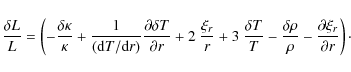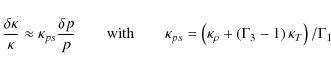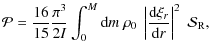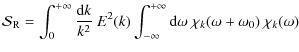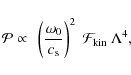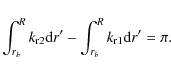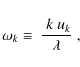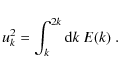| Issue |
A&A
Volume 510, February 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A6 | |
| Number of page(s) | 9 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913221 | |
| Published online | 29 January 2010 | |
Solar-like oscillations in massive main-sequence stars
I. Asteroseismic signatures of the driving and damping regions
K. Belkacem - M. A. Dupret - A. Noels
Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique, Université de Liège, Allée du 6 Août 17, 4000 Liège, Belgium
Received 31 August 2009 / Accepted 27 October 2009
Abstract
Motivated by the detection of stochastically excited modes in the massive star V1449 Aql, which is already known to be a ![]() Cephei star, we theoretically investigate the driving by turbulent
convection. By using a full non-adiabatic computation of the damping
rates, together with a computation of the energy injection rates, we
provide an estimate of the amplitudes of modes excited by both the
convective region induced by the iron opacity bump and the convective
core. Despite the uncertainties in the dynamical properties of these
convective regions, we demonstrate that both regions are able to
efficiently excite p
modes above the CoRoT observational threshold and the solar amplitudes.
In addition, we emphasise the potential asteroseismic diagnostics
provided by each convective region, which we hope will help us to
identify the region responsible for solar-like oscillations, and to
place constraints on this convective zone. A forthcoming work will be
dedicated to an extended investigation of the likelihood of solar-like
oscillations across the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
Cephei star, we theoretically investigate the driving by turbulent
convection. By using a full non-adiabatic computation of the damping
rates, together with a computation of the energy injection rates, we
provide an estimate of the amplitudes of modes excited by both the
convective region induced by the iron opacity bump and the convective
core. Despite the uncertainties in the dynamical properties of these
convective regions, we demonstrate that both regions are able to
efficiently excite p
modes above the CoRoT observational threshold and the solar amplitudes.
In addition, we emphasise the potential asteroseismic diagnostics
provided by each convective region, which we hope will help us to
identify the region responsible for solar-like oscillations, and to
place constraints on this convective zone. A forthcoming work will be
dedicated to an extended investigation of the likelihood of solar-like
oscillations across the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
Key words: convection - waves - stars: oscillations
1 Introduction
![]() Cephei-type stars are known to pulsate with large amplitude oscillations (Gautschy & Saio 1995,1996). The
Cephei-type stars are known to pulsate with large amplitude oscillations (Gautschy & Saio 1995,1996). The ![]() -mechanism is at the origin of those large amplitude oscillations and is related to the iron opacity bump at
-mechanism is at the origin of those large amplitude oscillations and is related to the iron opacity bump at
![]() (e.g; Pamyatnykh 1999).
Those modes are linearly unstable. In contrast, low-amplitude modes
have been observed in the Sun for years and are thought to be
intrinsically stable but stochastically excited by turbulent
convection. Their excitation is attributed to turbulent convection and
takes place in the uppermost
part of the Sun, which is a place of vigourous and turbulent motion.
Since the pioneering work of
Lighthill (1952), we know that a turbulent medium generates
incoherent acoustic pressure fluctuations (also called acoustic ``noise'').
In the past decade, solar-like oscillations have been detected in
numerous F-G type main sequence and red giant stars, in different evolutionary stages and with different
metallicities (see the recent review by Bedding & Kjeldsen 2007).
(e.g; Pamyatnykh 1999).
Those modes are linearly unstable. In contrast, low-amplitude modes
have been observed in the Sun for years and are thought to be
intrinsically stable but stochastically excited by turbulent
convection. Their excitation is attributed to turbulent convection and
takes place in the uppermost
part of the Sun, which is a place of vigourous and turbulent motion.
Since the pioneering work of
Lighthill (1952), we know that a turbulent medium generates
incoherent acoustic pressure fluctuations (also called acoustic ``noise'').
In the past decade, solar-like oscillations have been detected in
numerous F-G type main sequence and red giant stars, in different evolutionary stages and with different
metallicities (see the recent review by Bedding & Kjeldsen 2007).
As in the Sun, massive stars have convective regions, namely the
convective core, and two regions associated with the helium and iron
opacity bumps. The inner convective region (i.e., the convective core)
has an important impact on both the internal structure and the
subsequent evolution of the star by means of, for instance, the extent
of the region where the chemical elements are mixed (e.g; Kippenhahn & Weigert 1990).
In contrast, the external convective zones associated with opacity
bumps are generally thought to be unimportant since they transport only
a very small fraction of the energy flux, which is dominated by
radiation. It is only since the revision of the opacities (Iglesias et al. 1992), which led to an enhancement of the iron opacity bump and could thus account for the instability in ![]() Cephei stars, that a convective zone related to the iron opacity bump has been understood to be present in massive stars.
Much attention is now drawn to this convective region associated with the iron opacity bump
Cephei stars, that a convective zone related to the iron opacity bump has been understood to be present in massive stars.
Much attention is now drawn to this convective region associated with the iron opacity bump![]() , because it is of interest for the understanding of surface effects such as microturbulence or wind clumping (e.g; Cantiello et al. 2009).
However, both the convective core and the iron convection zone are
poorly understood. In particular, the typical length scale and time
scale of turbulent motions associated with these regions can only be
inferred from mixing-length arguments, as well as dynamical properties
such as the convective velocities.
, because it is of interest for the understanding of surface effects such as microturbulence or wind clumping (e.g; Cantiello et al. 2009).
However, both the convective core and the iron convection zone are
poorly understood. In particular, the typical length scale and time
scale of turbulent motions associated with these regions can only be
inferred from mixing-length arguments, as well as dynamical properties
such as the convective velocities.
