters.
All Figures
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f1.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg5.png)
|
Figure 1: DSS images of the four regions investigated in this article. The squares delimit the areas covered by the photometric measurement (East is at left and North at top): 1) Czernik 29 and Haffner 10; 2) Haffner 18 and Haffner 19; 3) NGC 2383 and NGC 2384; 4) Ruprecht 72 and Ruprecht 158. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=13cm,clip]{11583f2.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg25.png)
|
Figure 2: Contour plots derived in each frame. The density scale - star number per square arcminute - is shown in the respective inserts. Circles are adopted cluster boundaries. North is at the top and East to the left. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f3.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg29.png)
|
Figure 3: Upper left panel: the TCDs for the entire region. Middle upper panel: Haffner 10 area. Right upper panel: Czernik 29. The SKZ (solid line) is shown together with the colour excess relation for O3-, B3-, B6- (dashed lines) and A0-type stars (solid). The reference intrinsic fitting line from G00 to Czernik 29 sequence, for Z = 0.004, is discussed in the text. Lower panels: the correspondent CMDs where long-dashed lines are the isochrone [log (t)] fits from G00 to Haffner 10 and Czernik 29 CMD sequences, for Z = 0.008 and Z = 0.004, respectively as discussed in the text. Some stars, pointed out using our notation, are also discussed in the text. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{11583f4.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg31.png)
|
Figure 4: Upper panels: the V/V-I CMD for Haffner 10 ( left) and Czernik 29 ( right). Dashed lines are the isochrone [log (t)] fitting from G00 at the indicated metal content Z. Lower panels: the corresponding B-V/V-I TCDs. Straight lines show the colour excess relation for R = 3.1 and 3.7 (Dean et al. 1978). The curved lines are the mean intrinsic colours for stars of Luminosity Class V and III from Cousins (1978). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14cm,clip]{11583f5.eps}
\vspace*{2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg32.png)
|
Figure 5: Left: enlargement of the TCD of Czernik 29 in Fig. 3. The fitting of the SKZ (solid line) and the mean intrinsic curve for Z = 0.004 (short-dashed line) from G00 are indicated. The colour excess relation for A0-type stars is also shown. Middle: the same in the V/B-V CMD; the two best isochrones [log (t)] fittings at Z = 0.004 are pointed out. Right: same as in middle in the V/U-B CMD |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f6.eps}
\vspace*{2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg39.png)
|
Figure 6: Upper panels show the TCDs for the entire region ( left); Haffner 18 area (Haffner 18(1), filled squares, and Haffner 18(2), open squares) ( middle); and Haffner 19 ( right). The SKZ (solid line) is shown in its normal position and shifted to fit the respective cluster sequences. The colour excess relations for an O3-, B3-, B6- and A0-type stars are as in Fig. 3. Lower panels show the corresponding CMDs. Long-dashed lines in Haffner 18 area -Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2)- and in Haffner 19 are the isochrone fittings from G00, labeled log(t). The right lower panel shows the fitting to Haffner 19 of pre-main sequence isochrones (grey lines, solar metal content) from Siess et al. (2000) for 4 ( upper) and 5 ( lower) Myr (see text). A number of relevant stars is pointed out in Haffner 19 for a better judgement of their positions in both diagrams. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f7.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg46.png)
|
Figure 7: Left: enlargement of the upper middle panel, U-B/B-V, in Fig. 6. Right: enlargement of the lower middle panel, V/B-VCMD, from Fig. 6. Some relevant stars are pointed out for a simultaneous judgement of their positions in both diagrams. Symbols and lines have the same meaning as in Fig. 6. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{11583f8.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg52.png)
|
Figure 8: Left and right upper panels show the V/V-I CMD for Haffner 18 area [Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2)], and Haffner 19 respectively. Symbols and lines have the same meaning as in Fig. 6. Grey lines are the best pre-main sequence fitting from Siess et al. (2000). Left and right lower panels are the respective TCDs, B-V/V-I. Symbols have the same meaning as in Fig. 6. Solid lines as in Fig. 4. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6cm,clip]{11583f9.eps}
\vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg56.png)
|
Figure 9: The V/U-B CMD of Haffner 18(1) and Haffner 18(2); long-dashed lines represent the best isochrone [log (t)] fittings. Grey lines are the solar content pre-main sequence isochrones of 4 ( upper) and 5 ( lower) Myr from Siess et al. (2000). Symbols as in Fig. 6. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f10.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg60.png)
|
Figure 10: Upper panels show the TCDs for the entire region ( left), NGC 2383 ( middle) and NGC 2384 ( right). The SKZ is shown in its normal position and shifted to fit the respective cluster sequences. The colour excess relations for O3-, B3-, B6- and A0-type stars are indicated. Lower panels indicate the correspondent CMDs; long-dashed lines show two isochrone [log (t)] fittings from G00 at Z= 0.008 for NGC 2383 and at solar metal content in NGC 2384. Some stars in both clusters are pointed out using our notation -see text. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=11cm,clip]{11583f11.eps}
\vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg66.png)
|
Figure 11: Left: enlargement of the TCD of Fig. 10 The SKZ and the mean intrinsic line for Z = 0.008 from G00 (short-dashed). The colour excess relations as in Fig. 3. Right: long-dashed lines depict the two isochrone [log (t)] fittings at Z = 0.008 in the V/U-B CMD. Grey-solid line is the SKZ fitted to the distance modulus of NGC 2384 (see text). Stars -our notation- discussed in the text are pointed out. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{11583f12.eps} \vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg71.png)
|
Figure 12: Upper and lower panels have the same meaning as in Figs. 4 and 8 for the indicated Z content. Lower panels as in Figs. 4 and 8. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{11583f13.eps} \vspace*{-1.5mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg78.png)
|
Figure 13: Upper panels show the TCDs for the entire region ( left), Ruprecht 72 ( middle) and Ruprecht 158 ( right). The SKZ is shown in its normal position. The colour excess relations are indicated. Lower panels have the same meaning as in Figs. 3, 6 and 10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{11583f14.eps} \vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg81.png)
|
Figure 14: Upper and lower panels as in Figs. 4, 8 and 12. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{11583f15.eps}\vspace*{-2mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/03/aa11583-08/Timg82.png)
|
Figure 15:
Upper panel: the X-Y plane with the Sun at 0,0. Open
squares are CO clouds (the largest mean the most massive clouds)
in units of 105 |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
Copyright ESO 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