Solar-like oscillations (linearly damped and stochastically excited modes) are closely related to those dynamical properties, so their detection in these massive stars is a promising way to infer them. Stochastically excited modes have only been predicted and detected in solar-like and red giant stars (see Bedding & Kjeldsen 2007; de Ridder et al. 2009; Michel et al. 2008, for details). The data gathered by the CoRoT mission has allowed us to report the first detection of solar-like oscillations in a massive star, V1449 Aql (Belkacem et al. 2009b). Those oscillations exhibit mode amplitudes greater than solar, hence the issue of their excitation is of interest. Investigation of unstable modes can place constraints on the internal structure of massive stars (e.g. Dupret et al. 2004; Thoul et al. 2003; Pamyatnykh et al. 2004; Aerts et al. 2003) as well as the underlying excitation mechanisms (e.g; Dziembowski et al. 1993; Dziembowski & Pamiatnykh 1993; Dziembowski & Pamyatnykh 2008; Moskalik & Dziembowski 1992). The discovery of solar-like oscillations is thus an opportunity to go a step further in the understanding of those stars that still challenge theory (Dziembowski 2007).
Our objective in this work is to assess the excitation of solar-like oscillations in massive main-sequence stars, such as ![]() Cephei type stars, by turbulent convection. We aim to determine which
convective region is able to excite modes above the observational
threshold, as well as emphasising the possible asteroseismic diagnostic
that would permit us to identify the excitation region and place
constraints on this region. Since the amplitude of stochastically
excited modes is a balance between driving and damping, both must be
modelled. In this work, we use the formalism proposed by Samadi & Goupil (2001) and extended by Belkacem et al. (2008,2006a,b).
Damping rates are computed using the MAD code (Grigahcène et al. 2005; Dupret 2002),
which is based on a full non-radial non-adiabatic treatment. This first
paper of the series focuses on a benchmark model. An extended
investigation of the mode amplitude through the Hertzsprung-Russell
diagram will be the subject of the second paper in this series.
Cephei type stars, by turbulent convection. We aim to determine which
convective region is able to excite modes above the observational
threshold, as well as emphasising the possible asteroseismic diagnostic
that would permit us to identify the excitation region and place
constraints on this region. Since the amplitude of stochastically
excited modes is a balance between driving and damping, both must be
modelled. In this work, we use the formalism proposed by Samadi & Goupil (2001) and extended by Belkacem et al. (2008,2006a,b).
Damping rates are computed using the MAD code (Grigahcène et al. 2005; Dupret 2002),
which is based on a full non-radial non-adiabatic treatment. This first
paper of the series focuses on a benchmark model. An extended
investigation of the mode amplitude through the Hertzsprung-Russell
diagram will be the subject of the second paper in this series.
The paper is organised as follows. Section 2 introduces the general formalism used to compute mode amplitudes. In Sect. 3, we focus on mode damping rates and emphasise their frequency dependence. Excitation by the convective region associated with the iron convective region is also studied and a possible diagnostic is inferred. Section 4 presents the computation of the mode amplitude excited by the convective core. Our conclusions are formulated in Sect. 5.
2 Modelling mode amplitudes
2.1 Equilibrium stellar structure: a 10 M model as a benchmark
model as a benchmark
Our objective is to explore the potential of convective regions to
drive oscillations. As a benchmark, we investigate the driving of
radial acoustic modes by turbulent convection zones in a
![]() main-sequence star, which is typical of
main-sequence star, which is typical of ![]() Cephei stars (Pamyatnykh 1999).
A more systematic exploration of the HR diagram is dedicated to the second paper of this series.
Cephei stars (Pamyatnykh 1999).
A more systematic exploration of the HR diagram is dedicated to the second paper of this series.
2.1.1 Physical input
The stellar structure models used in this work were
obtained using the stellar evolution code CLÉS (Scuflaire et al. 2008).
In the interior model, we used the OPAL
opacities (Iglesias & Rogers 1996) that were extended to low temperatures with the
opacities of Alexander & Ferguson (1994) and the CEFF equation of state
(Christensen-Dalsgaard & Däppen 1992). The metallicity was assumed to be Z=0.02 for the
metal mixture derived by Grevesse & Noels (1993).
Convection was included according to
a Böhm-Vitense mixing-length (MLT) formalism and no
overshoot was allowed.
The effect of the mixing-length parameter is
discussed in Sects. 3.3 and 4.3.
We note, however, that the default value of the mixing-length is 1.8 (the Solar value) and
in the convective region associated with the iron opacity bump, the mixing-length is of the same order as
the extent of the convective region, i.e., ![]() of the star radius.
of the star radius.
The location of the benchmark model on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is plotted in
Fig. 1. The model has an effective temperature of
![]() ,
and a surface gravity of
,
and a surface gravity of
![]() .
.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig1.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg22.png)
|
Figure 1: Hertzsprung-Russell diagram for a ten solar mass model computed with the CLÉS code (see Sect. 2.1). The diamond corresponds to the benchmark model described in Sect. 2.1.1, and the triangle symbols corresponds to another model used for comparison in Sect. 3.2.2. Star symbols correspond to the different evolutionary stages displayed in Fig. 6 (bottom). Eventually, the square and triangle symbols are used to identify the models presented in Fig. 6 (top). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig2.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg23.png)
|
Figure 2:
The difference between the temperature gradient and the adiabatic one (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
2.1.2 Convective zones
In these massive stars, one can distinguish three convective regions, namely:
- -
- the convective zone associated with the helium II opacity bump. This region is located at
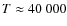 K (Fig. 2),
and is very weak in the sense that it is inefficient in transporting
energy with a negligible ratio of the convective heat flux to the
radiative one. In addition, this region is located close to the stellar
surface, where the density is low, and velocities are in the 10 to 20 m
s-1 range (low heat capacity is the cause of effective
smoothing of the temperature contrast and reduction of the buoyant
acceleration). Hence, the kinetic energy that could feed modes is
small.
K (Fig. 2),
and is very weak in the sense that it is inefficient in transporting
energy with a negligible ratio of the convective heat flux to the
radiative one. In addition, this region is located close to the stellar
surface, where the density is low, and velocities are in the 10 to 20 m
s-1 range (low heat capacity is the cause of effective
smoothing of the temperature contrast and reduction of the buoyant
acceleration). Hence, the kinetic energy that could feed modes is
small. - -
- the convective zone associated with the iron opacity bump, located at
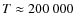 K (Fig. 2).
It has been shown (Cantiello et al. 2009)
that the occurrence of convection in the iron opacity peak is strongly
dependent on the luminosity and metallicity of the star. At a given
luminosity, a lower metallicity implies a lower opacity, which means
that a larger fraction of the total flux can be transported by
radiation. On the other hand, increasing the luminosity at a given Z
leads to a more important contribution of convection in the energy
transport. For a given metallicity, there is a luminosity threshold (of
the order of
K (Fig. 2).
It has been shown (Cantiello et al. 2009)
that the occurrence of convection in the iron opacity peak is strongly
dependent on the luminosity and metallicity of the star. At a given
luminosity, a lower metallicity implies a lower opacity, which means
that a larger fraction of the total flux can be transported by
radiation. On the other hand, increasing the luminosity at a given Z
leads to a more important contribution of convection in the energy
transport. For a given metallicity, there is a luminosity threshold (of
the order of
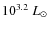 for Z=0.02) above which a convective zone is associated with the iron peak.
for Z=0.02) above which a convective zone is associated with the iron peak.
As for the helium convective region, the transport of energy by convection is very low. However, this region is located deeper than the helium one, where density is higher, with convective velocities of up to
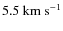 .
The kinetic energy flux is still negligible compared to the total flux
but the ratio of the kinetic energy flux of the iron convective zone to
the helium one is
.
The kinetic energy flux is still negligible compared to the total flux
but the ratio of the kinetic energy flux of the iron convective zone to
the helium one is
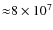 .
.
- -
- the convective core. Convection is fully adiabatic (Fig. 2) and a significant part of the total flux is transported by convection. The kinetic energy is four order of magnitudes higher than for the iron convective region, because of the high densities, with velocities around 300 m s-1.
2.2 Computation of mode amplitudes
We compute the mean-squared surface velocity for each radial mode as described in Belkacem et al. (2009a,2006b), i.e.,
where
The mode amplitude in terms of intensity is then deduced at the photosphere to be, as proposed by
Dziemblowski (1977) and Pesnell (1990), i.e.,
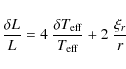
|
(4) |
where
2.2.1 Computation of the damping rates
As shown by Eq. (1), the computation of mode amplitudes requires the knowledge of both energy injection (
![]() )
and damping (
)
and damping (![]() )
rates. The latter has been computed using the full non-adiabatic
pulsation code MAD (Dupret 2002). This code includes a time-dependent convection
(TDC) treatment described by Grigahcène et al. (2005) that allows us to take into account the role played
by the variations in the convective flux, the turbulent pressure, and the dissipation rate of
turbulent kinetic energy.
)
rates. The latter has been computed using the full non-adiabatic
pulsation code MAD (Dupret 2002). This code includes a time-dependent convection
(TDC) treatment described by Grigahcène et al. (2005) that allows us to take into account the role played
by the variations in the convective flux, the turbulent pressure, and the dissipation rate of
turbulent kinetic energy.
The damping of acoustic modes is found to be dominated by the perturbation of the radiative flux. We note that, although crucial for the excitation, the upper convective regions do not affect the damping rates of the stars that we are considering. Convection is indeed very inefficient at transporting energy (compared to radiative transport) and the feedback of the convective background on the pulsation remains small. We numerically verified that the interaction between convection and pulsation does not affect damping rates as well as the effect of both the turbulent pressure and the dissipation rate of the turbulent kinetic energy.
Hence, the dominant contribution to the damping rate can be written as
where
Keeping only the radial contribution of the radiative flux in the energy equation
because of its dominant contribution, and neglecting the production of nuclear energy (
![]() ),
one obtains
),
one obtains
where
Finally, in the quasi-adiabatic approximation (which is valid inside the deep layers) one has
and
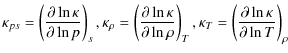
|
(9) |
2.2.2 Energy injection rates (
 )
)
The formalism that we use to compute energy injection rates of radial modes was developed by Samadi & Goupil (2001) and extended by Belkacem et al. (2006b,a). It takes two sources into account, the Reynolds stress tensor and the advection of the turbulent fluctuations of entropy by the turbulent motions (the entropy source term). The entropy contribution is found to be around ten percent of the Reynolds one.
The energy injection rate,
![]() ,
then mainly arises from the Reynolds stresses and can
be written as (see Eq. (21) of Belkacem et al. 2008)
,
then mainly arises from the Reynolds stresses and can
be written as (see Eq. (21) of Belkacem et al. 2008)
where
where is the source function, E(k) is the spatial kinetic energy spectrum,
![\begin{figure*}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{13221fig3.eps}
\end{figure*}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg50.png)
|
Figure 3:
Damping rates ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The rate (
![]() )
at which energy is injected into a mode is then
computed according to Eq. (8). Eigenfrequencies and eigenfunctions are computed
using the non-adiabatic pulsation code MAD.
In addition to the eigenfunctions and the density stratification,
Eq. (8) involves both the convective velocity and the turbulent kinetic energy spectrum.
The typical convective lengthscales are poorly known for main-sequence massive stars.
Hence, the classical mixing-length theory is used to find the injection
lengthscale (i.e., the scale on which the
turbulent kinetic energy spectrum reaches a maximum) and
a parameter
)
at which energy is injected into a mode is then
computed according to Eq. (8). Eigenfrequencies and eigenfunctions are computed
using the non-adiabatic pulsation code MAD.
In addition to the eigenfunctions and the density stratification,
Eq. (8) involves both the convective velocity and the turbulent kinetic energy spectrum.
The typical convective lengthscales are poorly known for main-sequence massive stars.
Hence, the classical mixing-length theory is used to find the injection
lengthscale (i.e., the scale on which the
turbulent kinetic energy spectrum reaches a maximum) and
a parameter ![]() is introduced (see Samadi & Goupil 2001, for details)
such that the associated wave-number is
is introduced (see Samadi & Goupil 2001, for details)
such that the associated wave-number is
![]() ,
where
,
where ![]() is the mixing-length.
One also has to specify the way in which turbulent eddies are temporally-correlated by defining
an eddy-time correlation function. A Lorentzian function
had been successfully used: in the solar case (Samadi et al. 2003b; Belkacem et al. 2006b),
as well as for
is the mixing-length.
One also has to specify the way in which turbulent eddies are temporally-correlated by defining
an eddy-time correlation function. A Lorentzian function
had been successfully used: in the solar case (Samadi et al. 2003b; Belkacem et al. 2006b),
as well as for ![]() Cen A, and HD49933 (Samadi et al. 2008; Samadi 2009), it indeed reproduces
the observational data.
Consequently, if not explicitly mentioned, this modelling will be used in the following.
Cen A, and HD49933 (Samadi et al. 2008; Samadi 2009), it indeed reproduces
the observational data.
Consequently, if not explicitly mentioned, this modelling will be used in the following.
3 Driving by the iron convective region
3.1 Damping rates
3.1.1 Efficiency of the damping
In Fig. 3, the fundamental mode is found to be linearly unstable with respect to the ![]() -mechanism associated with the iron opacity bump (Pamyatnykh 1999). Higher radial-order modes are found to be linearly stable. The damping rates range between one and three
-mechanism associated with the iron opacity bump (Pamyatnykh 1999). Higher radial-order modes are found to be linearly stable. The damping rates range between one and three ![]() Hz for
Hz for
![]() Hz, while they nearly vanish around the unstable mode. They are found to be dominated by the first two terms of Eq. (5).
Hz, while they nearly vanish around the unstable mode. They are found to be dominated by the first two terms of Eq. (5).
Concerning the first contribution (
![]() ),
as described for instance by Pamyatnykh (1999), the region where
),
as described for instance by Pamyatnykh (1999), the region where
![]() increases outwards tends to drive the mode while the region where
increases outwards tends to drive the mode while the region where
![]() decreases outwards damps the mode. This contribution then mainly
determines the damping rates of low-order modes, while the second term
of Eq. (5) begins to be important for higher order modes.
decreases outwards damps the mode. This contribution then mainly
determines the damping rates of low-order modes, while the second term
of Eq. (5) begins to be important for higher order modes.
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace{-1mm}\includegraphics[width=8.75cm,clip]{13221fig4.ep...
....5mm}\includegraphics[width=8.4cm,clip]{13221fig5.eps}
\vspace{6mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg58.png)
|
Figure 4:
Top: Cumulative work integral integrals (W) versus the logarithm of the temperature for the n=7, n=9 and n=12, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
3.1.2 Periodic variations
For high frequency modes, the damping in the range
![]() dominates over the driving region (
dominates over the driving region (
![]() ). This can be seen in Fig. 4,
in which the work integral is plotted, for three modes, which
correspond to the first and the second maxima and the minimum inbetween
the damping rate (see Fig. 3).
). This can be seen in Fig. 4,
in which the work integral is plotted, for three modes, which
correspond to the first and the second maxima and the minimum inbetween
the damping rate (see Fig. 3).
The oscillation of the damping rates for high-frequency modes (
![]() Hz) is related to the location of the node of
Hz) is related to the location of the node of
![]() with respect to the damping region.
By considering the pressure fluctuations (
with respect to the damping region.
By considering the pressure fluctuations (
![]() )
of three modes, namely n=7, n=9, and n=12, Fig. 4
shows that the damping reaches a minimum when there is a node in the
damping region and a maximum when the nodes are located at the edges of
those layers. The second maximum arises when two nodes of
)
of three modes, namely n=7, n=9, and n=12, Fig. 4
shows that the damping reaches a minimum when there is a node in the
damping region and a maximum when the nodes are located at the edges of
those layers. The second maximum arises when two nodes of
![]() straddle the damping region.
straddle the damping region.
This is easily explained by the set of equations Eqs. (3)-(6),
since a node in pressure fluctuations lowers the opacity fluctuations,
which appear to be given by the main damping term in Eq. (5). We note also that the second derivative of
![]() is negative when
is negative when
![]() is positive, which strengthens the radiative losses.
is positive, which strengthens the radiative losses.
It then creates the periodic variations observed in Fig. 3 for
![]() Hz.
Hence, the detection of this oscillation of mode line-width (damping)
would be a signature of the iron opacity bump and also an opportunity
to place constraints on the mode pressure perturbation in this region.
Hz.
Hence, the detection of this oscillation of mode line-width (damping)
would be a signature of the iron opacity bump and also an opportunity
to place constraints on the mode pressure perturbation in this region.
3.2 Energy injection rates
The poor knowledge of the dynamical properties of convective regions
associated with the iron opacity bump leads us to use a simple
description based on the MLT as explained in Sect. 2.2.2.
In terms of energy injection rates, two major features are to be
determined: the convective velocity and the injection lengthscale. As
for the superficial convective layers of the Sun, the iron convection
region is inefficient since it transports a negligible part of the
energy flux by means of convection. The Mach number (
![]() )
is similar to that found in the upper convective layers of the Sun in which
)
is similar to that found in the upper convective layers of the Sun in which
![]() .
The extent to which one can use the values of the parameters obtained
for the Sun is however difficult to assess and only numerical
simulations will provide a firm answer. By default, for the iron
convective region, we use the values of the convective velocity
provided by MLT using the assumed solar value (
.
The extent to which one can use the values of the parameters obtained
for the Sun is however difficult to assess and only numerical
simulations will provide a firm answer. By default, for the iron
convective region, we use the values of the convective velocity
provided by MLT using the assumed solar value (
![]() ).
In addition, the injection length scale is deduced from the numerical
simulations of the upper part of the solar convection zone as derived
by Samadi et al. (2003b), i.e., using
).
In addition, the injection length scale is deduced from the numerical
simulations of the upper part of the solar convection zone as derived
by Samadi et al. (2003b), i.e., using ![]() (see Sect. 2.2.2).
(see Sect. 2.2.2).
3.2.1 Efficiency of the excitation
A common feature of every modelling of stochastic excitation by
turbulent convection is that the energy injection rate is locally
proportional to the kinetic energy flux (e.g., Samadi & Goupil 2001; Goldreich et al. 1994). The contribution due to the Reynolds stresses can be approximated by (Samadi 2009)
where
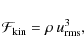
|
(13) |
where
The helium convective region is very inefficient in exciting modes because the kinetic energy flux is low (see Sect. 2.1.2).
The more favourable convective regions for exciting modes, in this
star, are the convective core and the one induced by the iron opacity
bump. Excitation of radial acoustic modes by the iron convective region
is found to be efficient for two reasons. First, the iron opacity bump
is located deeper inside the star compared to the helium bump, where
both density and turbulent velocities are higher. Thus, the energy
available for p modes is then higher. Second, the efficiency of the excitation depends on the timescales involved,
i.e., the convective time-scale and the modal period.
The latter is several hours and, using mixing-length arguments (i.e.,
![]() ), we find that the convective timescale is also several hours. Hence, excitation is nearly resonant.
), we find that the convective timescale is also several hours. Hence, excitation is nearly resonant.
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{3mm}\includegraphics[width=8.3cm,clip]{13221fig6.eps}\vspace*{1.5mm}
\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{13221fig7.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg73.png)
|
Figure 5:
Top: Rates (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
3.2.2 Periodic variation and seismic diagnostic
The power supplied to the mode by the iron convection zone exhibits periodic variations with frequency (Fig. 5, top). This behaviour is explained by the location of the iron convection zone relative to the radial component of the displacement. As shown by Eq. (8), the energy injection rate depends on the radial derivative of the radial component of the displacement in the driving regions. Hence, the location of the displacement nodes relative to the iron convective zone determines its derivative, and subsequently the efficiency of the excitation. This is oscillation is therefore a signature of the excitation by the iron convective region. Observational evidence would lead us to associate the driving with this region since, as will be shown in Sect. 4, no similar results are obtained if we assume that the convective core drives the modes.
The location of the iron convective zone can be inferred from the
energy injection rates by identifying the radial order of the first
maximum, which corresponds to the mode whose last node is located at
the bottom of the convective region (see Fig. 5, bottom). A second way to proceed is to use the frequencies of two of the maxima.
The successive maxima of the energy injection rates satisfy the relation
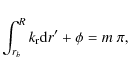
|
(14) |
where m is an integer,
From Eq. (13), one immediately sees that only the frequencies of the two consecutive maxima are needed to determine the depth of the bottom of the iron convective region. To illustrate this, we consider the limit of pure radial acoustic waves, such that Eq. (13) becomes
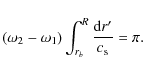
|
(16) |
Furthermore, by assuming that the sound speed is constant, one obtains the very simple analytic relation
Using the benchmark model described in Sect. 2.1, one then obtains
To illustrate this point, Fig. 6 (top) displays the energy injection rates as function of the radial order for two models at different evolution stages. The more evolved the star is, the deeper the location of the iron convective zone since the effective temperature decreases as the star evolves. The modes for which the energy injection rate reaches a maximum are found to shift toward lower radial-order. As a result, it is possible to follow and localise the depth of the convective region (see Fig. 6, bottom). We note that the energy injection rates are sensitive to the location of the bottom of the convective zone to less than one percent of the star radius, as shown in Fig. 6.
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{2.5mm}\includegraphics[width=8.4cm,clip]{13221fig8.eps}\vspace*{1mm}
\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig9.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg84.png)
|
Figure 6:
Top: Normalised energy injection rates for the two evolutionary stages (the two first successive models in Fig. 1) as a function of the mode radial order. Bottom:
Location of the bottom of the iron convection zone, with respect to the
surface, versus the radial-order of the first maximum of the energy
injection rates. Each point corresponds to the
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
3.3 Mode amplitude
Figure 7 displays the mode amplitudes excited by the iron convective region. By using the same parameters values as for the Sun, the amplitudes are found to be above both the solar maximum and the CoRoT detection threshold. In addition, Fig. 7 also shows that those results are very sensitive to the convective velocities. It shows that a factor of two change in the velocities leads to important discrepancies for mode amplitudes, so does the mixing length, since the convective velocities depend on the mixing-length to the third power for inefficient convection.
The development of numerical simulations is then the only way to obtain more reliable values of the mode amplitudes.
4 Driving by core convection
In contrast to the uppermost convective layers of the star, the inner convective core transports a non-negligible part of the total energy flux, convection is highly efficient at transporting energy. Hence, one cannot infer the properties of those regions by simply comparing them with those of the solar convective region. The physics in each case is different and the dynamical properties, which are of interest for computing the mode amplitude, are very uncertain. For instance, in the adiabatic regime the mixing-length has no significant impact on the determination of the star convective flux. The typical lengthscale and the convective velocities are, however, of crucial importance to determining the driving efficiency.
Recent 3D numerical simulations provide insight into those properties
for massive stars. A study of convection in the efficient regime was
proposed by Meakin & Arnett (2007)
using compressible 3D numerical simulations. They investigated the
convective regions during oxygen shell burning and during both hydrogen
core burning for a 23 ![]() star and proposed an extended description of the convective properties
and comparison with mixing-length theory as well as other 3D numerical
simulations of convective outer layers. They found that both the
velocities and the typical length scale are in good agreement with
mixing-length theory with a parameter (
star and proposed an extended description of the convective properties
and comparison with mixing-length theory as well as other 3D numerical
simulations of convective outer layers. They found that both the
velocities and the typical length scale are in good agreement with
mixing-length theory with a parameter (![]() )
of around 1.7.
)
of around 1.7.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.6cm,clip]{13221fig10.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg86.png)
|
Figure 7:
Mode amplitude as a function of mode frequency, computed as described in Sects. 2.2.2 and 2.2. Diamonds correspond to the computation of the energy injection rates using |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.6cm,clip]{13221fig11.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg87.png)
|
Figure 8:
Rates (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
4.1 Energy injection rates
As already pointed out in Sect. 2.1.2, the kinetic energy flux in the convective core is an order of magnitude higher than in the iron convective region. This high flux is due to the high densities and ensures that the convective core is a good candidate for exciting modes. However, the excitation efficiency also depends on the matching between both the convective timescales and mode periods and on the shape of the eigenfunctions (see Eqs. (8) and (9)).
Figure 8 displays the normalised energy injection rates as a function of frequency for radial p modes.
One can identify between two regions, namely at low
![]() Hz) and high
Hz) and high
![]() Hz)
frequencies.
In the low frequency range, the decrease in the energy injection rates
is dominated by the decrease in the ratio of the convective turnover
timescale to the modal period, and also the shape of the eigenfunctions
since
Hz)
frequencies.
In the low frequency range, the decrease in the energy injection rates
is dominated by the decrease in the ratio of the convective turnover
timescale to the modal period, and also the shape of the eigenfunctions
since
![]() depends on its radial derivative. In contrast, modes with higher
frequencies exhibit nodes close to the interface between the convective
and radiative zones explaining the modulation of energy injection
rates. In terms of absolute values of the energy injection rates, as
for the iron convection zone, they depend mainly on the injection
lengthscale but are not very sensitive to the mixing-length since
convection is efficient (see Sect. 4.3).
depends on its radial derivative. In contrast, modes with higher
frequencies exhibit nodes close to the interface between the convective
and radiative zones explaining the modulation of energy injection
rates. In terms of absolute values of the energy injection rates, as
for the iron convection zone, they depend mainly on the injection
lengthscale but are not very sensitive to the mixing-length since
convection is efficient (see Sect. 4.3).
4.2 Diagnostic on the eddy-time correlation function
Convective turnover timescales, evaluated within the MLT framework, are found to be of the order of a month, while the modal periods of acoustic standing waves are several hours. Hence, the excitation will be in an off-resonance regime and will therefore crucially depend on the way eddies are time-correlated. In this particular regime, the way that the eddies are temporally-correlated can lead to order of magnitude differences in terms of mode amplitudes, as shown by Samadi et al. (2003a) for the solar p modes and by Belkacem et al. (2009a) for solar g modes, where the effect is far stronger.
Therefore, we consider different types of modelling of this time-correlation function (see ![]() in Eq. (8)). Exponential and Lorentzian modelling are given by
in Eq. (8)). Exponential and Lorentzian modelling are given by
with the normalisation condition
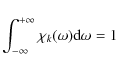
|
(20) |
where
where
The choice of an exponential function is motivated by experimental studies of homogeneous and isotropic turbulence. For instance, Mordant et al. (2004) demonstrated that the time-correlation of Lagrangian velocities follows an exponential decrease in agreement with the Kolmogorov (1941) phenomenology. However, the solar turbulent convection exhibits different physical conditions compared to experimental studies. The very large Reynolds numbers as well as the presence of coherent large-scale structures (plumes) make it likely that a specific description of
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{1.7mm}\includegraphics[width=8.43cm,clip]{13221fig12.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig13.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg97.png)
|
Figure 9:
Top: analytical eddy-time correlation function ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Figure 9 (top) displays analytical ![]() versus the ratio
versus the ratio
![]() ,
where
,
where ![]() is the eddy characteristic frequency at the wave-number k. By considering the most energetic eddies, the excitation of p modes is found to occur in the off-resonance regime with a ratio
is the eddy characteristic frequency at the wave-number k. By considering the most energetic eddies, the excitation of p modes is found to occur in the off-resonance regime with a ratio
![]() higher than around 20. In this regime, it appears that the choice of
higher than around 20. In this regime, it appears that the choice of ![]() is essential as well as the width
is essential as well as the width ![]() .
We also note that a Gaussian modelling leads to a vanishing driving since for these ratios
.
We also note that a Gaussian modelling leads to a vanishing driving since for these ratios
![]() ,
the correlation is almost zero.
Figure 9
(bottom) also shows the influence of the frequency behaviour of the
mode amplitudes with frequency. The shape of the eddy-time correlation
function has a significant impact on the shape of mode amplitudes. A
Lorentzian function, which slowly decreases with frequency, results in
a relatively small decrease in mode amplitude with increasing
frequency. In contrast, an exponential
,
the correlation is almost zero.
Figure 9
(bottom) also shows the influence of the frequency behaviour of the
mode amplitudes with frequency. The shape of the eddy-time correlation
function has a significant impact on the shape of mode amplitudes. A
Lorentzian function, which slowly decreases with frequency, results in
a relatively small decrease in mode amplitude with increasing
frequency. In contrast, an exponential ![]() leads to a steeper slope in the mode amplitude that makes the detection less likely.
leads to a steeper slope in the mode amplitude that makes the detection less likely.
In conclusion, we have shown that the efficiency of the driving by core
convection depends crucially on the way that the eddies are
temporally-correlated. We note that only a Lorentzian ![]() leads to efficient driving and that the resulting mode amplitudes
decrease with frequency in contrast to driving by the iron convection
zone. Hence, it constitutes a seismic diagnostic for identifying the
driving by the convective core and also determining the way in which
the eddies are temporally-correlated, an essential constraint on the
dynamical properties of turbulent convection in the cores of massive
stars.
leads to efficient driving and that the resulting mode amplitudes
decrease with frequency in contrast to driving by the iron convection
zone. Hence, it constitutes a seismic diagnostic for identifying the
driving by the convective core and also determining the way in which
the eddies are temporally-correlated, an essential constraint on the
dynamical properties of turbulent convection in the cores of massive
stars.
4.3 Mode amplitudes
Mode amplitudes are presented in Fig. 10.
To investigate the sensitivity to the injection lengthscale, we compute
the amplitude with an upper limit given by the convective core size and
a lower limit, and the minimum of the pressure length-scale in the
convective core. In the more optimistic estimate, relative magnitudes
are found to reach up to 90 ppm for the lowest frequency mode and tens
of ppm for higher frequency modes. This result demonstrates that
excitation by the convective core can lead to amplitudes well above the
CoRoT detection threshold (
![]() )
as well as the solar maximum (
)
as well as the solar maximum (
![]() ).
In the pessimistic case, the amplitude is near the CoRoT threshold, which makes the detection more difficult.
We note also, that these results assume a Lorentzian description of the eddy-time correlation function (
).
In the pessimistic case, the amplitude is near the CoRoT threshold, which makes the detection more difficult.
We note also, that these results assume a Lorentzian description of the eddy-time correlation function (![]() ),
and that using another prescription such as an exponential decrease or
a Gaussian one lead to very small amplitudes well below one ppm.
),
and that using another prescription such as an exponential decrease or
a Gaussian one lead to very small amplitudes well below one ppm.
Nevertheless, it is worthwhile to note that the frequency behaviour associated with the excitation by the convective core is very different from that obtained by excitation caused by the iron convection zone. Hence, it constitutes a seismic signature that would be a powerful tool for identifying the driving region.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig14.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg100.png)
|
Figure 10: Mode amplitude versus frequency, computed using the benchmark model (see Sect. 2.1) and a Lorentzian function to describe the eddy-time correlation function (see Eq. (17)). The upper line (with diamond dots) corresponds to the upper limit to the injection lengthscale. The lower line (with stars) corresponds to an injection lengthscale that corresponds to the minimum of the pressure scale height in the convective core. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
5 Conclusions
We have performed an exploratory study of the driving (and damping) of acoustic modes by turbulent convection in a
![]() star. We have found that both the convective region associated with the
iron opacity bump and the convective core are able to efficiently drive
acoustic modes so that mode amplitudes are found above the CoRoT
detection threshold (
star. We have found that both the convective region associated with the
iron opacity bump and the convective core are able to efficiently drive
acoustic modes so that mode amplitudes are found above the CoRoT
detection threshold (
![]() )
as well as the solar maximum
(
)
as well as the solar maximum
(
![]() ).
).
However, uncertainties associated with the computation of mode amplitudes are important and related to the poor knowledge of the dynamical properties of those convective regions. For the iron convective region, the main uncertainties originate in the convective velocities as well as the injection-length scale. For the convective core, the way that eddies are temporally-correlated is crucial since excitation occurs in the off-resonance regime.
Computation of mode amplitudes also permitted us to emphasise potential
seismic diagnostics. First, driving by the iron convective region
results in an oscillation of the energy injection rates (and mode
amplitudes) versus mode frequencies.We have shown that this behaviour
is potentially useful for determining the extent and the depth of this
convective region, as well as the dynamical properties of the driving
(e.g., turbulent velocities, injection lengthscales). Second, the way
that the eddies are temporally-correlated determines the efficiency of
the driving by the convective core and the frequency behaviour. Hence,
it provides an opportunity to strongly constrain ![]() .
.
The detection of solar-like oscillations in a massive star such as V1449 Aql (Belkacem et al. 2009b) and the determination of the mode parameter in this star are a promising way to identify the driving region, since both have very different signatures, and provides physical constraints on the still poorly known treatment of convective regions. The presence of high frequency power in SPB stars (Degroote et al. 2009) would also help us to constrain the nature of the driving zone since these stars have luminosities that are definitively below the threshold value for the presence of a convective zone associated with the iron peak (Cantiello et al. 2009). It should however be kept in mind that microscopic diffusion coupled with radiation acceleration could induce an accumulation of iron in the iron peak. A convective iron zone could thus also be present in stars whose luminosity are slightly below the threshold.
AcknowledgementsWe are indebted to J. Leibacher for his careful reading of the manuscript and to R. Samadi and M.J. Goupil for their helpful remarks. K.B. also acknowledges financial support through a postdoctoral fellowship from the ``Subside fédéral pour la recherche 2009'', University of Liège.
References
- Aerts, C., Thoul, A., Daszynska, J., et al. 2003, Science, 300, 1926 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, D. R., & Ferguson, J. W. 1994, ApJ, 437, 879 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Balmforth, N. J. 1992, MNRAS, 255, 603 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bedding, T. R., & Kjeldsen, H. 2007, Commun. Asteroseismol., 150, 106 [Google Scholar]
- Belkacem, K., Samadi, R., Goupil, M. J., & Kupka, F. 2006a, A&A, 460, 173 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Belkacem, K., Samadi, R., Goupil, M. J., Kupka, F., & Baudin, F. 2006b, A&A, 460, 183 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Belkacem, K., Samadi, R., Goupil, M.-J., & Dupret, M.-A. 2008, A&A, 478, 163 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Belkacem, K., Samadi, R., Goupil, M. J., et al. 2009a, A&A, 494, 191 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Belkacem, K., Samadi, R., Goupil, M.-J., et al. 2009b, Science, 324, 1540 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello, M., Langer, N., Brott, I., et al. 2009, A&A, 499, 279 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin, W. J., Houdek, G., Elsworth, Y., et al. 2005, MNRAS, 360, 859 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., & Däppen, W. 1992, A&ARv, 4, 267 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- de Ridder, J., Barban, C., Baudin, F., et al. 2009, Nature, 459, 398 [Google Scholar]
- Degroote, P., Aerts, C., Ollivier, M., et al. 2009, A&A, 506, 471 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Dupret, M.-A. 2002, Bull. Soc. Roy. Sc. Liège, 5-6, 249 [Google Scholar]
- Dupret, M.-A., De Ridder, J., Neuforge, C., Aerts, C., & Scuflaire, R. 2002, A&A, 385, 563 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Dupret, M.-A., Thoul, A., Scuflaire, R., et al. 2004, A&A, 415, 251 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Dziemblowski, W. 1977, Acta Astron., 27, 95 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Dziembowski, W. A. 2007, Commun. Asteroseismol., 150, 175 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dziembowski, W. A., & Pamiatnykh, A. A. 1993, MNRAS, 262, 204 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dziembowski, W. A., & Pamyatnykh, A. A. 2008, MNRAS, 385, 2061 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Dziembowski, W. A., Moskalik, P., & Pamyatnykh, A. A. 1993, MNRAS, 265, 588 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Gautschy, A., & Saio, H. 1995, ARA&A, 33, 75 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gautschy, A., & Saio, H. 1996, ARA&A, 34, 551 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Goldreich, P., Murray, N., & Kumar, P. 1994, ApJ, 424, 466 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Grevesse, N., & Noels, A. 1993, in Origin and Evolution of the Elements, ed. N. Prantzos, E. Vangioni-Flam, & M. Casse, 15-25 [Google Scholar]
- Grigahcène, A., Dupret, M.-A., Gabriel, M., Garrido, R., & Scuflaire, R. 2005, A&A, 434, 1055 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, C. A., & Rogers, F. J. 1996, ApJ, 464, 943 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, C. A., Rogers, F. J., & Wilson, B. G. 1992, ApJ, 397, 717 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kippenhahn, R., & Weigert, A. 1990, Stellar Structure and Evolution (Berlin: Springer-Verlag) [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, M. J. 1952, Roy. Soc. Lond. Proc. Ser. A, 211, 564 [Google Scholar]
- Meakin, C. A., & Arnett, D. 2007, ApJ, 667, 448 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Michel, E., Baglin, A., Auvergne, M., et al. 2008, Science, 322, 558 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel, E., Samadi, R., Baudin, F., et al. 2009, A&A, 495, 979 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Mordant, N., Lévêque, E., & Pinton, J.-F. 2004, New J. Phys., 6, 116 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Moskalik, P., & Dziembowski, W. A. 1992, A&A, 256, L5 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Pamyatnykh, A. A. 1999, Acta Astron., 49, 119 [Google Scholar]
- Pamyatnykh, A. A., Handler, G., & Dziembowski, W. A. 2004, MNRAS, 350, 1022 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pesnell, W. D. 1990, ApJ, 363, 227 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, R. 2009, Lectures Notes in Physics, in press [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, R., & Goupil, M. . 2001, A&A, 370, 136 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, R., Nordlund, Å., Stein, R. F., Goupil, M. J., & Roxburgh, I. 2003a, A&A, 404, 1129 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, R., Nordlund, Å., Stein, R. F., Goupil, M. J., & Roxburgh, I. 2003b, A&A, 403, 303 [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, R., Belkacem, K., Goupil, M. J., Dupret, M.-A., & Kupka, F. 2008, A&A, 489, 291 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Scuflaire, R., Théado, S., Montalbán, J., et al. 2008, Ap&SS, 316, 83 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Stein, R. F. 1967, Sol. Phys., 2, 385 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Thoul, A., Aerts, C., Dupret, M. A., et al. 2003, A&A, 406, 287 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
Footnotes
- ... bump
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.png)
- In the following, this convective region will be referred to as the iron convective region.
All Figures
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig1.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg22.png)
|
Figure 1: Hertzsprung-Russell diagram for a ten solar mass model computed with the CLÉS code (see Sect. 2.1). The diamond corresponds to the benchmark model described in Sect. 2.1.1, and the triangle symbols corresponds to another model used for comparison in Sect. 3.2.2. Star symbols correspond to the different evolutionary stages displayed in Fig. 6 (bottom). Eventually, the square and triangle symbols are used to identify the models presented in Fig. 6 (top). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig2.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg23.png)
|
Figure 2:
The difference between the temperature gradient and the adiabatic one (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure*}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{13221fig3.eps}
\end{figure*}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg50.png)
|
Figure 3:
Damping rates ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace{-1mm}\includegraphics[width=8.75cm,clip]{13221fig4.ep...
....5mm}\includegraphics[width=8.4cm,clip]{13221fig5.eps}
\vspace{6mm}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg58.png)
|
Figure 4:
Top: Cumulative work integral integrals (W) versus the logarithm of the temperature for the n=7, n=9 and n=12, |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{3mm}\includegraphics[width=8.3cm,clip]{13221fig6.eps}\vspace*{1.5mm}
\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{13221fig7.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg73.png)
|
Figure 5:
Top: Rates (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{2.5mm}\includegraphics[width=8.4cm,clip]{13221fig8.eps}\vspace*{1mm}
\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig9.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg84.png)
|
Figure 6:
Top: Normalised energy injection rates for the two evolutionary stages (the two first successive models in Fig. 1) as a function of the mode radial order. Bottom:
Location of the bottom of the iron convection zone, with respect to the
surface, versus the radial-order of the first maximum of the energy
injection rates. Each point corresponds to the
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.6cm,clip]{13221fig10.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg86.png)
|
Figure 7:
Mode amplitude as a function of mode frequency, computed as described in Sects. 2.2.2 and 2.2. Diamonds correspond to the computation of the energy injection rates using |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.6cm,clip]{13221fig11.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg87.png)
|
Figure 8:
Rates (
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{1.7mm}\includegraphics[width=8.43cm,clip]{13221fig12.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig13.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg97.png)
|
Figure 9:
Top: analytical eddy-time correlation function ( |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{13221fig14.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/Timg100.png)
|
Figure 10: Mode amplitude versus frequency, computed using the benchmark model (see Sect. 2.1) and a Lorentzian function to describe the eddy-time correlation function (see Eq. (17)). The upper line (with diamond dots) corresponds to the upper limit to the injection lengthscale. The lower line (with stars) corresponds to an injection lengthscale that corresponds to the minimum of the pressure scale height in the convective core. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| In the text | |
Copyright ESO 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



![\begin{displaymath}
\eta = \frac{1}{2 ~ \omega_0 I} \int_{0}^{M} \mathcal{I}m \l...
...ta S\right) \left(\Gamma_3 - 1\right) \right] \textrm{d}m ~ ,
\end{displaymath}](/articles/aa/full_html/2010/02/aa13221-09/img36.png)